Ginseng has been used as an adaptogen in traditional medicine for several thousand years [
1]. Although ginseng has pharmacological effects on psychologic fuction, immune system, and diabetes, some adverse effects including nausea, diarrhea, euphoria, headaches, hypertension, hypotension, mastalgia and vaginal bleeding are also existed [
2].
Pharmacologically, the main active compounds of ginseng are ginsenosides which are named as 'Rx' and classified into the 20(S)-protopanaxadiol (PPD) (Rb1, Rb2, Rb3, Rc, Rd, Rg3, Rh2, Rs1) and the 20(S)-protopanaxatriol (Re, Rf, Rg1, Rg2, Rh1) [
3]. Ginsenosides show anti-cancer [
4], anti-inflammatory [
5], and neuroprotective effects [
6,
7,
8]. In our previous study, we also reported that oral administration of a novel Rd and Rg3 extract improves exercise capacity and fatigue recovery [
9].
In this study, we have examined the potential subchronic toxicity of UG0712, a new ginsenoside extract processed from ginseng leaves (Rg3 derivatives: ~10% and total ginsenosides: ~70%) by repeated oral administration in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted under Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) of the Korea Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) and performed in compliance with Testing Guidelines for Safety Evaluation of Drugs (Notification No. 2000-63 issued by the KFDA).
Preparation of UG0712
UG0712 was prepared by blending the partially hydrolyzed with ginseng leaf extract to meet constant content of ginsenosides Rd and Rg3. Briefly, ginseng leaf extract which was purchased from Hongju Biotech Co., Ltd (Yanbian, China) was easily hydrolyzed under acidic condition. UG0712 was standardized with above 5% of ginsenoside Rd, above 10% of ginsenoside Rg3 derivatives (Rg3, Rg5 and Rk1).
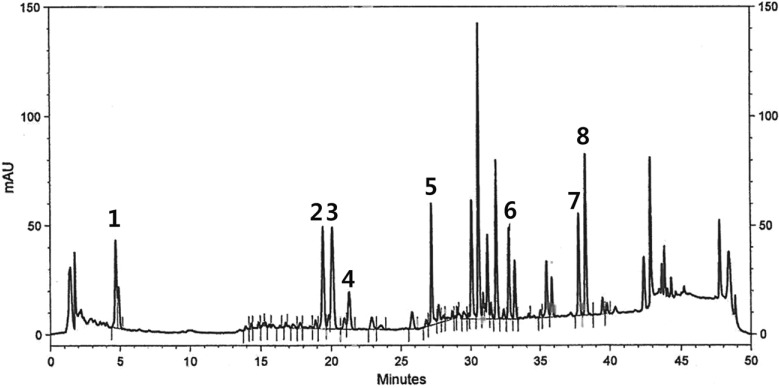
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis of UG0712
For analyzing freeze-dried ginseng extracts, it was dissolved in methanol with 2 mg/mL concentration, respectively. HPLC analysis was conducted on a HITACHI HPLC system equipped with L-7455 detector. A capcell PAK C18 column (5 µm, 3.0 mm * 75 mm) was used and maintained at 40℃. A gradient solvent composition of acetonitrile and deionized water was used. The flow rate and injection volume were 0.5 mL/min and 10 µL, respectively. The chromatograms were obtained at a wavelength of 203 nm with UV detector. Standard sample of ginsenoside was prepared with 0.2 mg/mL concentration.
Test substance and formulation
UG0712, an extract powder processed from ginseng leaves (Lot No. UG0712-BL05002), was supplied by Unigen, Inc (Cheonan, Chugnam, Korea). For administration, the test substance was suspended into the vehicle (Corn oil, Sigma-Aldrich Inc., MO, USA) and dosing formulations were prepared daily.
Animals
Male and female 5-6 weeks old SD rats were obtained from the Orientbio Inc. (Sungnam, Gyeonggi, Korea). The body weight range on receipt ranged from 112.8 to 137.7 g for males and 91.1 to 120.4 g for female. The animals were used after 6 day acclimatization and housed one animal to a stainless wire cage in a room with a barrier system controlled for the light-dark cycle (12-12 h), air exchange (10-15 changes/h), and temperature (19.8-24.7℃) during the study.
Feed and water
Animals were provided Teklad cerified global 18% protein rodent diet (Harlan Teklad, WI, USA) and filtered municipal tap water. Food and water were provided ad libitum.
Administration and study design
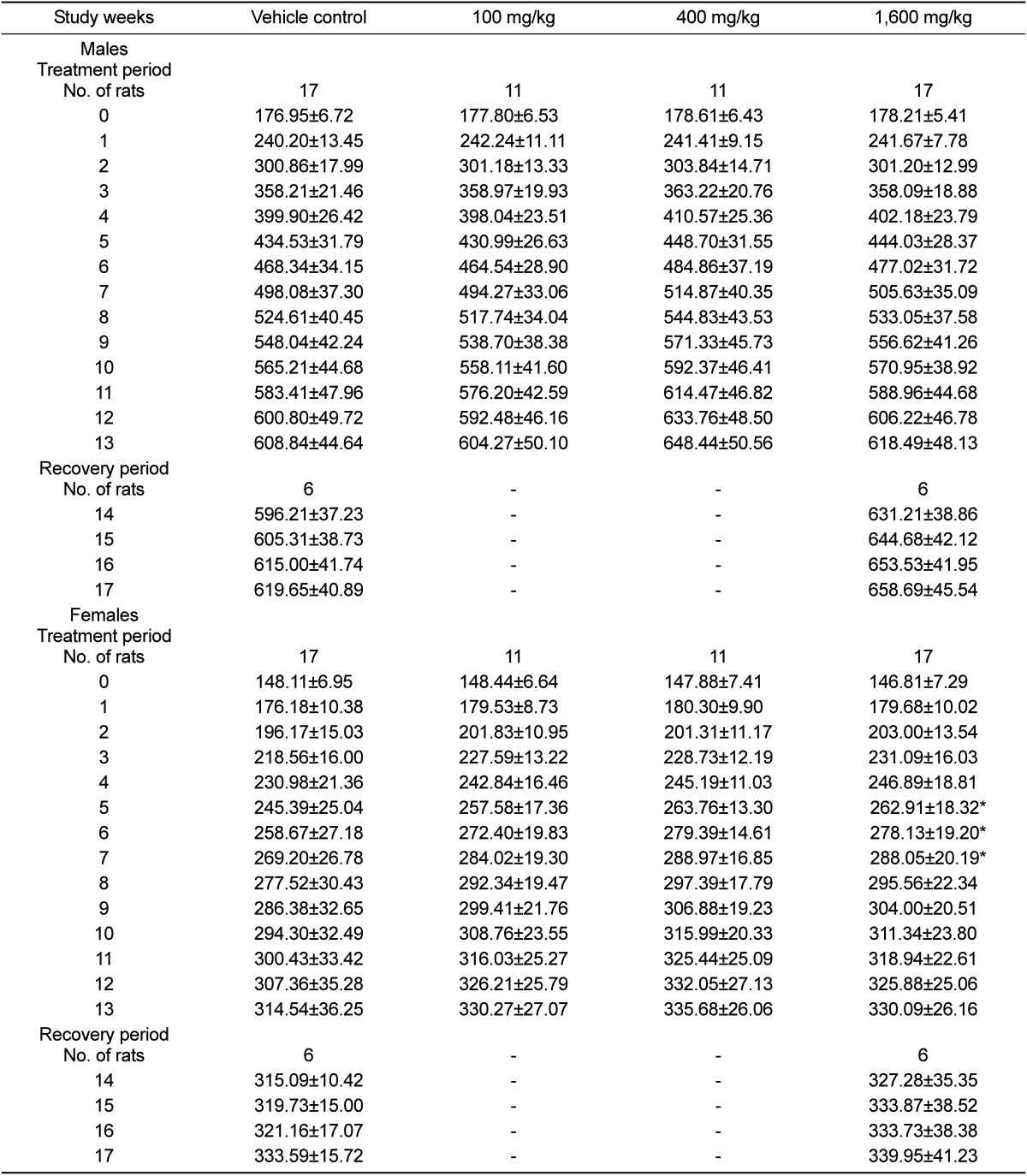
At the end of the quarantine and acclimation period, animals with findings in clinical signs and abnormalities in body weight increment were eliminated from the randomization pool. One-hundred twelve animals (56 males and 56 females) were randomly divided into four groups and administered test substance at doses of 0 (vehicle), 100, 400, 1,600 mg/kg. The dosing volume was 5 mL/kg. Test substance and vehicle were orally administered inside the stomach using a sonde attached by a disposable syringe once a day. The repeated dose toxicity included both a 13-week treatment period for all dosing groups (main groups) and a 4-week recovery period for 0 and 1,600 mg/kg dosing groups (recovery groups). During the treatment period, all animals were observed for clinical signs at least once daily. Body weights and food consumptions were measured just before dosing, once weekly for 13 weeks and the day of necropsy.
Ophthalmic examination and urinalysis
Ophthalmic evaluation was conducted once prior to the necropsy through macroscopic and ophthalmoscopic examinations (PRACTITIONER, Keeler, UK).
The urine samples were collected for urinalysis from animals prior to the necropsy. The urinalysis was performed using urine analyzer (MIDITRON Junior II, Roche, Germany) and stick (Combur10 Test® M, Roche, Germany) to evaluate the following parameters; color, transparency, volume, specific gravity, pH, protein, glucose, ketone, bilirubin, and erythrocyte. The sediment test was also performed microscopically.
Hematology and serum biochemistry
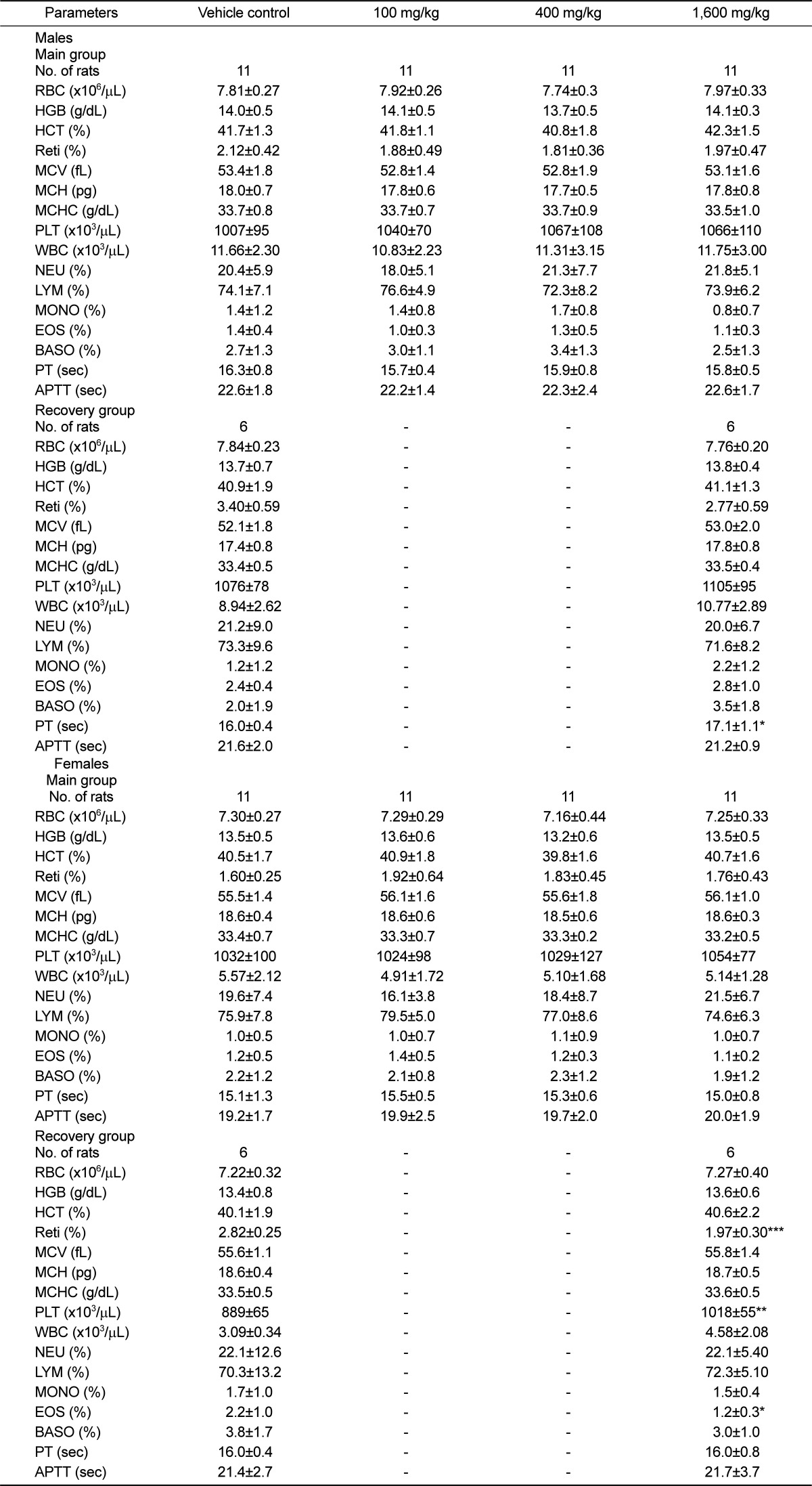
Hematological and serum biochemical determinations were performed from samples collected from an abdominal artery. Hematology samples were taken into tubes containing ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) and analyzed using the hematological autoanalyzer (CELLDYN 3700, Abbott, USA). Parameters including total red blood cell count (RBC), hemoglobin concentration (HGB), hematocrit (HCT), RBC indices, total white blood cell count (WBC), platelet (PLT), WBC differential count, and reticulocyte (Retic). The blood smear specimens were prepared and stained with Diff-Quick stain (Hemacolor®, Merk, Germany) for the calculation of the leukocyte percentage and new methylene blue dye for reticulocyte calculation. In addition, blood samples treated with 3.2% sodium citrate were analyzed for prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) by the automatic coagulation time meter (ACL 7000, Instrumental Laboratory, USA).
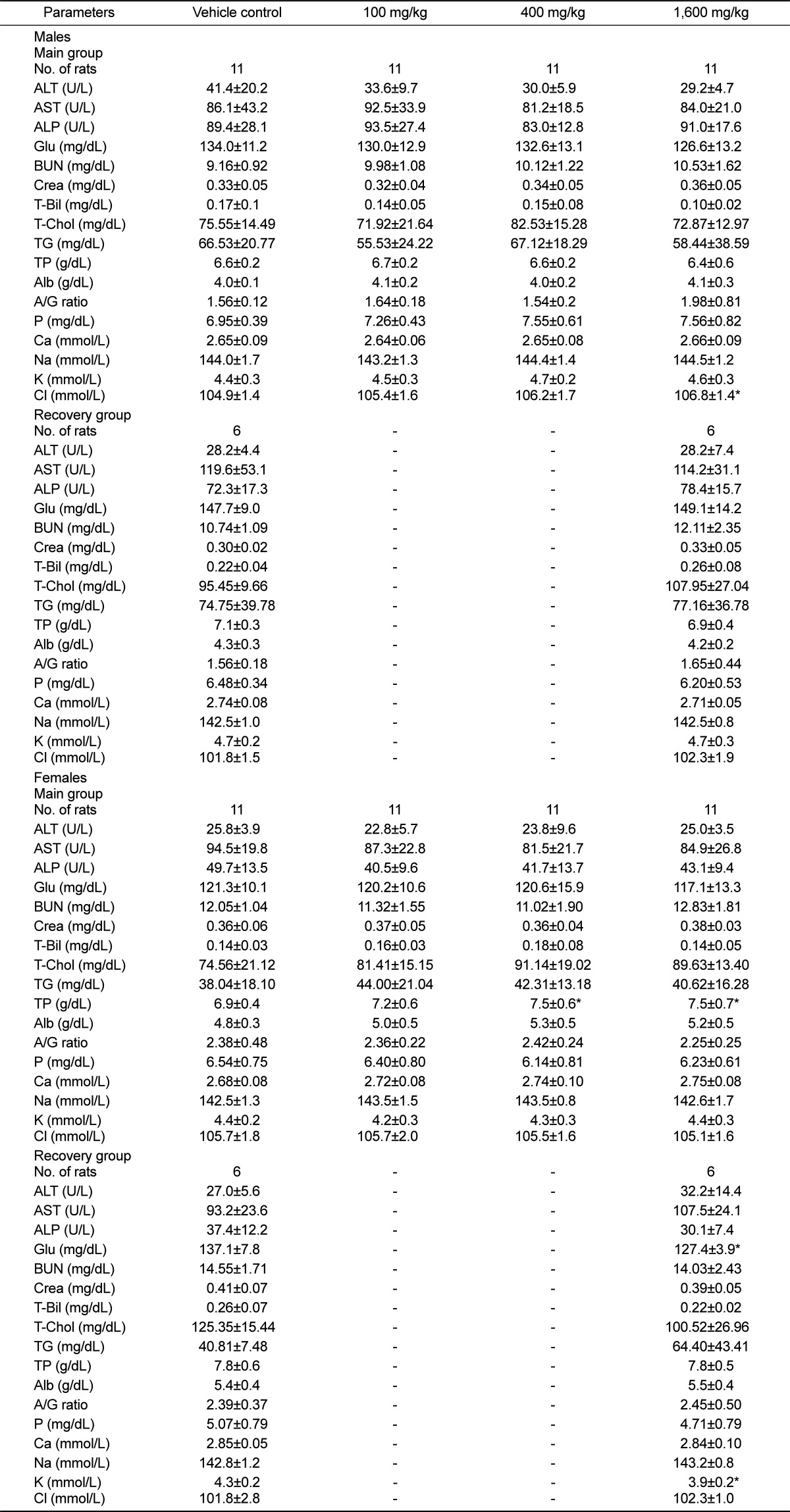
Serum biochemistry measurements of the following parameters were performed by INTEGRA 400 (Roche, Germany) and AVL9181 (Roche, Germany): Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), γ-gluramyltranspeptidase (γ-GT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (Creat), total bilirubin (T-Bili), total protein (TP), albumin (Alb), albumin/globulin ratio (A/G), total cholesterol (T-Chol), triglycerides (TG), phosphorus (P), glucose (Glu), calcium (Ca), chloride (Cl), sodium (Na), and potassium (K).
Gross observation and organ weights
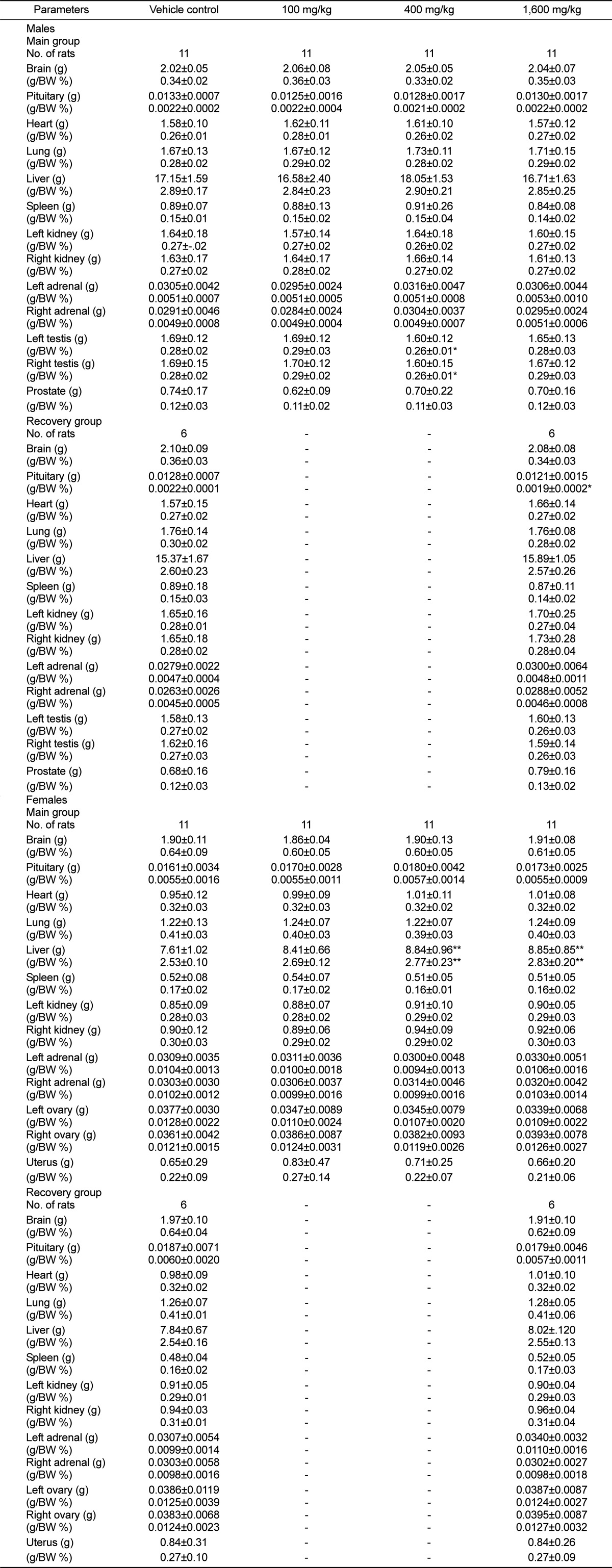
All animals were exsanguinated after the blood collection, recorded gross findings about full external surface, cranial cavity, and organs of thoracic and abdominal cavities. The absolute and relative (organ-to-body weight ratios) weights of organs including liver, heart, brain, kidneys, testes, ovaries, spleen, lungs, pituitary, adrenals, prostate, and uterus were measured.
Histopathology
Following tissues were collected and preserved at the 10% neutral buffer formalin except for testes which were fixed in the Davidson fixative: Liver, trachea, kidneys, spleen, esophagus, duodenum, ileum, colon, pancreas, brain, thyroids, testes, prostate, ovaries, lung, heart, adrenals, thymus, stomach, jejunum, cecum, rectum, submandibular gland, pituitary, urinary bladder, epididymides, seminal vesicle, and uterus. Fixed tissues were embedded in paraffin to make 3 µm tissue sectioned and stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin. Histopathological assessment was performed on all tissues of the control and highest dose group animals microscopically.
Statistical analysis
For the data including body weight, food consumption, urine volume, hematology and serum biochemisty and organ weight parameters, the Levene's test was conducted to test for variance of homogeneity. In the case of heterogeneity, proper data transformation was used to stabilize the variance. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was employed on homogeneous or transformed data and then, if significant, followed by Dunnett's test for multiple comparisons.
Go to :

Discussion
This study was conducted to assess the cumulative toxicity of UG0712, a new ginsenoside extract processed from ginseng leaves, when orally administered once daily to SD rats for a period of 13 weeks and to assess the reversibility of any effects after a 4-week recovery phase. The prospected clinical dose of UG0712 was 10 mg/kg if human eats maximum 600 mg/day/60 kg. Through the results of 4-week dose range finding study, treatment-related alterations were noted in the blood chemistry data in 2,000 mg/kg treated animals, but systemic toxicity attributed to treatment was not recognized (data not shown). Therefore, the dose levels were established as 100 mg/kg (10 times of the prospected clinical dose), 400 mg/kg, and 1,600 mg/kg with the geometric ratio of 4 in this study.
Under the conditions of our study, no treatment-related death was observed. Salivation was observed but this finding is considered to be the temporary sign due to the administration of test substance. Soft stool, diarrhea and mucous stool were occasionally observed in 1,600 mg/kg treated groups. Excessive administration of ginsenoside can cause the symptoms because unabsorbed ginsenoside into gastrointestinal duct can be excreted [
16,
17]. The temporal significant increase in body weights and food consumptions were observed in female with 1,600 mg/kg, consistent with the previous study [
18]. Opthalmological examination failed to detect any abnormalities and urinalysis parameters were unaffected. The increase of prothrombin time and the decreases of platelet, reticulocyte and eosinophil were observed in the recovery group. However, since these changes could not be observed in the main group, they were not considered a toxicological result of UG0712 treatment.
Serum chemistry data showed that chloride (Cl) and total protein (TP) were dose-dependently increased. Generally, the highest concentration of anion was contained in crude drugs and increased intake of Cl- via oral and intravenous may also lead to hyperchloremia [
19]. Yamamoto et al. (1978) had shown that protein synthesis was increased by ginsenoside. In addition, these values were within the normal range and no differences were found in a recovery period.
The absolute and relative liver weights were changed due to UG0712 treatment. However, there were no abnormalities at serum chemistry data, and histopathological changes also not identified in liver. It was also reported that Korean red ginseng accelerated the liver generation and ameliorated liver injury after hepatectomy in rats and dogs [
20,
21]. Therefore, the increase of liver weight was considered to be pharmacological effect attributed to treatment with UG0712. Although the relative weights of testes and pituitary in males were increased, their absolute weights and histopathological changes were not observed. Thus, these changes were not considered as a UG0712-induced abnormality.
In conclusion, repeated oral dose administration of UG0712 to SD rats for 13 weeks did not cause any toxic effects in rats of either sex up to dose of 1,600 mg/kg/ day. The NOAEL(no observed adverse effect level) was considered to be more than 1,600 mg/kg.
Go to :





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download