Abstract
Rectal prolapse is a protrusion of one or more layers of the rectum through the anus. A 5-year-old laboratory cynomolgus monkey who had suffered from recurrent diarrhea died after surgical resection of a prolapsed rectum. On examination, the prolapsed rectum was a cylinder-shaped tissue whose surface was moist and dark red with a small amount of hemorrhage. Histologically, the rectum was characterized by a segmental to diffuse cellular infiltration in the submucosa and muscle layers. Inflammation in the rectum resulted in irritation of the myenteric plexus, which could cause hypermotility of the intestines, leading to chronic diarrhea. Rectal prolapse would result in economical loss or death of laboratory animals. However, rectal prolapse in the laboratory monkey could be easily overlooked because diarrhea or other symptoms resulting from rectal prolapse could be sometimes misunderstood as a primary problem. Therefore, researchers should suspect rectal prolapse if intestinal symptoms in the laboratory monkey are untreatable.
References
Anderson, D.E. and Miesner, M.D. (. 2008. ). Rectal prolapse. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 24:403–408.
Andrews, N.J. and Jones, D.J. (. 1992. ). ABC of colorectal diseases: Rectal prolapse and associated conditions. BMJ. 305:243–246.
Bertelsen, M.F., Olberg, R.A., Mehren, K.G., Smith, D.A. and Crawshaw, G.J. (. 2004. ). Surgical management of rectal prolapse in an Indian rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 35:245–247.
DeBowes, R.M. (. 1991. ). Standing rectal and tail surgery. Vet. Clin. North Am. Equine Pract. 7:649–667.
Ediger, R.D., Kovatch, R.M. and Rabstein, M.M. (. 1974. ). Colitis in mice with a high incidence of rectal prolapse. Lab. Anim. Sci. 24:88–94.
Elker, B. and Modransky, P. (. 1991. ). Rectal prolapse in food animals. Part 1. Cause and conservative management. Comp. Cont. Educ. Pract. 13:1869–1873.
Garden, S. (. 1988. ). Rectal prolapse in pigs. Vet. Rec. 123, 654. Greiner, T.P. (1973) Surgery of the rectum and anus. Vet. Clin. North Am. 2:167–180.
Kalema-Zikusoka, G. and Lowenstine, L. (. 2001. ). Rectal prolapse in a free-ranging mountain gorilla (gorilla beringei beringei): Clinical presentation and surgical management. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 32:509–513.
Kumar, M.J.M., Nagarajan, P., Venkatesan, R. and Juyal, R.C. (. 2004. ). Case Report and Short Communication: Rectal prolapse associated with an unusual combination of pinworms and citrobacter species infection in FVB mice colony. Scand. J. Lab. Anim. Sci. 31:221–223.
Marjani, M., Selk, G.M. and Moosakhani, F. (. 2009. ). Rectal prolapse secondary to antibiotic-associated colitis in a dog. Clin. Pathol. 18:473–475.
Miller, R.E. and Boever, W.J. (. 1983. ). Repair of rectal stricuture and prolapse in a pygmy hippopotamus (Choeropsis liberiensis). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 14:63–66.
Olivier, A., Lane, E., Volkmann, D.H., Hofmeyr, M. and Stegmann, G.F. (. 2001. ). Rectal prolapse associated with a healed pelvic fracture in a pregnant free-ranging African black rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis). Part 2: Surgery and necropsy. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 72:242–244.
Popovitch, C.A., Holt, D. and Bright, R. (. 1994. ). Colopexy as a treatment for rectal prolapse in dogs and cats: a retrospective study of 14 cases. Vet. Surg. 23:115–118.
Remfry, J. (. 1978. ). The incidence, pathogenesis and treatment of helminth infections in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Lab. Anim. 12:213–218.
Romero, A., Grau, M.T., Villamayor, F., Sacristán, A. and Ortiz, J.A. (. 1997. ). Subacute toxicity of ebrotidine in rats and dogs. Arzneimittelforschung. 47:492–497.
Shakespeare, A. (. 2000. ). Intussusception as a complication of rectal prolapse replacement in a ewe. Vet. Rec. 147:78–79.
Tribe, G.W. (. 1965. ). Rectal prolapse in a Macaca mulatta monkey. Vet. Rec. 77, 551. West, G.A., Golshani, K.J., Doyle, K.P., Lessov, N.S., Hobbs, T.R., Kohama, S.G., Pike, M.M., Kroenke, C.D., Grafe, M.R., Spector, M.D., Tobar, E.T., Simon, R.P. and Stenzel-Poore, M.P. (2009) A New model of cortical stroke in the rhesus macaque. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 29:1175–1186.
Figure 1.
Rectal prolapse of the laboratory cynomolgus monkey. Cylinder-shaped prolapsed rectum was protruded through the anus. The surface of the prolapsed rectum is moist and dark red with a small amount of hemorrhage.
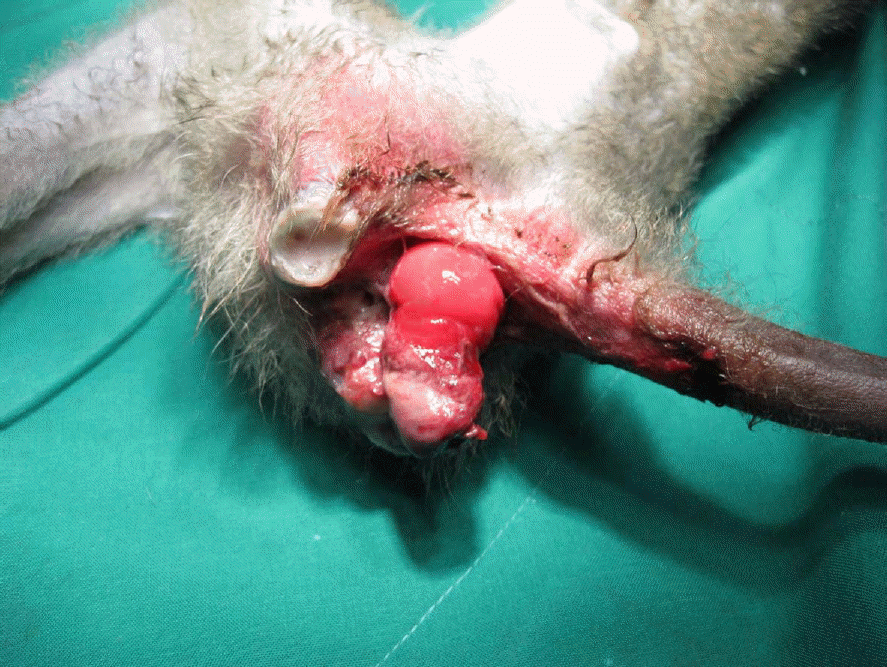
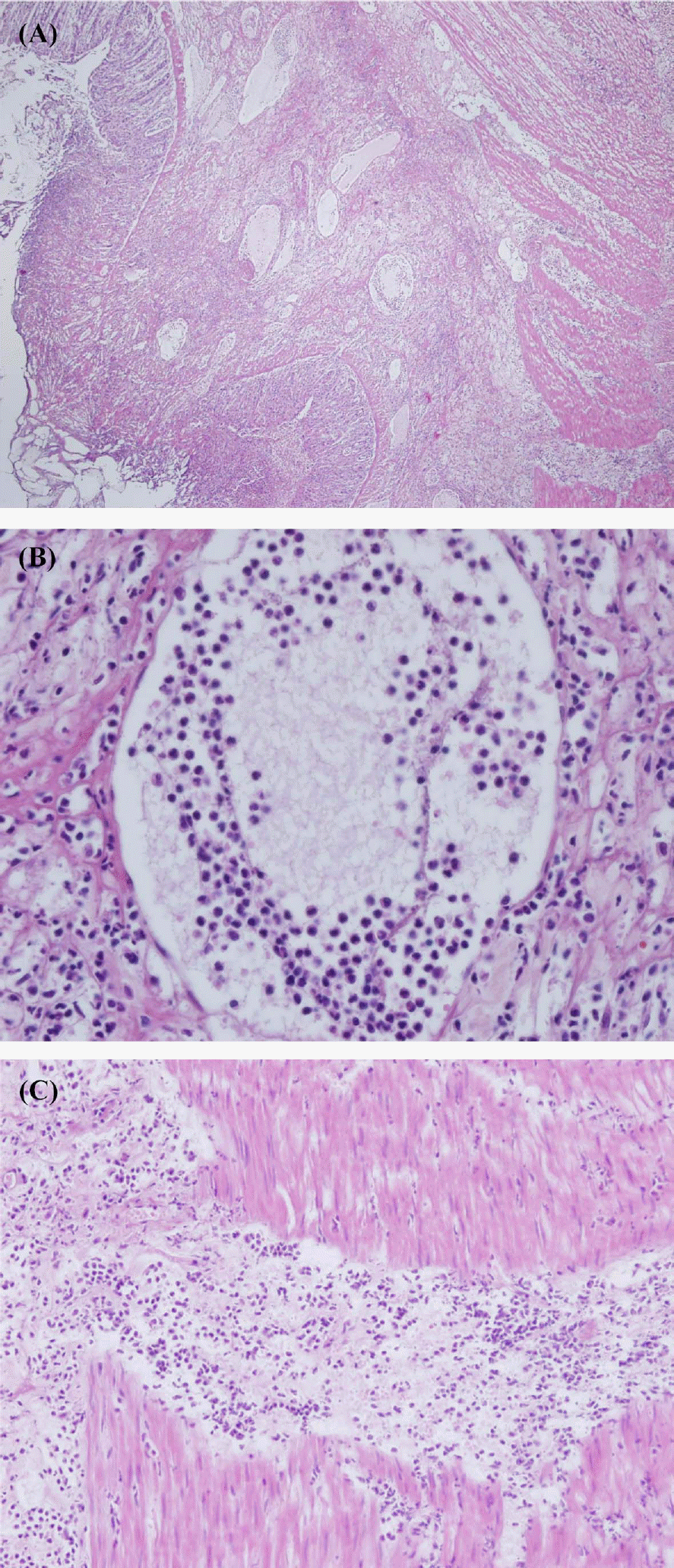
Figure 2.
Histological findings of the prolapsed rectum of the laboratory cynomolgus monkey. (A) The rectum is characterized by a segmental to diffuse cellular infiltration in the submucosa and muscle layers. H&E stain (×40). (B) In the submucosa, the lymphatic vessels were markedly dilated and contain a number of neutrophils admixed with a few number of monocytes and lymphocyte and abundant amount of fibrin (×400). (C) Numerous neutrophils with a few lymphocyte in the submucosa penetrated into muscle layers (×200).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download