Abstract
Because of the low incidence of type 1 diabetes in Korea, some Korean patients with type 1 diabetes are still being treated like type 2 diabetes patients. In 2011, the national health insurance launched a reimbursement program for the use of blood glucose test strips in type 1 diabetes. The initiation of the reimbursement program could provide an opportunity to assess the national status of type 1 diabetes management. In this context, we will discuss the lessons from the studies involving major national type 1 diabetes registries and the results of recent studies on multiple daily injection of insulin, continuous glucose monitoring, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, use of sensor-augmented insulin pumps, and the structure education program for patients with type 1 diabetes.
Go to : 
References
1. Shin CH. Epidemiologic characteristics of type 1 diabetes in children aged 14 years or under in Korea, 1985–2000. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:569–75.

2. Ko KW, Yang SW, Cho NH. The incidence of IDDM in Seoul from 1985 to 1988. Diabetes Care. 1994; 17:1473–5.

3. Rhee BD, Lee HK. Characteristics of diabetes developed under 35 years of age in 1994. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1995; 19(Suppl 1):43.
4. Rhee BD. Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus among Korean population. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2003; 27:173–8.
5. DIAMOND Project Group. Incidence and trends of childhood Type 1 diabetes worldwide 1990–1999. Diabet Med. 2006; 23:857–66.
7. Cho YM, Kim JT, Ko KS, Koo BK, Yang SW, Park MH, Lee HK, Park KS. Fulminant type 1 diabetes in Korea: high prevalence among patients with adult-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:2276–9.

8. Hong EG. Anti-GAD antibody in patients with adult-onset diabetes in Korea. Korean Diabetes J. 2009; 33:13–5.

9. Knerr I, Wolf J, Reinehr T, Stachow R, Grabert M, Schober E, Rascher W, Holl RW. DPV Scientific Initiative of Germany and Austria. The ‘accelerator hypothesis': relationship between weight, height, body mass index and age at diagnosis in a large cohort of 9,248 German and Austrian children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2005; 48:2501–4.

10. Mortensen HB, Hougaard P. Comparison of metabolic control in a cross-sectional study of 2,873 children and adolescents with IDDM from 18 countries. The Hvidøre Study Group on Childhood Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1997; 20:714–20.
11. Beck RW, Tamborlane WV, Bergenstal RM, Miller KM, DuBose SN, Hall CA. T1D Exchange Clinic Network. The T1D Exchange clinic registry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:4383–9.

12. Miller KM, Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Goland RS, Haller MJ, McGill JB, Rodriguez H, Simmons JH, Hirsch IB. T1D Exchange Clinic Network. Evidence of a strong association between frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels in T1D exchange clinic registry participants. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:2009–14.

Go to : 
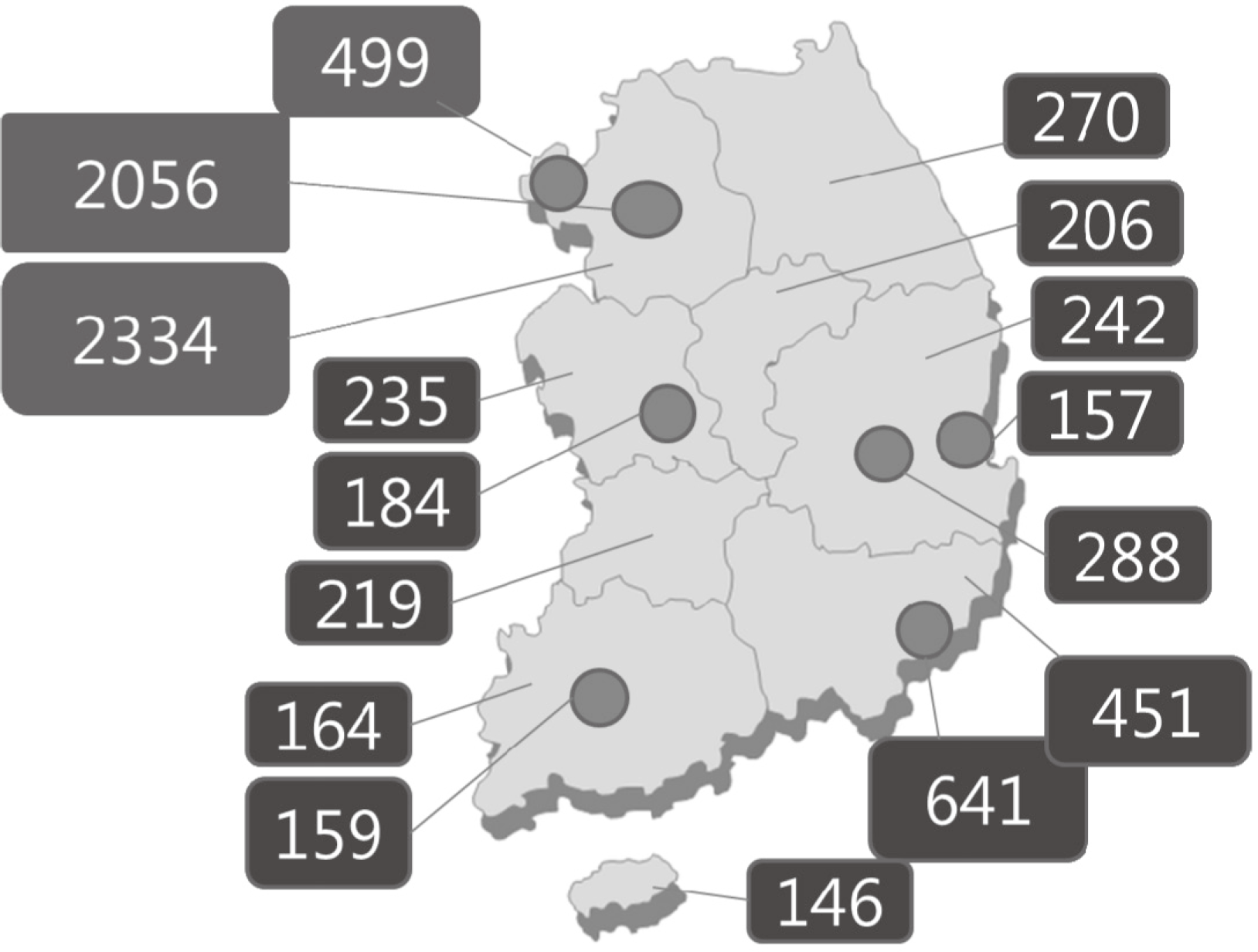 | Fig. 1.Regional distribution of type 1 diabetes patients registered for reimbursement of blood glucose test strips. |
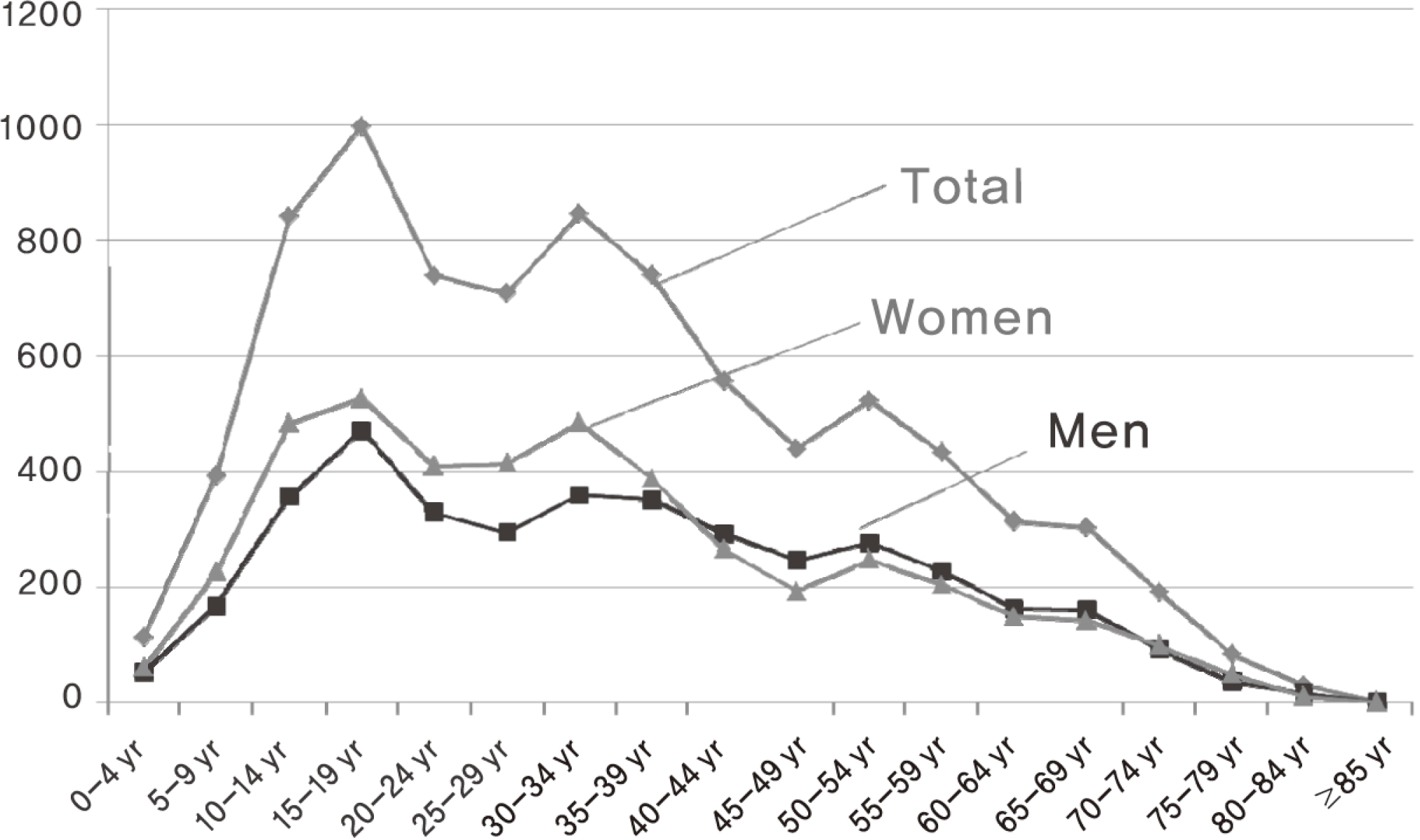 | Fig. 2.Age and gender distribution of type 1 diabetes patients registered for reimbursement of blood glucose test strips. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


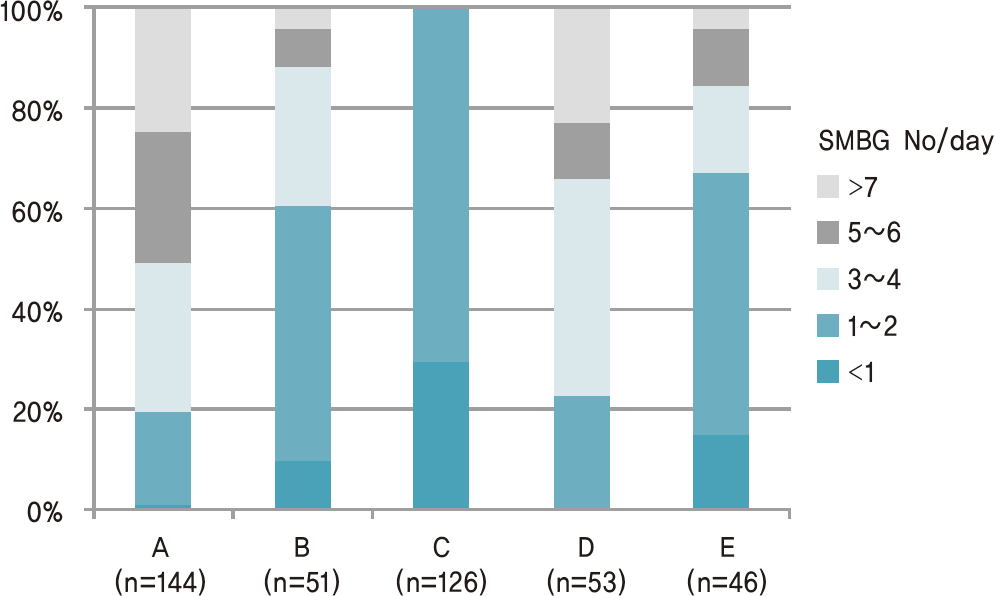
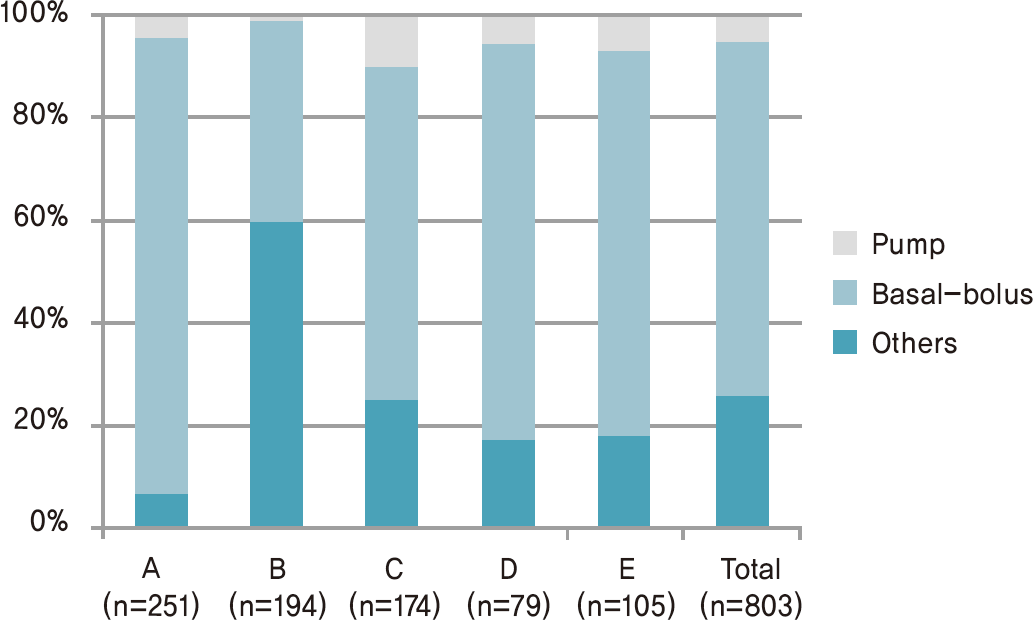
 XML Download
XML Download