Materials and Methods
Care and use of OLETF rats
Preparation of AEtLP
Treatment of AEtLP and detection of glucose level
Serum biochemical analysis
Quantification of insulin and adiponectin by ELISA
Immunohistochemistry
Western blot
Statistical analysis
Results
Effects of AEtLP on body weight
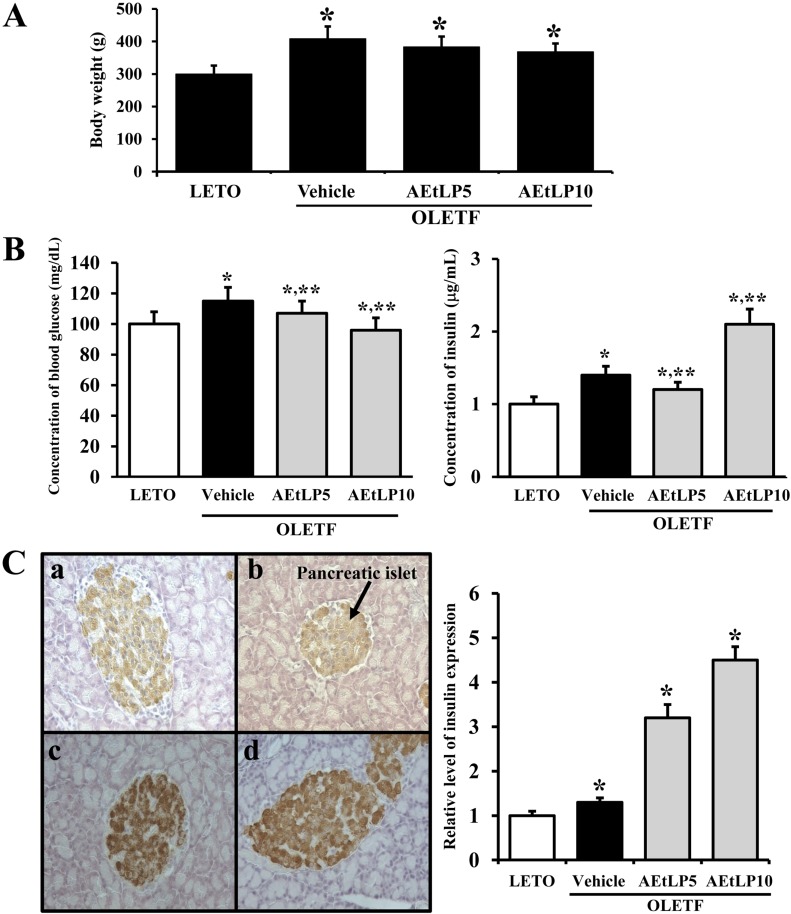 | Figure 1Effects of AEtLP on body weight and blood glucose and insulin levels. (A) Body weight analysis. At 24 h after final AEtLP treatment, body weight of rats was measured with an electronic balance electronic scale. (B) Glucose and insulin concentration analysis. Blood was collected from abdominal veins of vehicle- and AEtLP-treated OLETF rats. Glucose level was measured using a CareSence Kit, and insulin level was determined using an insulin ELISA kit. (C) Immunohistochemistry. Expression level of insulin was detected in pancreatic islets of vehicle-treated and AEtLP-treated OLETF rats by immunostaining analysis. High intensity was observed in pancreatic islets of AEtLP10-treated OLETF rats as compared with vehicle-treated mice at 200x magnification. Data represent the mean±SD from three replicates. *P<0.05 is the significance level compared to LETO rats. **P<0.05 is the significance level compared to vehicle-treated group in OLETF rats. |
Effects of AEtLP on insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis
AEtLP effects on abdominal fat mass and adiponectin concentration
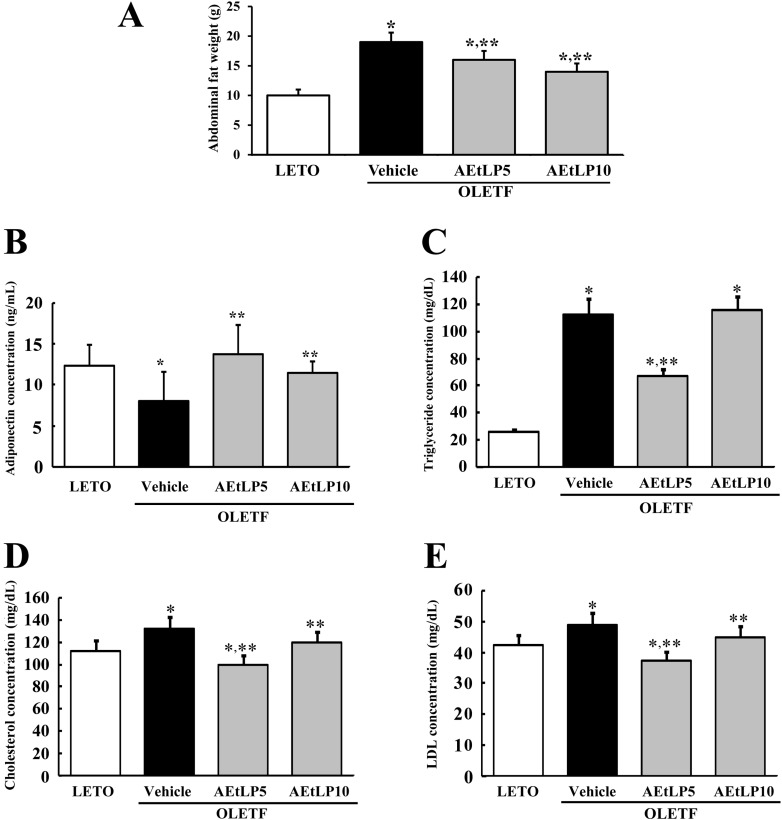 | Figure 2Effects of AEtLP on abdominal fat mass and lipid concentration. (A) At 24 h after final AEtLP treatment, abdominal fat collected from abdominal region of rats and their weight was measured with an electronic balance. Blood was collected from abdominal veins of rats, and (B) adiponectin level in serum was analyzed using an ELISA kit. This kit has 0.1 ng/mL of sensitivity, and the interassay coefficient of variation was between 2.86-5.17. (C-E) Levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and LDL were analyzed in triplicate using a serum biochemical analyzer. Data represent the mean±SD from three replicates. *P<0.05 is the significance level compared to LETO rats. **P<0.05 is the significance level compared to vehicle-treated group in OLETF rats. |
AEtLP effects on lipid concentration in OLETF rats
Effects of AEtLP on regulation of Glut-1 expression through the insulin signaling pathway
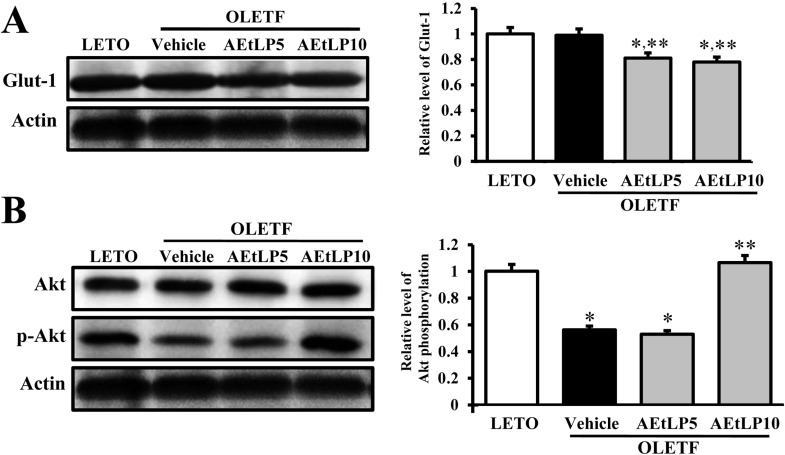 | Figure 3Glut-1 expression and its regulatory mechanism in liver. Tissue lysates were prepared from liver tissues of LETO, vehicle-, and AEtLP-treated OLETF rats. Fifty micrograms of protein per sample was immunoblotted with antibody for each protein. Glut-1 protein expression was detected with primary antibodies for Glut-1 (A), Akt and p-Akt (B), and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Intensity of each protein was calculated using an imaging densitometer. Three out of 4 to 5 rats per group were assayed in duplicate by western blot. Data represent the mean±SD. *P<0.05 is the significance level compared to LETO rats. **P<0.05 is the significance level compared to vehicle-treated group in OLETF rats. |
Effects of AEtLP on regulation of Glut-3 expression through the insulin signaling pathway
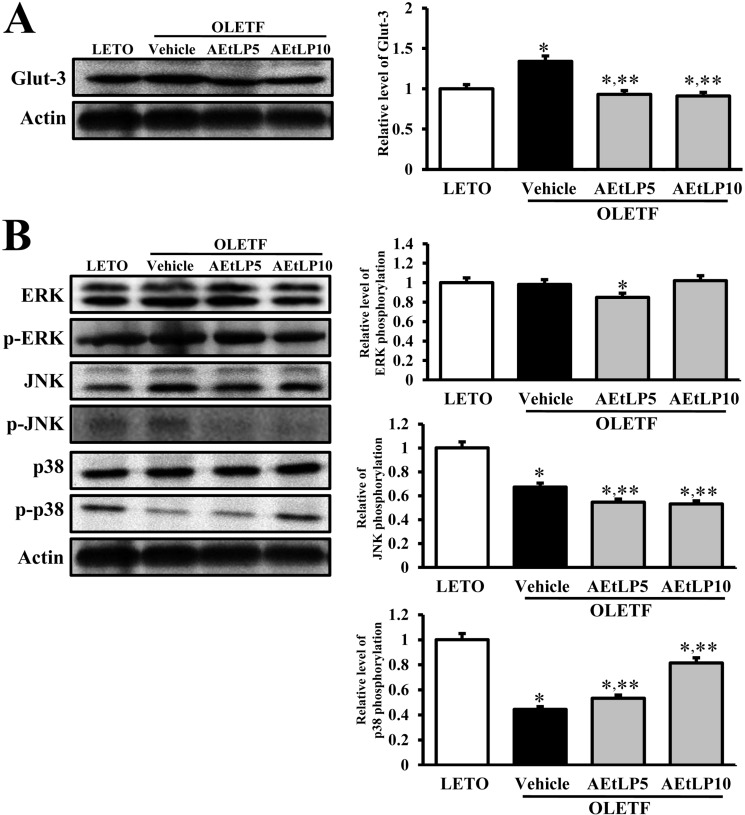 | Figure 4Glut-3 expression and its regulatory mechanism in the liver. Fifty micrograms of protein per sample was immunoblotted with antibody for p-ERK, ERK, p-JNK, JNK, p38, p-p38, or actin. Intensity of each protein was calculated using an imaging densitometer. Three out of 4 to 5 rats per group were assayed in duplicate by western blot. Data represent the mean±SD. *P<0.05 is the significance level compared to LETO rats. **P<0.05 is the significance level compared to vehicle-treated group in OLETF rats. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download