Abstract
Allergic diseases are common in sports athletes, as they are in the general population. Any physician who involved in the care of athletes will commonly face the management of allergic conditions. Exercise-aggravated or exercise-induced allergic disorders are significant health problems to competitive athletes, although the majority of these disorders are mild and symptomatically annoying, several allergic diseases carry the risk of anaphylaxis and even sudden death. Meticulous approach in the diagnosis and management of allergic conditions is essential for the sports medicine physicians to afford all athletes can compete safely with their highest physical and mental level.
REFERENCES
1. Maiolo C, Fuso L, Todaro A, et al. Prevalence of asthma and atopy in Italian Olympic athletes. Int J Sports Med. 2004; 25:139–44.

2. Admas F. The extant works of Aretaeus the Cappadocian. London: Syndenham Society;1856.
3. Floyer J. A treatise of the asthma. London: R. Wilkin;1698.
4. Vichyanond P, Anuraklekha P, Ruengruk S. Exercise-induced asthma among Thai asthmatic children. J Med Assoc Thai. 2002; 85(Suppl 2):S579–85.
5. Jones RS, Buston MH, Wharton MJ. The effect of exercise on ventilatory function in the child with asthma. Br J Dis Chest. 1962; 56:78–86.

6. Poppius H, Muittari A, Kreus KE, Korhonen O, Viljanen A. Exercise asthma and disodium cromoglycate. Br Med J. 1970; 4:337–9.

7. Schwartz LB, Delgado L, Craig T, et al. Exercise-induced hypersensitivity syndromes in recreational and competitive athletes: a PRACTALL consensus report (what the general practitioner should know about sports and allergy). Allergy. 2008; 63:953–61.

8. Del Giacco Sr, Manconi PE, Del Giacco GS. Allergy and sports. Allergy. 2001; 56:215–23.
9. Wilde AD, Ell SR. The effect on nasal resistance of an external nasal splint during isometric and isotonic exercise. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1999; 24:414–6.

10. Cho SH KY, Sohn JW, et al. Prevalence of chronic rhinitis in Korean children and adolescents. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 19:452–8.
11. Kwon JW, Seo JH, Yu J, et al. Relationship between the prevalence of allergic rhinitis and allergen sensitization in children of Songpa area, Seoul. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:47–55.

12. Kremer B, den Hartog HM, Jolles J. Relationship between allergic rhinitis, disturbed cognitive functions and psychological well-being. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1310–5.

13. Simons FE, Simons KJ. Histamine and H1-antihistamines: celebrating a century of progress. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:1139–50. .e4.

14. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilo MB, et al. World allergy organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:13–37.

15. Jang GC, Chang YS, Choi SH, et al. Overview of anaphylaxis in Korea: diagnosis and management. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:181–96.

16. Zuberbier T, Bindslev-Jensen C, Canonica W, et al. EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF guideline: definition, classification and diagnosis of urticaria. Allergy. 2006; 61:316–20.

17. Zuberbier T, Bindslev-Jensen C, Canonica W, et al. EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF guideline: management of urticaria. Allergy. 2006; 61:321–31.

18. Morton AR, Fitch KD. Asthmatic drugs and competitive sport. An update. Sports Med. 1992; 14:228–42.
19. Carlsen KH, Hem E, Stensrud T, Held T, Herland K, Mowinckel P. Can asthma treatment in sports be doping? The effect of the rapid onset, long-acting inhaled beta2-agonist formoterol upon endurance performance in healthy well- trained athletes. Respir Med. 2001; 95:571–6.
20. Kindermann W. Do inhaled beta(2)-agonists have an ergo-genic potential in non-asthmatic competitive athletes? Sports Med. 2007; 37:95–102.
21. World Anti-Doping Agency. Therapeutic use exemptions- medical information to support the decisions of TUECs [Internet]. Montreal (CA): World Anti-Doping Agency;c2013. [cited 2014 Mar 12]. Available from:. http://www.wada-ama.org/Documents/Science_Medicine/Medical_info_to_support_TUECs/WADA-Medical-info-Asthma-5.0-EN.pdf.
22. World Anti-Doping Agency. Medical information to support the decisions of TUE Committees: Post infectious cough [Internet]. Montreal (CA): World Anti-Doping Agency;c2011. [cited 2014 Mar 12]. Available from:. http://www.wada-ama.org/Documents/Science_Medicine/Medical_info_to_support_TUECs/WADA_Medical_info_Post_Infectious_Cough_3.0_EN.pdf.
23. World Anti-Doping Agency. Medical information to support the decisions of TUE Committees: sinusitis/rhinosinusitis [Internet]. Montreal (CA): World Anti-Doping Agency;c2012. [cited 2014 Mar 12]. Available from:. http://www.wada-ama.org/Documents/Science_Medicine/Medical_info_to_support_TUECs/WADA_Medical_info_Sinusitis_Rhinosinusitis_V1.0_EN.pdf.
Fig. 1.
Lung function change in exercise induced asthma patient after exercise provocation test. FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
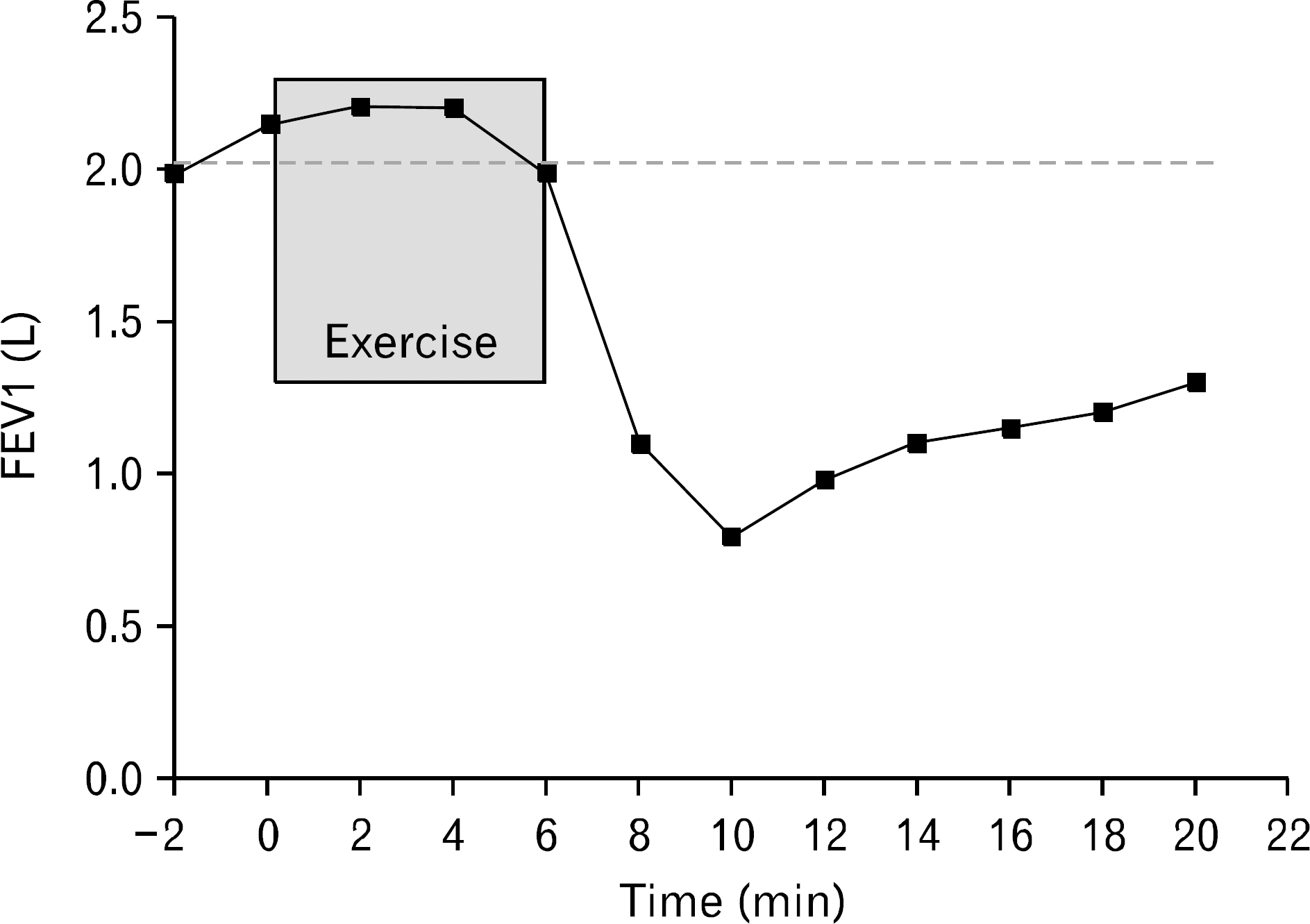
Table 1.
Diagnostic exercise required to obtain approval from the Medical Comission (MC) of the International Olympi Committee (IOC) for the use of inhaled β2-agonists




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download