Abstract
Recently, the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MOHW) announced a policy that patients that are only slightly ill cannot go a general hospital or a tertiary facility without bearing some of the medicine expense themselves. The MOHW has established a committee to make decisions on what constitutes a slight illness, and the committee has defined 51 diseases as such. Unfortunately, all type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been included, with the exceptions of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome. Why do MOHW administrators and committee members consider T2DM to be similar to the common cold as a slight illness? My intention is they don't know the fact that chronic disease, such as T2DM, not managed effectively without general hospitals. If they think so, they do not know the importance of the management and outcome of T2DM. I sincerely recommend that MOHW and committee members withdraw such an absurd policy and create an alternative policy.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Lim KJ, Choi JW, Choi EJ. Analysis of the OECD Health Data 2010. Seoul: Research Institute for Healthcare Policy, Korean Medical Association;2011.
2. Research Institute for Healthcare Policy Korean Medical Association. Research Institute for Healthcare Policy KMA: Analysis of OECD health data 2010. Seoul: 2011 [cited 2011 Jun 12]. Available from:. http://www.rihp.re.kr/research/sub_06_01_read.asp?idx=409&page=1&bbs_sec=420&strSearchWord=&strSearchString=.
Go to : 
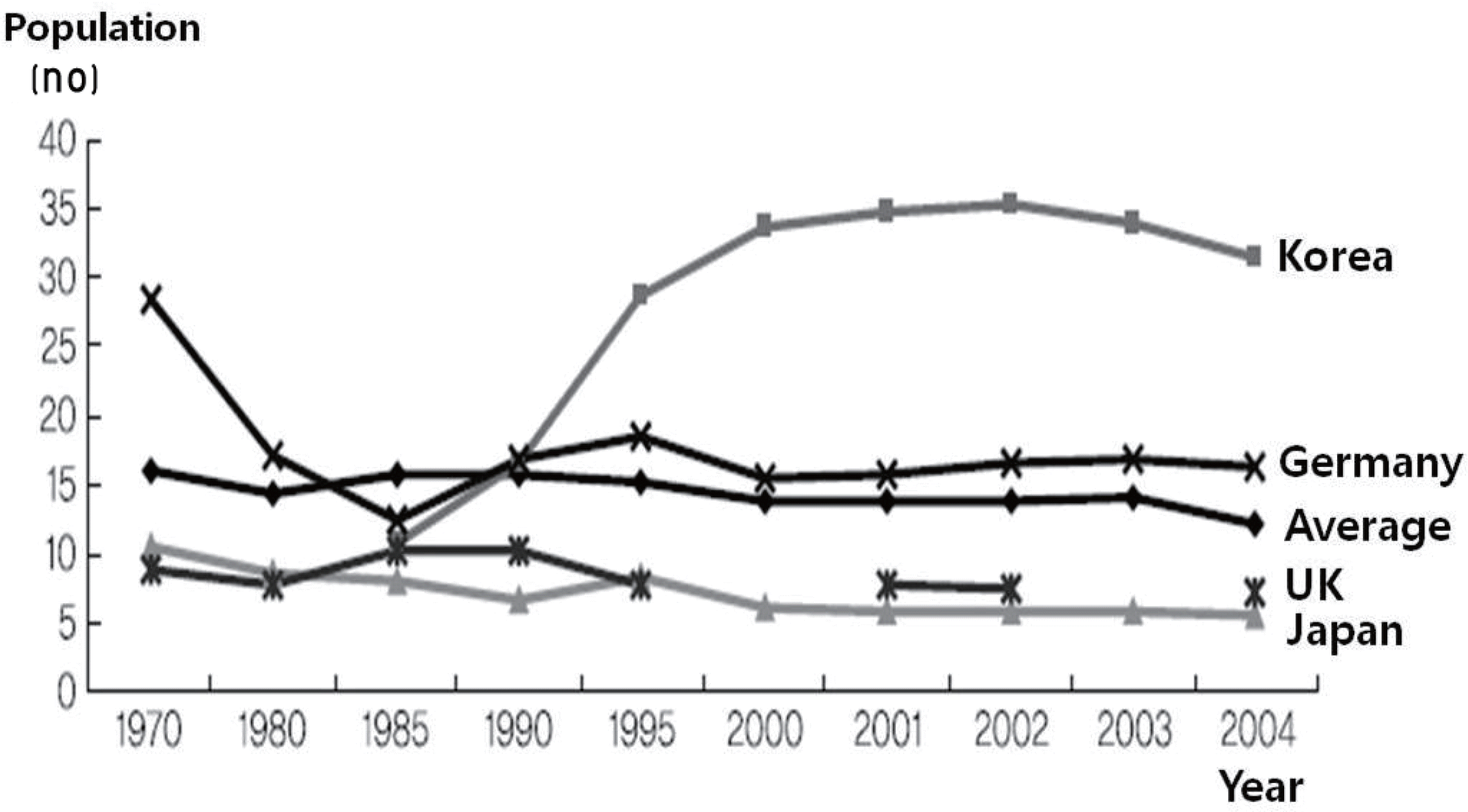 | Fig. 2.Diabetes mortality rate change by national comparison. Adapted from Research Institute for Healthcare Policy Korean Medical Association [2]. |
Table 1.
Patient charge ratio of medical treatment and medicine expense by medical institution classification
Table 2.
1999-2009 Cause of death ranking by mortality rate change
| Rank | 1999 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | Cause of death | Death rate | Cause of death | Death rate | Cause of death | Number of death | Portion | Death rate |
| 1 | Malignant neoplasm | 114.2 | Malignant neoplasm | 139.5 | Malignant neoplasm | 69,780 | 28.3 | 140.5 |
| 2 | CVDa | 72.9 | CVDa | 56.5 | CVDa | 25,838 | 10.5 | 52.0 |
| 3 | Cardiac disease | 38.9 | Cardiac disease | 43.4 | Cardiac disease | 22,347 | 9.0 | 45.0 |
| 4 | Traffic accident | 26.2 | Suicide | 26.0 | Suicide | 15,413 | 6.2 | 31.0 |
| 5 | Liver disease | 23.4 | Diabetes mellitus | 20.7 | Diabetes mellitus | 9,757 | 4.0 | 19.6 |
| 6 | Diabetes mellitus | 21.8 C | Chronic lower respiratory diseas | e 14.9 | Traffic accident | 7,147 | 2.9 | 14.4 |
| 7 | Suicide | 15.0 | Traffic accident | 14.7 C | Chronic lower respiratory disease | 6,914 | 2.8 | 13.9 |
| 8 | Chronic lower respiratory diseas | e 13.7 | Liver disease | 14.5 | Liver disease | 6,868 | 2.8 | 13.8 |
| 9 | Hypertensive disease | 7.5 | Pneumonia | 11.1 | Pneumonia | 6,324 | 2.6 | 12.7 |
| 10 | Pneumonia | 6.7 | Hypertensive disease | 9.6 | Hypertensive disease | 4,749 | 1.9 | 9.6 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download