1. Alghazzawi TF. Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: Options for practical implementation. J Prosthodont Res. 2016; 60:72–84.
2. Borba M, Miranda WG Jr, Cesar PF, Griggs JA, Bona AD. Evaluation of the adaptation of zirconia-based fixed partial dentures using micro-CT technology. Braz Oral Res. 2013; 27:396–402.
3. Nedelcu RG, Persson AS. Scanning accuracy and precision in 4 intraoral scanners: an in vitro comparison based on 3-dimensional analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 112:1461–1471.
4. Ahlholm P, Sipilä K, Vallittu P, Jakonen M, Kotiranta U. Digital versus conventional impressions in fixed prosthodontics: A review. J Prosthodont. 2016; 08. 02.
5. Mahl D, Glenz F, Marinello CP. Digital implant impression taking - an overview. Swiss Dent J. 2014; 124:165–186.
6. Ting-Shu S, Jian S. Intraoral digital impression technique: A review. J Prosthodont. 2015; 24:313–321.
7. Gjelvold B, Chrcanovic BR, Korduner EK, Collin-Bagewitz I, Kisch J. Intraoral digital impression technique compared to conventional impression technique. A randomized clinical trial. J Prosthodont. 2016; 25:282–287.
8. Abdel-Azim T, Rogers K, Elathamna E, Zandinejad A, Metz M, Morton D. Comparison of the marginal fit of lithium disilicate crowns fabricated with CAD/CAM technology by using conventional impressions and two intraoral digital scanners. J Prosthet Dent. 2015; 114:554–559.
9. Berrendero S, Salido MP, Valverde A, Ferreiroa A, Pradíes G. Influence of conventional and digital intraoral impressions on the fit of CAD/CAM-fabricated all-ceramic crowns. Clin Oral Investig. 2016; 20:2403–2410.
10. Shembesh M, Ali A, Finkelman M, Weber HP, Zandparsa R. An in vitro comparison of the marginal adaptation accuracy of CAD/CAM restorations using different impression systems. J Prosthodont. 2016; 02. 08.
11. Zarauz C, Valverde A, Martinez-Rus F, Hassan B, Pradies G. Clinical evaluation comparing the fit of all-ceramic crowns obtained from silicone and digital intraoral impressions. Clin Oral Investig. 2016; 20:799–806.
12. Anadioti E, Aquilino SA, Gratton DG, Holloway JA, Denry IL, Thomas GW, Qian F. Internal fit of pressed and computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing ceramic crowns made from digital and conventional impressions. J Prosthet Dent. 2015; 113:304–309.
13. Ender A, Zimmermann M, Attin T, Mehl A. In vivo precision of conventional and digital methods for obtaining quadrant dental impressions. Clin Oral Investig. 2016; 20:1495–1504.
14. Ng J, Ruse D, Wyatt C. A comparison of the marginal fit of crowns fabricated with digital and conventional methods. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 112:555–560.
15. Pradíes G, Zarauz C, Valverde A, Ferreiroa A, Martínez-Rus F. Clinical evaluation comparing the fit of all-ceramic crowns obtained from silicone and digital intraoral impressions based on wavefront sampling technology. J Dent. 2015; 43:201–208.
16. Ueda K, Beuer F, Stimmelmayr M, Erdelt K, Keul C, Güth JF. Fit of 4-unit FDPs from CoCr and zirconia after conventional and digital impressions. Clin Oral Investig. 2016; 20:283–289.
17. Boitelle P, Mawussi B, Tapie L, Fromentin O. A systematic review of CAD/CAM fit restoration evaluations. J Oral Rehabil. 2014; 41:853–874.
18. Anadioti E, Aquilino SA, Gratton DG, Holloway JA, Denry I, Thomas GW, Qian F. 3D and 2D marginal fit of pressed and CAD/CAM lithium disilicate crowns made from digital and conventional impressions. J Prosthodont. 2014; 23:610–617.
19. Quaas S, Rudolph H, Luthardt RG. Direct mechanical data acquisition of dental impressions for the manufacturing of CAD/CAM restorations. J Dent. 2007; 35:903–908.
20. Aboushelib MN. Fatigue and fracture resistance of zirconia crowns prepared with different finish line designs. J Prosthodont. 2012; 21:22–27.
21. Jalalian E, Atashkar B, Rostami R. The effect of preparation design on the fracture resistance of zirconia crown copings (Computer Associated Design/Computer Associated Machine, CAD/CAM System). J Dent (Tehran). 2011; 8:123.
22. Beuer F, Aggstaller H, Edelhoff D, Gernet W. Effect of preparation design on the fracture resistance of zirconia crown copings. Dent Mater J. 2008; 27:362–367.
23. Chai J, Chong KH. Probability of failure of machined zirconia dental ceramic core materials. Int J Prosthodont. 2009; 22:340–341.
24. Comlekoglu M, Dundar M, Ozcan M, Gungor M, Gokce B, Artunc C. Influence of cervical finish line type on the marginal adaptation of zirconia ceramic crowns. Oper Dent. 2009; 34:586–592.
25. Aykul H, Toparli M, Dalkiz M. A calculation of stress distribution in metal-porcelain crowns by using three-dimensional finite element method. J Oral Rehabil. 2002; 29:381–386.
26. Mitov G, Anastassova-Yoshida Y, Nothdurft FP, von See C, Pospiech P. Influence of the preparation design and artificial aging on the fracture resistance of monolithic zirconia crowns. J Adv Prosthodont. 2016; 8:30–36.
27. Komine F, Iwai T, Kobayashi K, Matsumura H. Marginal and internal adaptation of zirconium dioxide ceramic copings and crowns with different finish line designs. Dent Mater J. 2007; 26:659–664.
28. Re D, Cerutti F, Augusti G, Cerutti A, Augusti D. Comparison of marginal fit of Lava CAD/CAM crown-copings with two finish lines. Int J Esthet Dent. 2014; 9:426–435.
29. Euán R, Figueras-Álvarez O, Cabratosa-Termes J, Oliver-Parra R. Marginal adaptation of zirconium dioxide copings: influence of the CAD/CAM system and the finish line design. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 112:155–162.
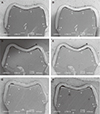
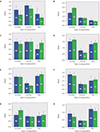











 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download