Abstract
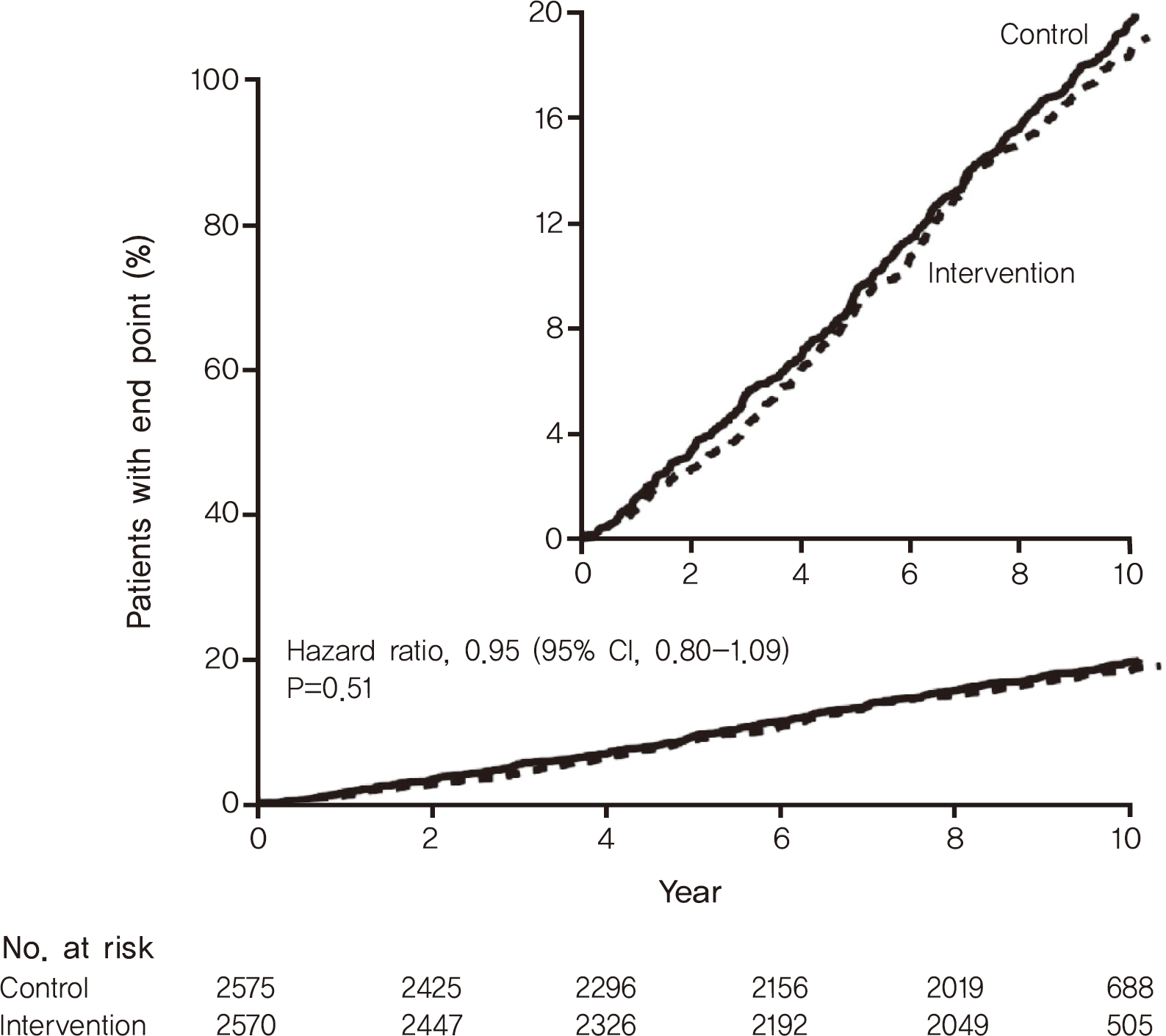
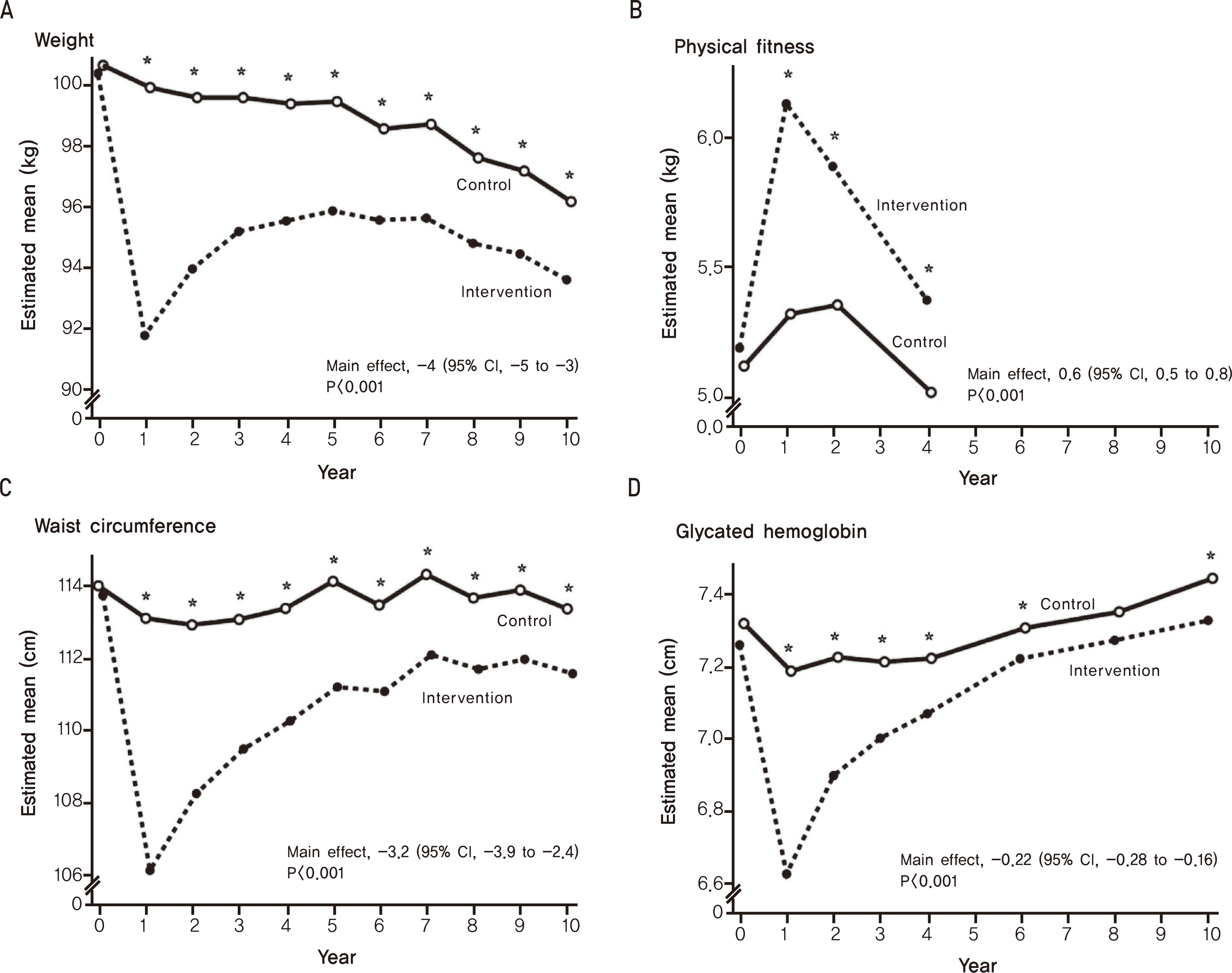
The universal first step for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia or atherosclerotic disease is therapeutic lifestyle change (TLC). However, in most cases, longterm sincere maintenance of TLC is very difficult. The Look-AHEAD study was initiated based on the results of the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) trial that evaluated the effects of TLC on the prevention of diabetes. However, the look-AHEAD trial failed to demonstrate the benefit of intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) for the prevention of CVD or CVD-associated mortality. Several explanations were suggested, including that the ILI group did not maintain effective weight loss, and that the intervention and control groups both received the same high-quality medical treatments. The participants of the look-AHEAD trial were very highly motivated, and the investigators of the trial systematically pursued their patients to achieve the desired end result, which is quite different from the usual clinical practice setting. Simple advisement for patients to perform diet restriction and moderate intensity regular physical exercise typically fails and is ineffective for the prevention of CVD in actual clinical practice. Concomitant sincere control of other risk factors is necessary for longterm CVD prevention. Further research on practical and effective methods for achievement of successful TLC is needed.
REFERENCES
1. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998; 352:837–53.
2. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2560–72.
3. Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, Zieve FJ, Marks J, Davis SN, Hayward R, Warren SR, Goldman S, McCarren M, Vitek ME, Henderson WG, Huang GD. VADT Investigators. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:129–39.

4. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2545–59.
5. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year followup of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1577–89.

6. Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hämäläinen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, Salminen V, Uusitupa M. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1343–50.

7. Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, Nathan DM. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:393–403.

8. Pan XR, Li GW, Hu YH, Wang JX, Yang WY, An ZX, Hu ZX, Lin J, Xiao JZ, Cao B, Liu PA, Jiang XG, Jiang YY, Wang JP, Zheng H, Zhang H, Bennett PH, Howard BV. Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 1997; 20:537–44.

9. Kosaka K, Noda M, Kuzuya T. Prevention of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle intervention: a Japanese trial in IGT males. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005; 67:152–62.

10. Lindström J, Ilanne-Parikka P, Peltonen M, Aunola S, Eriksson JG, Hemiö K, Hämäläinen H, Härkönen P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Mannelin M, Paturi M, Sundvall J, Valle TT, Uusitupa M, Tuomilehto J. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Sustained reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle intervention: followup of the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Lancet. 2006; 368:1673–9.

11. Look AHEAD Research Group. Wing RR, Bolin P, Brancati FL, Bray GA, Clark JM, Coday M, Crow RS, Curtis JM, Egan CM, Espeland MA, Evans M, Foreyt JP, Ghazarian S, Gregg EW, Harrison B, Hazuda HP, Hill JO, Horton ES, Hubbard VS, Jakicic JM, Jeffery RW, Johnson KC, Kahn SE, Kitabchi AE, Knowler WC, Lewis CE, Maschak-Carey BJ, Montez MG, Murillo A, Nathan DM, Patricio J, Peters A, Pi-Sunyer X, Pownall H, Reboussin D, Regensteiner JG, Rickman AD, Ryan DH, Safford M, Wadden TA, Wagenknecht LE, West DS, Williamson DF, Yanovski SZ. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:145–54.
12. Li G, Zhang P, Wang J, An Y, Gong Q, Gregg EW, Yang W, Zhang B, Shuai Y, Hong J, Engelgau MM, Li H, Roglic G, Hu Y, Bennett PH. Cardiovascular mortality, all-cause mortality, and diabetes incidence after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance in the Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study: a 23-year followup study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:474–80.

13. Carlsson LM, Peltonen M, Ahlin S, Anveden Å, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, Jacobson P, Lönroth H, Maglio C, Näslund I, Pirazzi C, Romeo S, Sjöholm K, Sjöström E, Wedel H, Svensson PA, Sjöström L. Bariatric surgery and prevention of type 2 diabetes in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:695–704.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download