Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness of ultrasouond-guided salivary gland injection of botulinum toxin A (BTX-A) for posterior drooling.
Method
11 patients with brain lesion (9 cerebral palsy, 1 hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and 1 mental retardation) with posterior drooling (an initial PDAS score greater than 2) and related pulmonary problems were recruited. Drooling severity was measured at baseline, 4 weeks, 3 months and 6 months after botulinum toxin A injection, by using Teacher Drooling Scale (TDS), Visual Analogue Scales (VAS), Drooling Score System (DSS)-severity, frequency and Posterior Drooling/Aspiration System (PDAS).
Figures and Tables
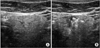 | Fig. 1These figure shows the ultrasound guided botulinum toxin injection into salivary gland. Submandibular gland before botulinum toxin injection (A) after botulinum toxin injection (B). |
References
1. Blasco PA, Allarie JH. Drooling in the developmentally disabled: management practices and recommendations. Consortium on Drooling. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1992. 34:849–862.
2. Jongerius PH, Hulst K, Hoogen FJ, Rotteveel JJ. The treatment of posterior drooling by botulinum toxin in a child with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 41:351–353.
3. Jeong MH, Yun MS, Ko TS. Parotid and submandibular botulinum toxin A injection for excessive Drooling children. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2008. 16:71–77.
4. Pena AH, Cahill AM, Gonzalez L, Baskin KM, Kim HK, Towbin RB. Botulinum toxin A injection of salivary glands in children with drooling and chronic aspiration. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009. 20:368–373.
5. Kang IS, Kwon JG, Lee SU, Lee ZI, Park GY, Park HW. Detection of saliva aspiration using salivagram in bedridden patients with brain lesion. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010. 34:503–507.
6. Park HW, Sim YJ, Bang MS. A survey of drooling in children with cerebral palsy. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2007. 31:535–540.
7. Savarese R, Diamond M, Elovic E, Millis SR. Intraparotid injection of botulinum toxin A as a treatment to control sialorrhoea in children with cerebral palsy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004. 83:304–311.
8. Suskind DL, Tilton A. Clinical study of botulinum-A toxin in the treatment of sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy. Laryngoscope. 2002. 112:73–81.
9. Bushara KO. Sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a hypothesis of a new treatment-botulinum toxin A injections of the parotid glands. Med Hypotheses. 1997. 48:337–339.
10. Banerjee KJ, Glasson C, O'Flaherty SJ. Parotid and submandibular botulinum toxin A injections for sialorrhoea in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006. 48:883–887.
11. Dogu O, Apaydin D, Sevim S, Talas DU, Aral M. Ultrasound-guided versus 'blind' intraparotid injections of botulinum toxin-A for the treatment of sialorrhoea in patients with Parkinson's disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2004. 106:93–96.
12. Gerlinger I, Szalai G, Hollody K, Nemeth A. Ultrasound-guided, intraglandular injection of botulinum toxin A in children suffering from excessive salivation. J Laryngol Otol. 2007. 121:947–951.
13. Jongerius PH, Rotteveel JJ, van den Hoogen F, Joosten F, van Hulst K, Gabreels FJ. Botulinum toxin A: a new option for treatment of drooling in children with cerebral palsy. Presentation of a case series. Eur J Pediatr. 2001. 160:509–512.
14. Jongerius PH, Joosten F, Hoogen FJ, Gabreels FJ, Rotteveel HH. The treatment of drooling by ultrasound-guided intraglandular injections of botulinum toxin type A into the salivary glands. Laryngoscope. 2003. 113:107–111.
15. Jongerius PH, Frank JA, van den Hoogen FJ, van Limbeek J, Gabreels FJ, van Hulst K, Rotteveel JJ. Effect of botulinum toxin in the treatment of drooling: A controlled clinical trial. Pediatrics. 2004. 114:620–627.
16. Jongerius PH, Rotteveel JJ, van Limbeek J, Gabreels FJ, van Hulst K, van den Hoogen FJ. Botulinum toxin effect on salivary flow rate in children with cerebral palsy. Neurology. 2004. 63:1371–1375.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download