Abstract
Background
The effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on adipokines remain obscure. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of the addition of vildagliptin on visfatin, an adipokine that represents inflammatory biomarkers of adipose tissue, in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with prior metformin monotherapy.
Methods
In this 16-week, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study, 71 patients were randomly assigned to vildagliptin 50 mg twice a day (n = 35) or placebo (n = 36) added to ongoing metformin therapy. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), plasma lipids, and visfatin levels were measured at baseline and 16 weeks after treatment.
Results
After 16 weeks, significant reduction in HbA1c and FPG was observed with vildagliptin add-on treatment compared to placebo (‒0.54 ± 0.52%, P = 0.001 and ‒14.80 ± 19.21 mg/dL, P = 0.004, respectively). However, no other clinically meaningful changes in lipid parameters or visfatin were observed.
Go to : 
References
1. Ouchi N. Parker JL, L ugus JJ, W alsh K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011; 11:85–97.

2. Samal B, Sun Y, Stearns G, Xie C, Suggs S, McNiece I. Cloning and characterization of the cDNA encoding a novel human pre-B-cell colony enhancing factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994; 14:1431–7.
3. Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K, Matsuki Y, Murakami M, Ichisaka T, Murakami H, Watanabe E, Takagi T, Akiyoshi M, Ohtsubo T, Kihara S, Yamashita S, Makishima M, Funahashi T, Yamanaka S, Hiramatsu R, Matsuzawa Y, Shimomura I. Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science. 2005; 307:426–30.

4. Cosford SR, Bajpeyi S, Pasarica M, Albarado DC, Thomas SC, Xie H, Church TS, Jubrias SA, Conley KE, Smith SR. Scheletal muscle NAMPT is induced by exercise in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 98:E117–E126.
5. Garten A, Petzold S, Barnikol-Oettler A, Körner A. Thasler WE, Kratzsch J, Kiess W, Gebhardt R. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT/PBEF-visfatin) is contitutively realsed from human hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010; 391:376–81.
6. Aeghate E. Visfatin: structure, function and relation to diabetes mellitus and other dysfunctions. Curr Med Chem. 2008; 15:1851–62.
7. Sanja Stojsavljević, Marija Gomerčić Palčić, Lucija Virović Jukić, Lea Smirčić Duvnjak, Marko Duvnjak. Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:18070–91.
8. Díaz-Soto G, de Luis DA, Conde-Vicente R, Izaola-Jaurequi O, Ramos C, Romero E. Beneficial effects of liraglutide on adipocytokines, insulin sensitivity parameters and cardiovascular risk biomarkers in patients with Type 2 diabetes: A prospective study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014; 104:92–6.

9. Matsuzawa Y. Adipocytokines and emerging therapeutic targets. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2005; 7:58–62.
10. Revollo JR, Körner A, Mills KF, Satoh A, Wang T, Garten A, Dasgupta B, Sasaki Y, Wolberger C, Townsend RR, Milbrandt J, Kiess W, Imai S. Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin regulates insulin secretion in beta cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme. Cell Metab. 2007; 6:363–75.
11. Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K, Matsuki Y, Murakami M, Ichisaka T, Murakami H, Watanabe E, Takagi T, Akiyoshi M, Ohtsubo T, Kihara S, Yamashita S, Makishima M, Funahashi T, Yamanaka S, Hiramatsu R, Matsuzawa Y, Shimomura I. Retraction. Science. 2007; 318:565.

12. Sonoli SS, Shivprasad S, Prasad CV, Patil AB, Desai PB, Somannavar MS. Visfatin: a review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011; 15:9–14.
13. Bala M, Martin J, Kopp A, Hanses F, Buechler C, Schäffler A. In vivo suppression of visfatin by oral glucose uptake: evidence for a novel incretin-like effect by glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:2493–501.
14. Derosa G, Carbone A, D'Angelo A, Querci F, Fogari E, Cicero AF, Maffioli P. Variations in inflammatory biomarkers following the addition of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes not controlled with metformin. Intern Med. 2013; 52:2179–87.

15. Ahren B, Gomis R, Standl E, Mills D, Schweizer A. Twelve- and 52-week efficacy of the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor LAF237 in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:2874–80.
Go to : 
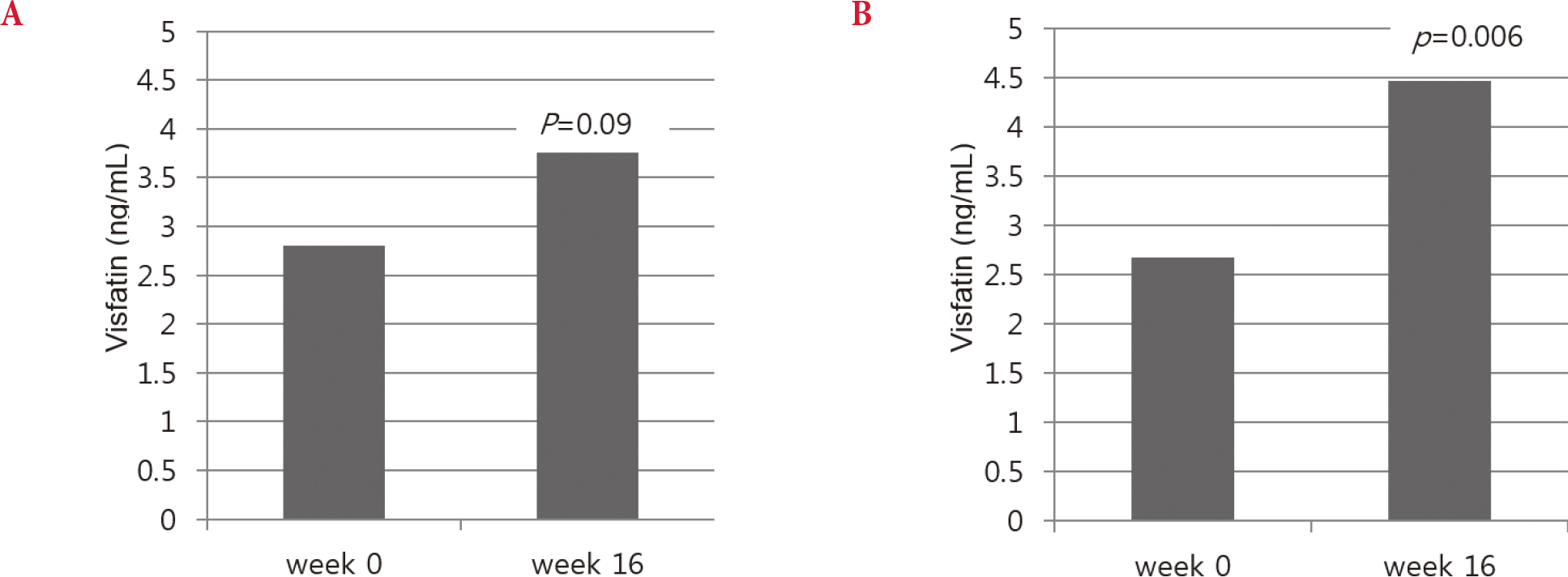 | Fig. 1.Changes of plasma visfatin concentration after 16-weeks treatment. (A) Metformin + Placebo group, (B) Metformin + Vildagliptin group. |
Table 1.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristic of the patients
| Metformin + Vildagliptin (n = 35) | Metformin + Placebo (n = 36) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 53.66 ± 10.94 | 52.53 ± 10.33 | 0.656a |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 21 (60.00) | 19 (52.80) | 0.540b |
| Female | 14 (40.00) | 17 (47.20) | |
| Weight (kg) Height (cm) | 68.78 ± 10.78 164.25 ± 8.68 | 67.19 ± 10.49 163.36 ± 8.10 | 0.530a 0.654a |
| Waist circumference (cm) BMI (kg/m2) | 88.81 ± 8.01 25.39 ± 2.56 | 86.66 ± 15.34 25.05 ± 2.67 | 0.464a* 0.590a |
| Duration of diabetes (y) | 11.18 ± 5.65 | 11.61 ± 5.93 | 0.755a |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.35 ± 0.73 | 7.94 ± 1.06 | 0.008a |
| FBS (mg/dL) | 134.00 ± 26.99 | 144.75 ± 36.83 | 0.166a |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 127.46 ± 11.59 | 123.53 ± 12.65 | 0.177a |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 75.60 ± 8.50 | 72.06 ± 8.03 | 0.075a |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 166.54 ± 36.74 | 164.67 ± 33.73 | 0.823a |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 166.54 ± 36.74 96.26 ± 29.44 | 164.67 ± 33.73 97.17 ± 32.81 | 0.823 0.903a |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 43.86 ± 10.42 | 44.75 ± 10.25 | 0.717a |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 43.86 ± 10.42 160.91 ± 98.21 | 44.75 ± 10.25 143.64 ± 96.77 | 0.717 0.458a |
| Visfatin (ng/mL) | 2.68 ± 2.17 | 2.80 ± 2.63 | 0.834a |
Table 2.
Changes in efficacy from week 0(baseline) to week 16
| Metformin + Placebo group | Metformin + Vildagliptin group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| week 0 | week 16 | week 0 | week 16 | |
| Weight (kg) | 67.17 ± 10.64 | 65.60 ± 11.46 c | 69.02 ± 10.85 | 68.35 ± 11.34 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.94 ± 1.06 | 8.14 ± 1.36 | 7.35 ± 0.73 | 6.81 ± 0.74 c |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 144.75 ± 36.83 | 148.33 ± 43.75 | 134.00 ± 26.99 | 119.20 ± 24.48 cd |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 164.67 ± 33.73 | 156.78 ± 33.74 | 166.54 ± 36.74 | 153.74 ± 30.12 a |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 97.17 ± 32.81 | 88.28 ± 26.22 | 96.26 ± 29.44 | 82.17 ± 22.63 b |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 44.75 ± 10.25 | 44.50 ± 12.45 | 43.86 ± 10.42 | 42.09 ± 9.93 a |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 143.64 ± 96.77 | 132.03 ± 79.96 | 160.91 ± 98.21 | 169.23 ± 100.08 |
| Visfatin (ng/mL) | 2.80 ± 2.63 | 3.94 ± 3.13 | 2.68 ± 2.17 | 4.47 ± 3.20 b |
| HOMA-IR (score) | 2.41 ± 1.90 | 2.16 ± 1.69 | 2.23 ± 1.93 | 2.05 ± 1.54 |
| HOMA-β (%) | 38.13 ± 50.50 | 31.10 ± 24.36 | 33.51 ± 22.41 | 53.25 ± 58.85 ad |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download