Abstract
PEA-15 is a small phosphoprotein (15 kDa) that is enriched in brain astrocytes. PEA-15 acts as an important modulator of cellular function including apoptosis and signal integration. This study investigated the expression of PEA-15 in focal cerebral ischemic injury. Cerebral ischemia was surgically induced in adult male rats by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), and brains were collected 24 hr after MCAO. A proteomic approach demonstrated decreases of PEA-15 protein spots in MCAO-operated animals in comparison to sham-operated animals. Western blot analysis clearly demonstrated that MCAO induces decreases in PEA-15 levels. We previously showed that glutamate toxicity induces cell death in a hippocampus-derived cell line (HT22). Glutamate exposure induces decreases of PEA-15 levels in HT22 cells. The results of this study suggest that focal cerebral ischemia induces cell death through downregulation of PEA-15 protein.
REFERENCES
Araujo H.., Danziger N.., Cordier J.., Glowinski J.., Chneiweiss H.1993. Characterization of PEA-15, a major substrate for protein kinase C in astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 268(8):5911–5920.

Danziger N.., Yokoyama M.., Jay T.., Cordier J.., Glowinski J.., Chneiweiss H.1995. Cellular expression, developmental regulation, and phylogenic conservation of PEA-15, the astrocytic major phosphoprotein and protein kinase C substrate. J. Neurochem. 64(3):1016–1025.

Dawson D.A.., Martin D.., Hallenbeck J.M.1996. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha reduces focal cerebral ischemic injury in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Neurosci. Lett. 218(1):41–44.

Ferrer I.., Planas A.M.2003. Signaling of cell death and cell survival following focal cerebral ischemia: life and death struggle in the penumbra. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62(4):329–339.

Jia J.., Guan D.., Zhu W.., Alkayed N.J.., Wang M.M.., Hua Z.., Xu Y.2009. Estrogen inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis in experimental stroke. Exp. Neurol. 215(1):48–52.

Koh P.O.2007. 17Beta-estradiol prevents the glutamate-induced decrease of Akt and its downstream targets in HT22 cells. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 69(3):285–288.

Koh P.O.2008. Melatonin prevents the injury-induced decline of Akt/forkhead transcription factors phosphorylation. J. Pineal Res. 45(2):199–203.

Koh P.O.2010. Proteomic analysis of focal cerebral ischemic injury in male rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 72(2):181–185.

Krueger J.., Chou F.L.., Glading A.., Schaefer E.., Ginsberg M.H.2005. Phosphorylation of phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes (PEA-15) regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent transcription and cell proliferation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 16(8):3552–3561.

Li Y.., Chopp M.., Powers C.., Jiang N.1997. Apoptosis and protein expression after focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Brain Res. 765(2):301–312.

Longa E.Z.., Weinstein P.R.., Carlson S.., Cummins R.1989. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20(1):84–91.

Maher P.., Davis J.B.1996. The role of monoamine metabolism in oxidative glutamate toxicity. J. Neurosci. 16(20):6394–6401.

Renault F.., Formstecher E.., Callebaut I.., Junier M.P.., Chneiweiss H.2003. The multifunctional protein PEA-15 is involved in the control of apoptosis and cell cycle in astrocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 66(8):1581–1588.

Sharif A.., Canton B.., Junier M.P.., Chneiweiss H.2003. PEA-15 modulates TNF alpha intracellular signaling in astrocytes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1010:43–50.
Figure 1.
PEA-15 protein spots identified by MALDI-TOF. Arrows indicate the protein spots. The intensity of spots was measured using PDQuest software. The ratio of intensity is described as spots intensity of MCAO-operated animal to spots intensity of sham-operated animal. Data are shown as mean± S.E.M. ∗P<0.05 (vs. Sham). Mw and IP indicate molecular weight and isoelectrical point, respectively.
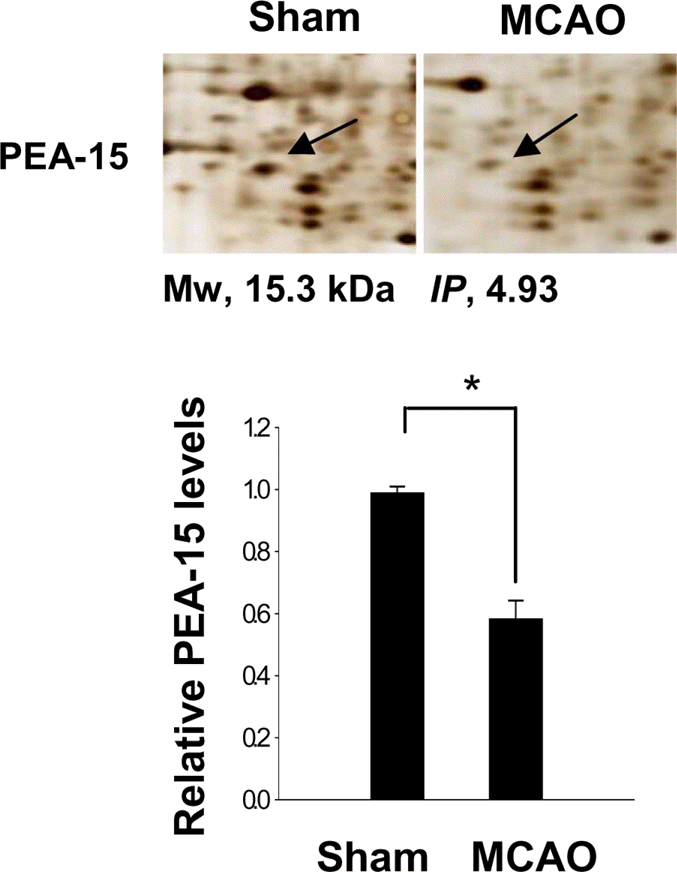
Figure 2.
Western blot analysis of PEA-15 in the cerebral cortex from sham-operated and MCAO-operated animals. Each lane represents an individual experimental animal. Densitometric analysis of PEA-15 levels is represented as intensity of PEA-15 to intensity of actin. Data are shown as mean±S.E.M. ∗P<0.05 (vs. Sham).
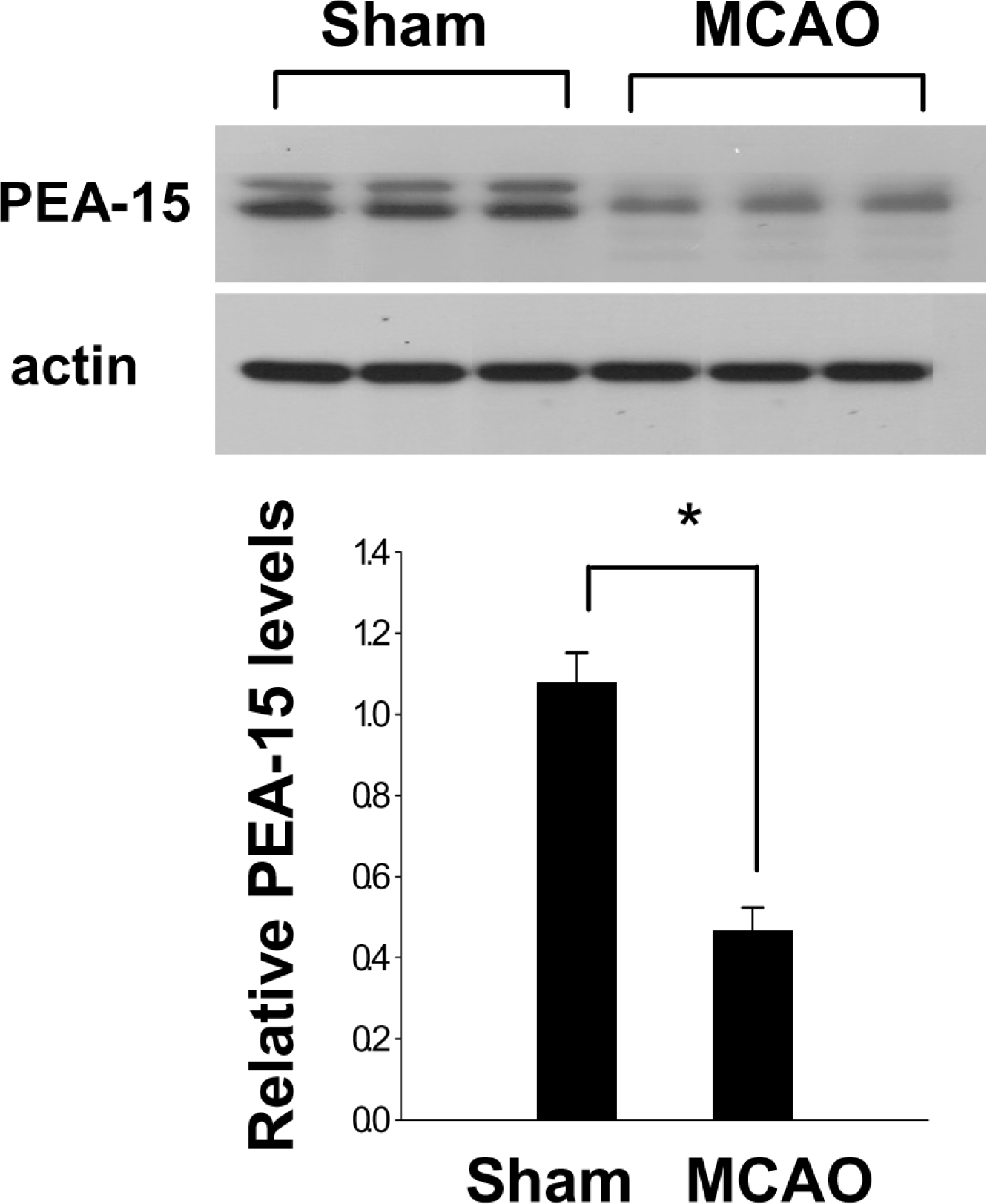
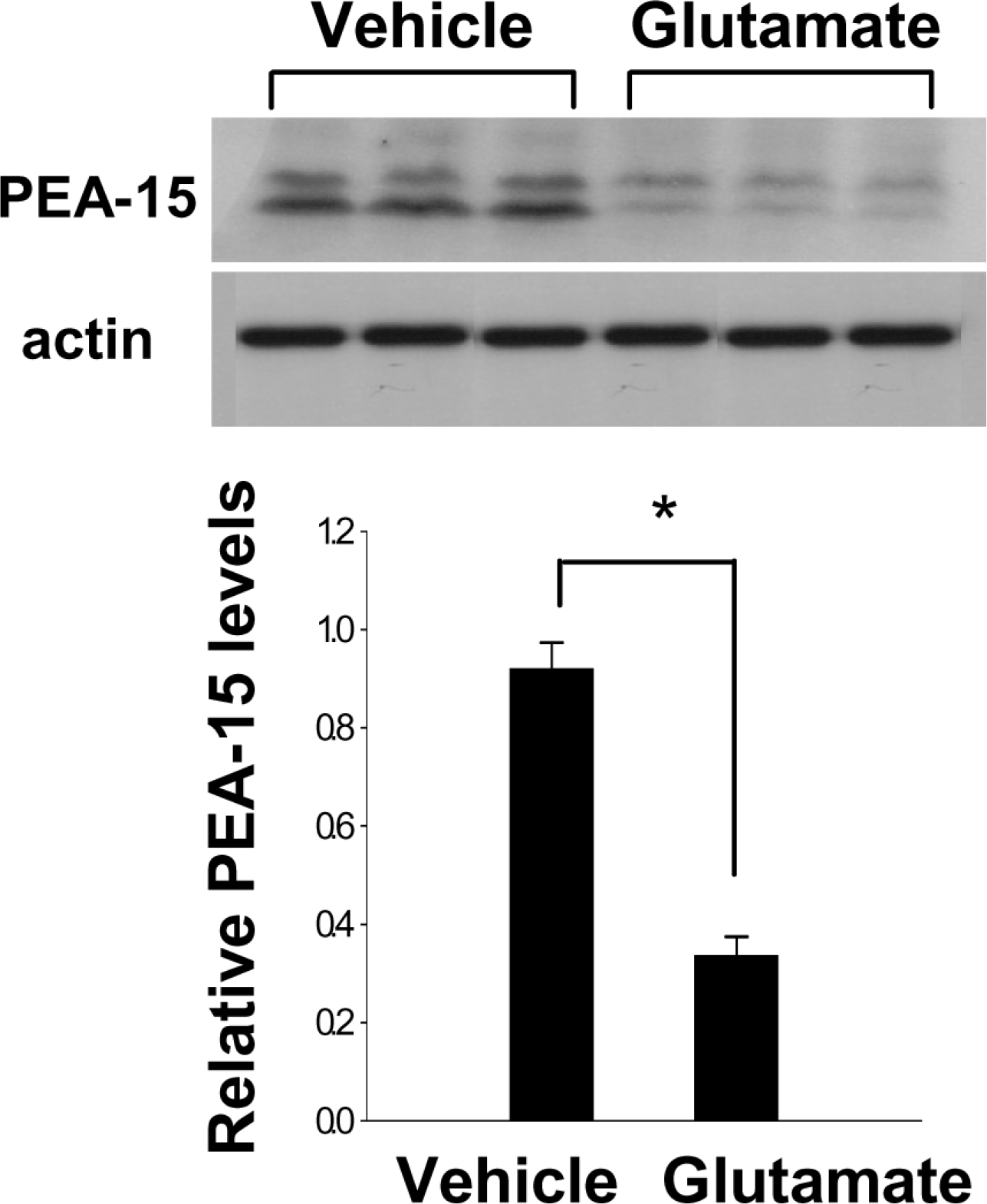
Figure 3.
Western blot analysis of PEA-15 in HT22 cells. Vehicle or glutamate (5 mM) was exposed to HT22 cells for 24 hr. Each lane represents an individual experimental animal. Densitometric analysis of PEA-15 levels is represented as intensity of PEA-15 to intensity of actin. Data are shown as mean±S.E.M. ∗P<0.05 (vs. Vehicle).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download