Abstract
Phlegmonous esophagogastritis is a rare bacterial infection that has been reported to result in mortality. The pathophysiology of phlegmonous gastrointestinal infection is unclear, but some predisposing factors are reported. Those include immunocompromised status, alcohol abuse, malignancy and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. We report two cases of phlegmonous esophagogastritis with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus. A 26-year-old woman and a 56-year-old woman individually visited our hospital for sore throat, neck pain and fever. The laboratory findings of both patients demonstrated leukocytosis, and elevated serum glucose levels. HbA1c of both patients was above 11%. Enhanced computed tomography of young woman showed submucosal edema with intramural abscess along the esophagus and stomach, and that of older woman showed the same defined to esophagus. In both cases, empirical antibiotic therapy with intravenous third generation cephalosporin and metronidazole were started. Later, we identified Klebsiella pneumonia through pus culture in both cases. The symptoms of case 1 improved with conservative management with antibiotics only. However, case 2 required surgical drainage and esophagectomy. Early radiologic diagnosis of this disease and accurate identification of pathogens are important factors for good prognosis. Therefore, we emphasize suspicion of such a rare disease is needed, especially when the patient has risk factors such as diabetes mellitus.
Go to : 
References
1. Kim HS, Hwang JH, Hong SS, Chang WH, Kim HJ, Chang YW, Kwon KH, Choi DL. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1532–5.

2. Hsu CY, Liu JS, Chen DF, Shih CC. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: report of a survived case. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996; 43:1347–52.
3. Lee CR, Lee JH, Choi SJ, Lee DS, Kim WS, Han SR, Chung NW, Park HS, Choi SH. A case of acute phlegmonous esophagitis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 20:119–23.
4. Yun CH, Cheng SM, Sheu CI, Huang JK. Acute phlegmonous esophagitis: an unusual case (2005: 8b). Eur Radiol. 2005; 15:2380–1.

5. Karimata H, Nishimaki T, Oshita A, Nagahama M, Shimoji H, Inamine M, Kinjyo T. Acute phlegmonous esophagitis as a rare but threatening complication of chemoradiotherapy: report of a case. Surg Today. 2014; 44:1147–51.

7. Kim NY, Park JS, Lee KJ, Yun HK, Kim JS. A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis causing gastroparesis and cured with medical treatment alone. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:309–14.

8. Iwakiri Y, Kabemura T, Yasuda D, Okabe H, Soejima A, Miyagahara T, Okadome K. A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis successfully treated with antibiotics. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999; 28:175–7.

9. I H, Park CS, Kim YD. Treatment of phlegmonous esophagitis combined with mediastinitis. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007; 40:711–4.
10. Park CW, Kim A, Cha SW, Jung SH, Yang HW, Lee YJ, Lee HIe, Kim SH, Kim YH. A case of phlegmonous gastritis associated with marked gastric distension. Gut Liver. 2010; 4:415–8.

11. Min SY, Kim YH, Park WS. Acute phlegmonous gastritis complicated by delayed perforation. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:3383–7.

12. Jung C, Choi YW, Jeon SC, Chung WS. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: radiologic diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:862–3.

13. Kim GY, Ward J, Henessey B, Peji J, Godell C, Desta H, Arlin S, Tzagournis J, Thomas F. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:168–74.

14. Song MA, Chang JH, Jung ME, Son SW, Kim TH, Kim CW, Han SW. A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis diagnosed with endoscopic submucosal biopsy and bacterial culture and improved by antibiotics treatment. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2013; 13:202–6.

15. Morton JJ, Stabins SJ. Phlegmonous gastritis: of Bacillus aerogenes capsultus (B. welchii) origin. Ann Surg. 1928; 87:848–54.
Go to : 
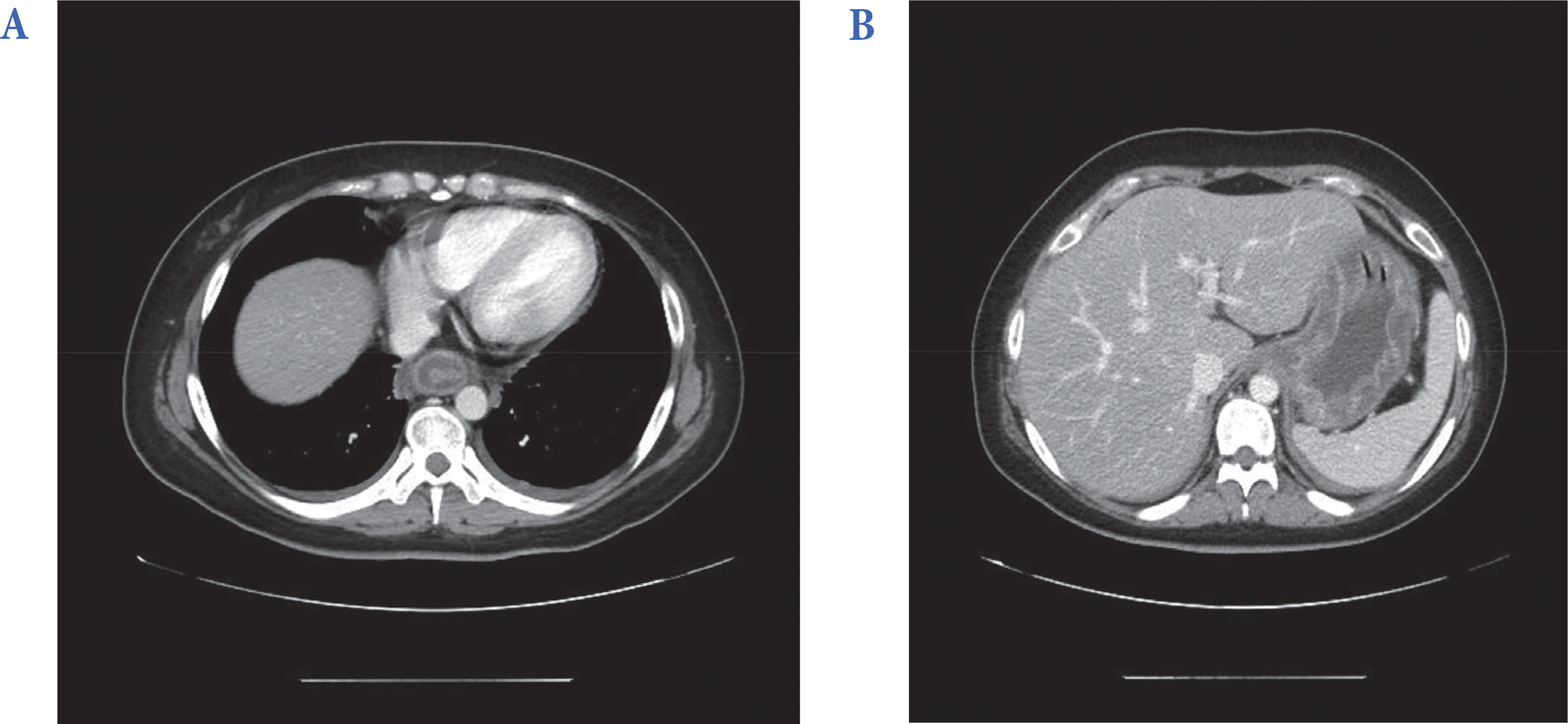 | Fig. 1.Abdomen computed tomography shows concentric wall thickening with intramural low attenuation of lower esophagus (A) and entire stomach (B). |
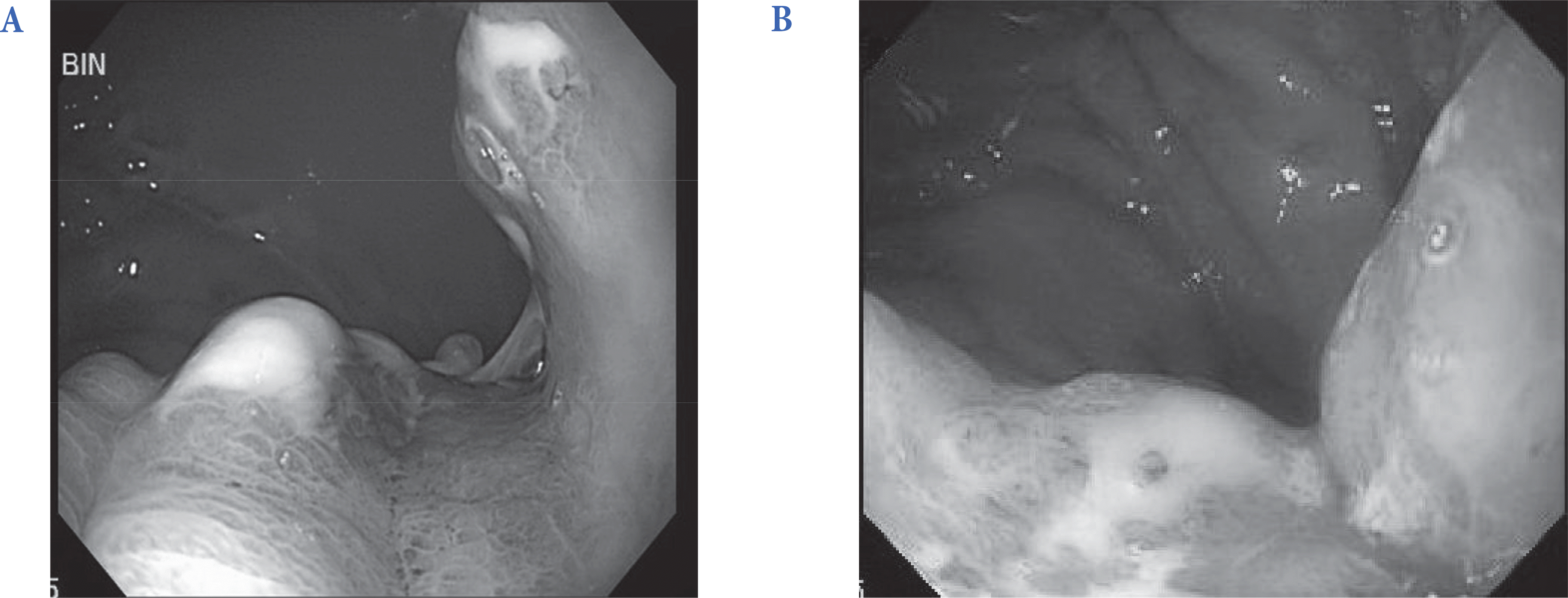 | Fig. 2.Duodenogastroscopy demonstrated diffuse hypertrophic mucosal change (B) with pus discharge (A). |
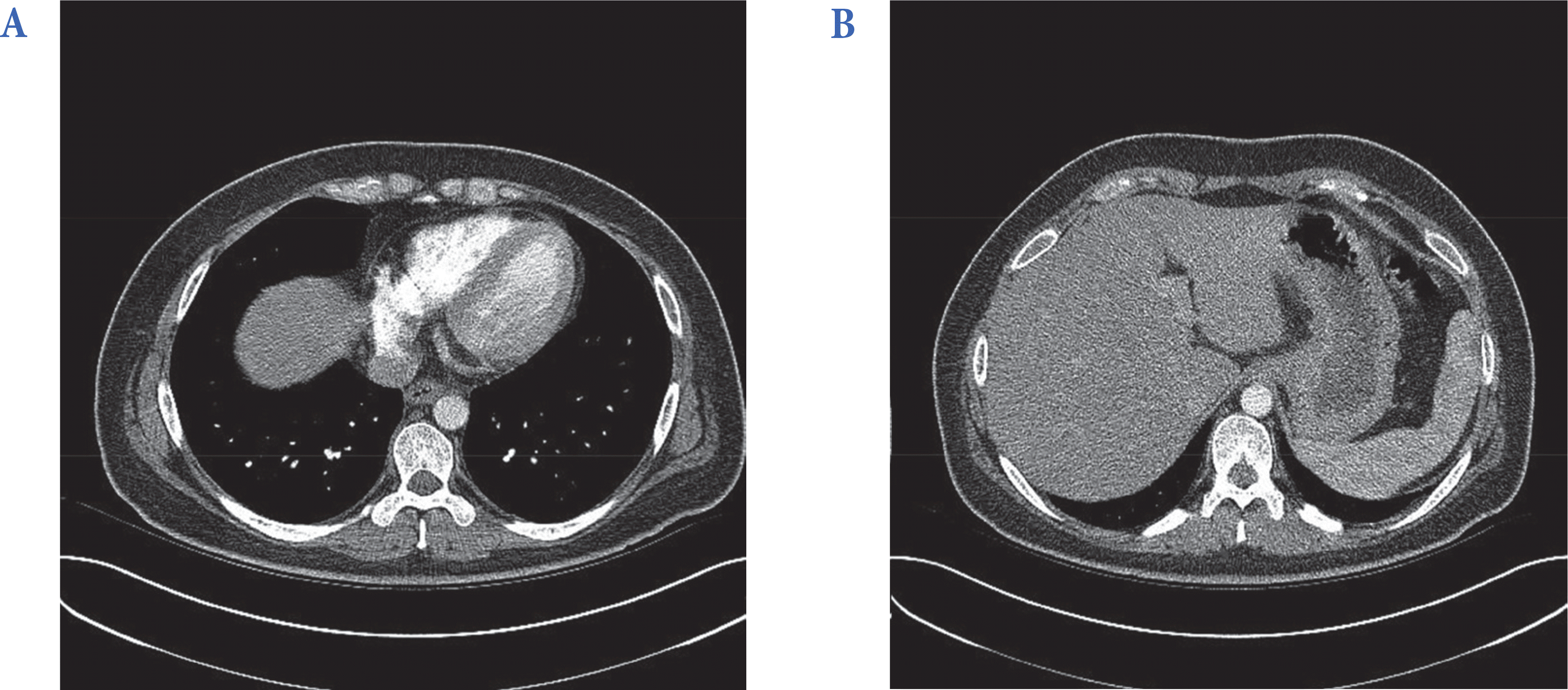 | Fig. 3.Follow up abdomen computed tomography shows improved low attenuated wall thickening of esophagus (A) and stomach (B). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download