Abstract
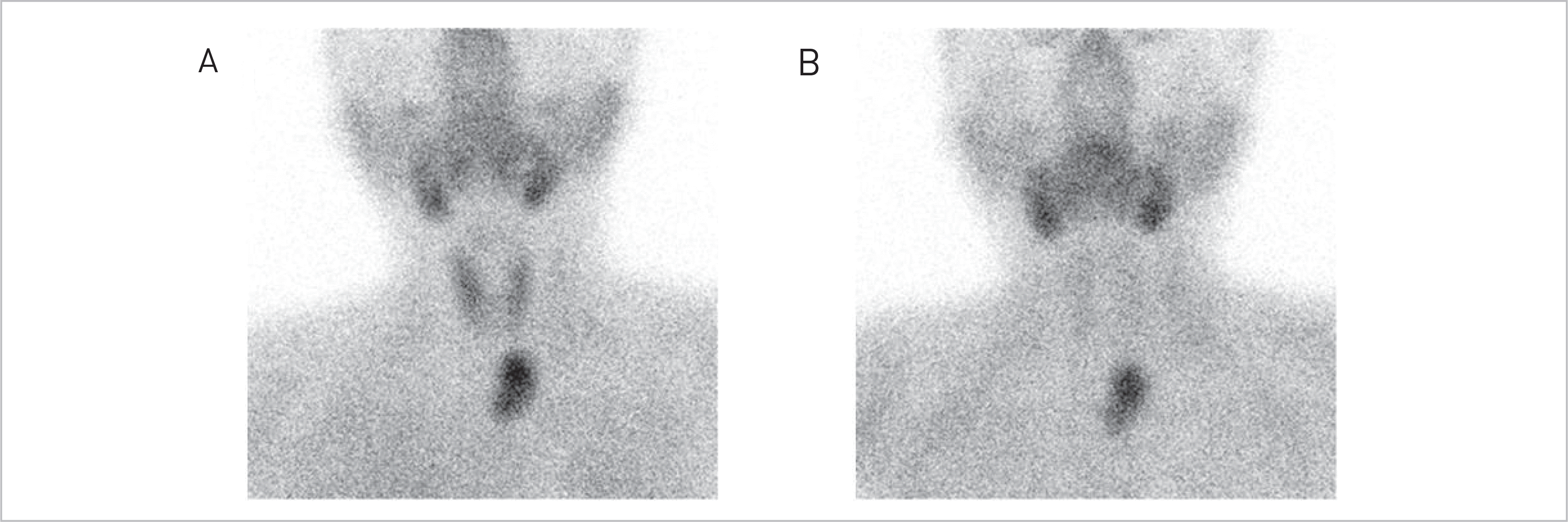
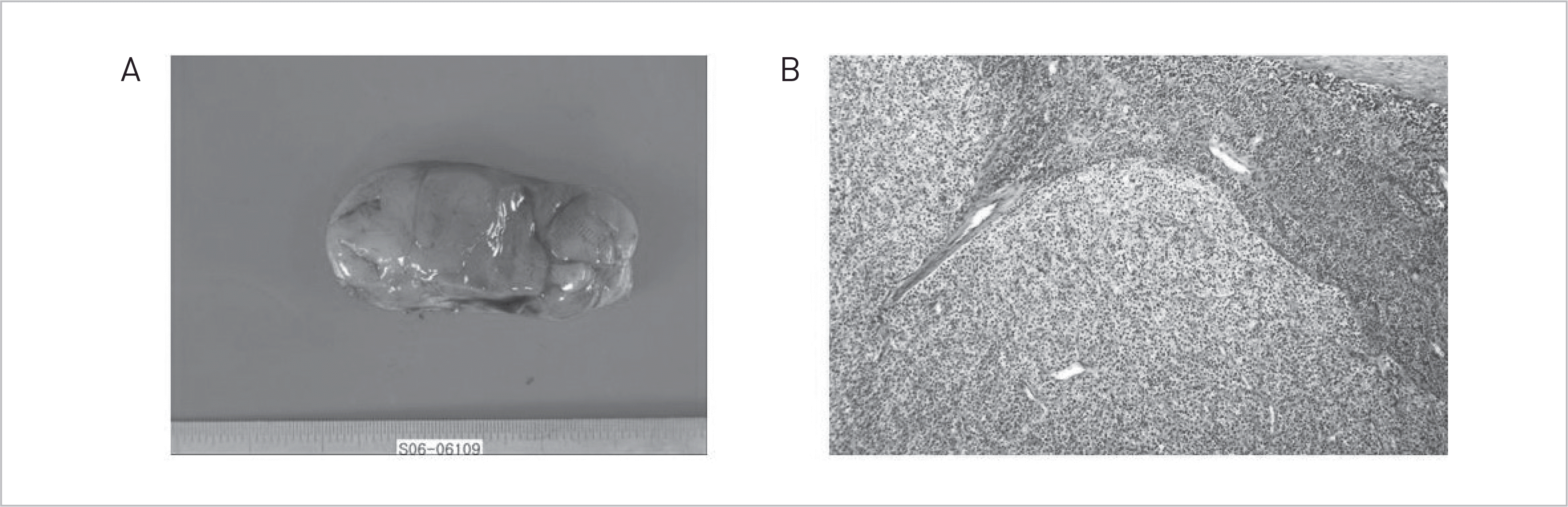
Patients with primary hyperparathyroidism often exhibit insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. In previous studies, glucose intolerance was improved by parathyroidectomy in primary hyperparathyroidism. We report a case of type 2 diabetes mellitus that improved after resection of a parathyroid adenoma along with a review of the literature.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Taylor WH. Khaleeli AA. Coincident diabetes mellitus and primary hyperparathyroidism. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001; 17:175–80.
2. Taylor WH, Khaleeli AA. Prevalence of primary hyperparathyroidism in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 1997; 14:386–9.

3. Akgun S, Ertel NH. Hyperparathyroidism and coexisting diabetes mellitus: altered carbohydrate metabolism. Arch Intern Med. 1978; 138:1500–2.

5. Suliburk JW, Perrier ND. Primary hyperthyroidism. Oncologist. 2007; 12:644–53.
6. Mundy GR, Cove DH, Fisken R. Primary hyper parathyroidism: changes in the pattern of clinical presentation. Lancet. 1980; 1:1317–20.
7. Yasuda K, Hurukawa Y, Okuyama M, Kikuchi M, Yoshinaga K. Glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in patients with parathyroid disorders. N Engl J Med. 1975; 292:501–4.

8. De Fronzo RA, Lang R. Hypophosphatemia and glucose intolerance: evidence for tissue insensitivity to insulin. N Engl J Med. 1980; 303:1259–63.

9. Drazin B. Intacellular calcium, insulin secretion and action. Am J Med. 1998; 85:44–58.
10. Sun G, Vasdev S, Martin GR, Gadag V, Zhang H. Altered calcium homeostasis is correlated with abnormalities of fasting serum glucose, insulin resistance, and beta-cell function in the Newfoundland population. Diabetes. 2005; 54:3336–9.
11. Fadda GZ, Akmal M, Lipson LG, Massry SG. Direct effect of parathyroid hormone on insulin secretion from pancreatic islet. Am J Physiol. 1990; 258:975–84.
12. Kautzky WA, Pacini G, Niederie B, Schernthaner G, Prager R. Insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity and hepatic insulin extraction in primary hyperparathyroidism before and after surgery. Clin Endocrinol. 1992; 37:147–55.

13. Draznin B, Lewis D, Houlder N, Sherman N, Adamo M, Garvey WT, LeRoith D, Sussman K. Mechanism of insulin resistance induced by sustained levels of cytosolic free calcium in rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1989; 125:2341–9.

14. Drazin B. Cytosolic calcium and insulin resistance. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993; 6:63–8.
15. Sun G, Vasdev S, Martin GR, Gadag V, Zhang H. Altered calcium homeostasis is correlated with abnormalities of fasting serum glucose, insulin resistance, and beta-cell function in the Newfoundland population. Diabetes. 2005; 54:3336–9.
16. Cheung PSY, Thompson NW, Brothers TE, Vinik AI. Effect of Hyperparathyroidism on the control of diabetes mellitus. Surgery. 1986; 100:1039–47.
17. Chun SH, Choi YS, Lee GY, Lim IS, Ihm SH, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Park SW. Evaluation of glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in two patients with primary hyperparathyroidism before and after surgery. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1994; 9:54–8.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download