Abstract
Recently, we demonstrated that a large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel (BKCa) in human umbilical cord vein-derived mesenchymal cells (hUC-MSCs). In this study, we studied effects of quercetin, the flavonoid used for the modulator of cell cycle and the treatment of anti-tumor, on BKca in hUC-MSCs using single channel and/or whole cell configuration. Single channel conductance was 277.8±36.2 pS in hUC-MSCs and the value is similar to that of typical BKCa channel reported in other cells. The single channel current was activated by increasing of intracellular Ca2+. Quercetin (30~100 µM) increased BKCa in whole cell patch configuration whereas EGCG was not affected on the channel. The activation effect of quercetin on BKCa channel was also observed in inside-out configuration. The quercetin-induced BKCa was increased a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 19.9 µM. Taken together, BKCa in hUC-MSCs can be an important target for the action of quercetin and the channels are partly may contribute to maintaining homeostasis by regulation of K ion flux in hUC-MSCs.
REFERENCES
Cermak R.., Follmer U.., Wolffram S.1998. ).Dietary flavonol quercetin induces chloride secretion in rat colon. Am. J. Physiol. 275(5 Pt 1):G1166–1172.
Choi J. A.., Kim J. Y.., Lee J. Y.., Kang C. M.., Kwon H. J.., Yoo Y. D.., Kim T. W.., Lee Y. S.., Lee S. J.2001. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by quercetin. Int. J. Oncol. 19(4):837–844.

Cogolludo A.., Frazziano G.., Briones A. M.., Cobeno L.., Moreno L.., Lodi F.., Salaices M.., Tamargo J.., Perez-Vizcaino F.2007. The dietary flavonoid quercetin activates BKCa currents in coronary arteries via production of H2O2. Role in vasodilatation. Cardiovasc. Res. 73(2):424–431.
Duarte J.., Perez-Palencia R.., Vargas F.., Ocete M. A.., Perez-Vizcaino F.., Zarzuelo A.., Tamargo J.2001. Antihypertensive effects of the flavonoid quercetin in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 133(1):117–124.

Hertog M. G.., Hollman P. C.1996. Potential health effects of the dietary flavonol quercetin. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50(2):63.
Kuhlmann C. R.., Schaefer C. A.., Kosok C.., Abdallah Y.., Walther S.., Ludders D. W.., Neumann T.., Tillmanns H.., Schafer C.., Piper H. M.., Erdogan A.2005. Quercetin-induced induction of the NO/cGMP pathway depends on Ca2+-activated K+ channel-induced hyperpolarization-mediated Ca2+-entry into cultured human endothelial cells. Planta Med. 71(6):520–524.
Lee E. H.., Meissner G.., Kim D. H.2002a. Effects of quercetin on single Ca2+ release channel behavior of skeletal muscle. Biophys. J. 82(3):1266–1277.
Lee L. T.., Huang Y. T.., Hwang J. J.., Lee P. P.., Ke F. C.., Nair M. P.., Kanadaswam C.., Lee M. T.2002b. Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase activity by quercetin and luteolin leads to growth inhibition and apoptosis of pancreatic tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 22(3):1615–1627.
Lin R. W.., Chen C. H.., Wang Y. H.., Ho M. L.., Hung S. H.., Chen I. S.., Wang G. J.2009. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate inhibition of osteoclastic differentiation via NF-kappaB. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 379(4):1033–1037.
Park K. S.., Jung K. H.., Kim S. H.., Kim K. S.., Choi M. R.., Kim Y.., Chai Y. G.2007. Functional expression of ion channels in mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord vein. Stem Cells. 25(8):2044–2052.

Park K. S.., Jung K. H.., Chai Y. G.., Kim C. H.., Shin E. Y.., Kim Y.2008. Riluzole-induced activation of BKCa channels and inhibition of voltage-gated Na+ channel in human umbilical cord vein-derived mesenchymal cells. Lab. Anim. Res. 24(3):287–292.
Rassi C. M.., Lieberherr M.., Chaumaz G.., Pointillart A.., Cournot G.2005. Modulation of osteoclastogenesis in porcine bone marrow cultures by quercetin and rutin. Cell Tissue Res. 319(3):383–393.

Roger S.., Potier M.., Vandier C.., Le Guennec J. Y.., Besson P.2004. Description and role in proliferation of iberiotoxin-sensitive currents in different human mammary epithelial normal and cancerous cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1667. (2):190–199.
Sanchez M.., Galisteo M.., Vera R.., Villar I. C.., Zarzuelo A.., Tamargo J.., Perez-Vizcaino F.., Duarte J.2006. Quercetin downregulates NADPH oxidase, increases eNOS activity and prevents endothelial dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 24(1):75–84.
Saponara S.., Sgaragli G.., Fusi F.2002. Quercetin as a novel activator of L-type Ca2+ channels in rat tail artery smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 135(7):1819–1827.
Shin D. W.., Kim S. N.., Lee S. M.., Lee W.., Song M. J.., Park S. M.., Lee T. R.., Baik J. H.., Kim H. K.., Hong J. H.., Noh M.2009. (-)-Catechin promotes adipocyte differentiation in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through PPAR gamma transactivation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77(1):125–133.
Figure 1.
The effect EGCG (epigallocatechin 3-gallate) and quercetin on outward in hUC-MSCs. hUC-MSCs were voltage-clamped under whole cell configuration at -80 mV. Voltage steps of 200 ms duration were then applied from -40 mV to 50 mV in 10-mV increments every 10 s, showing outward currents a rapidly activating current with noisy oscillation, similar to large conductance Ca2+ activated K+ current (BKCa). The pipette solution consisted of 140 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM Mg-ATP and 2 mM EGTA; the bath solution contained 143 mM NaCl, 5.4 mM KCl, 0.5 mM NaH2PO4, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 5 mM HEPES and 10 mM glucose. (A) Membrane currents were recorded in the presence of EGCG. (A-1) The current-voltage relationship (I-V relationship) was plotted from A. Current-voltage relationship showed in the control (■), 50 µM EGCG (●) and wash (▲). (B) Quercetin increased outward current in hUC-MSCs. (B-1) The current-voltage relationship (I-V relationship) was plotted from B. I-V relationships showed in the control (■), 100 µM quercetin (●) and wash (▲).
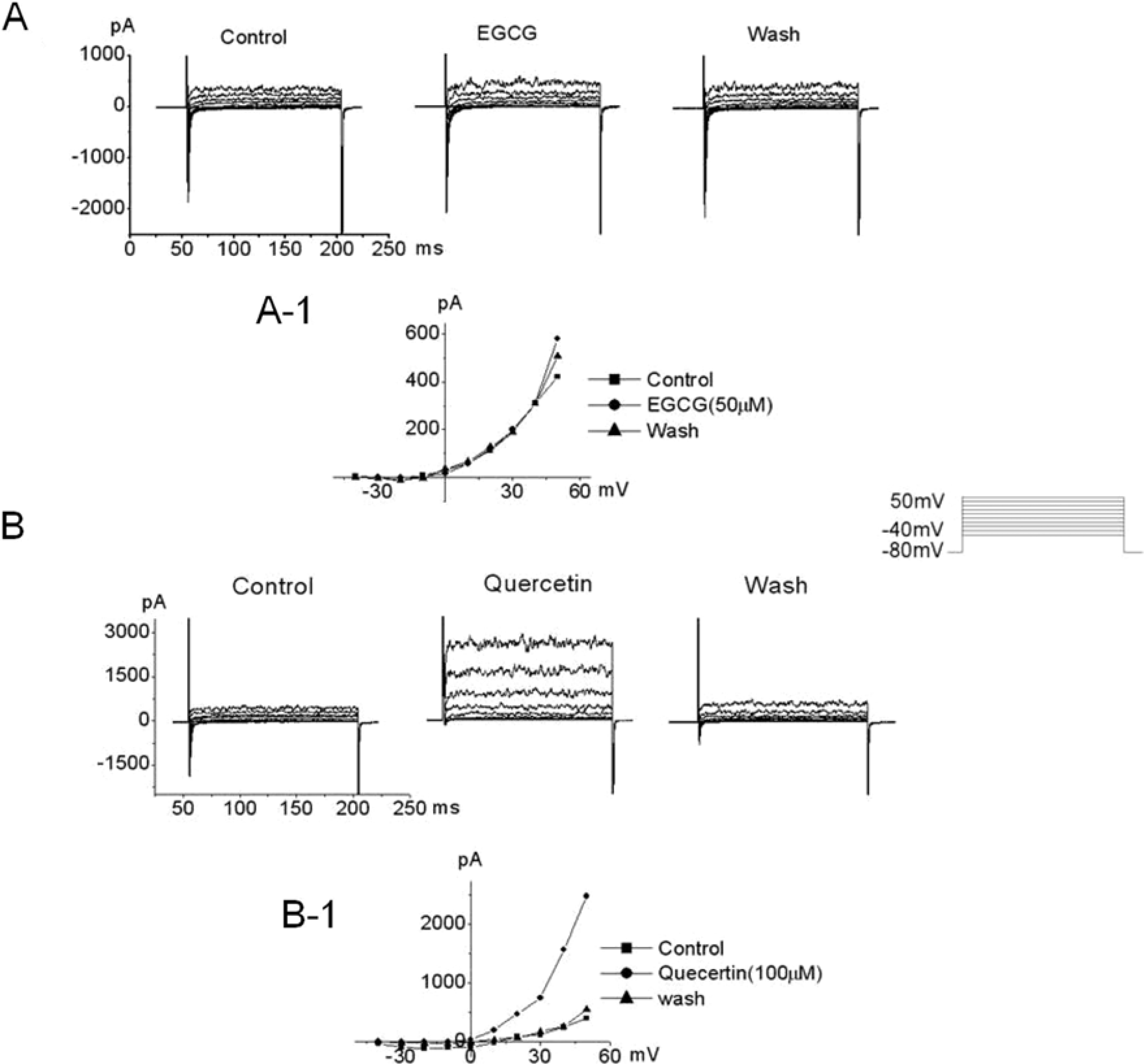
Figure 2.
Effect of extracellular quercetin on the outward current in hUC-MSCs. (A) Ramp pulse was applied from -120 to 60 mV for 250 ms at a holding potential of -80 mV and the pulse was applied at every 10 s. The x-axis shows time and the y-axis shows current. The outward current was activated by quercetin. Currents were reached a stable level in 2 min after the application of quercetin (100 µM) and recovered after washing with quercetin-free solution. (A-1) Quercetin -induced typical outward-rectifying current vs. voltage. (B) Dose dependence of quercetin-induced outward current in hUC-MSC using the whole cell patch configuration. Currents were measured at 50 mV and IC50 was 19.9 µM. (n=3 cells per concentration).
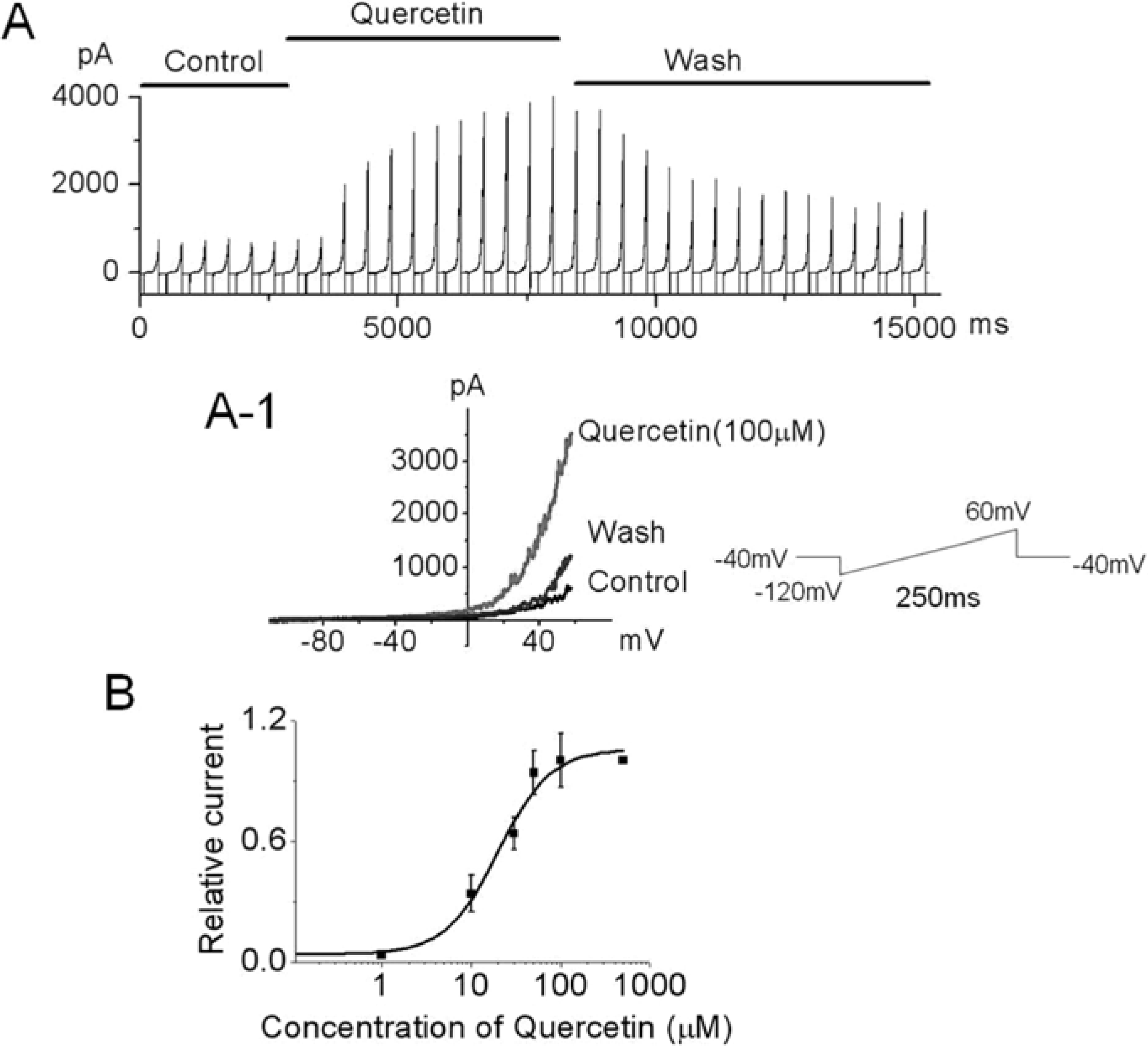
Figure 3.
The effect of intracellular quercetin on large conductance Ca2+ activated K+ channels (BKCa) using single channel recording in hUC-MSCs. Data were obtained from estimates of relative channel activity. (A) The trace shown the effect of intracellular Ca2+. Single channel currents recorded at +40mV from an inside-out patch configuration. Pipette solution contained 150 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EGTA, and 10 mM HEPES. The bath solution consisted of 150 mM KCl 150 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EGTA, and 10 mM HEPES and 0 µM, 1 µM CaCl2. The channel activity was increased by [Ca2+]i dependently. The letter “a” and “b” show an expanded scale of the A. Current amplitude of 1 main peak is about 12 pA. (B) The traces were showed the effect of quercetin on BKCa channels. The channel activity was increased by intracellular application of quercetin (30 µM). The letter “a” and “b” show an expanded scale of the A. The recording potential was +60mV. Current amplitude of 1 main peak is about 15 pA. The letter “close” represents the closed channel level and the letter “open” represents the open channel level. Abbreviations: min, minutes; ms, milliseconds; pA, picoampere.
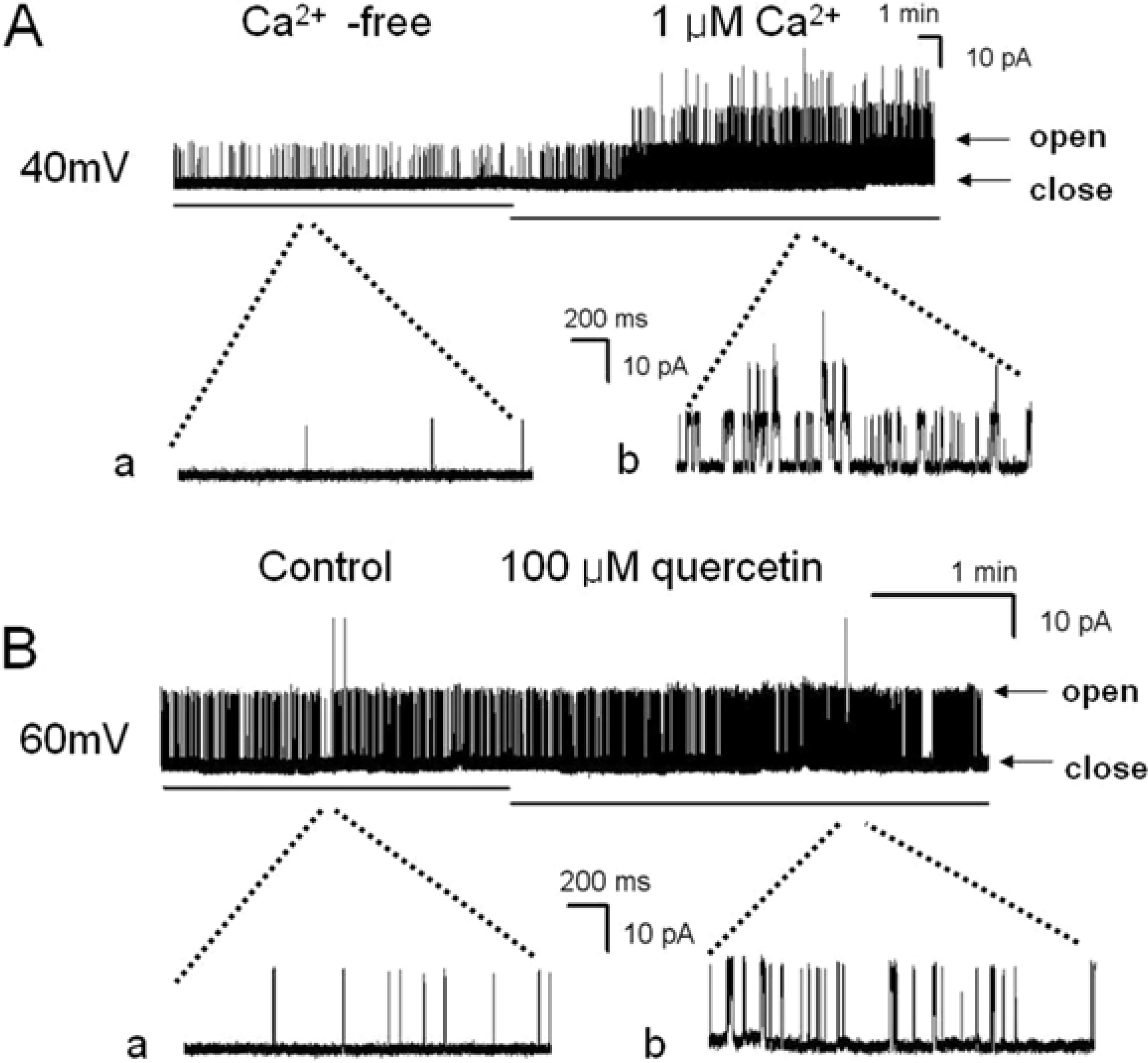
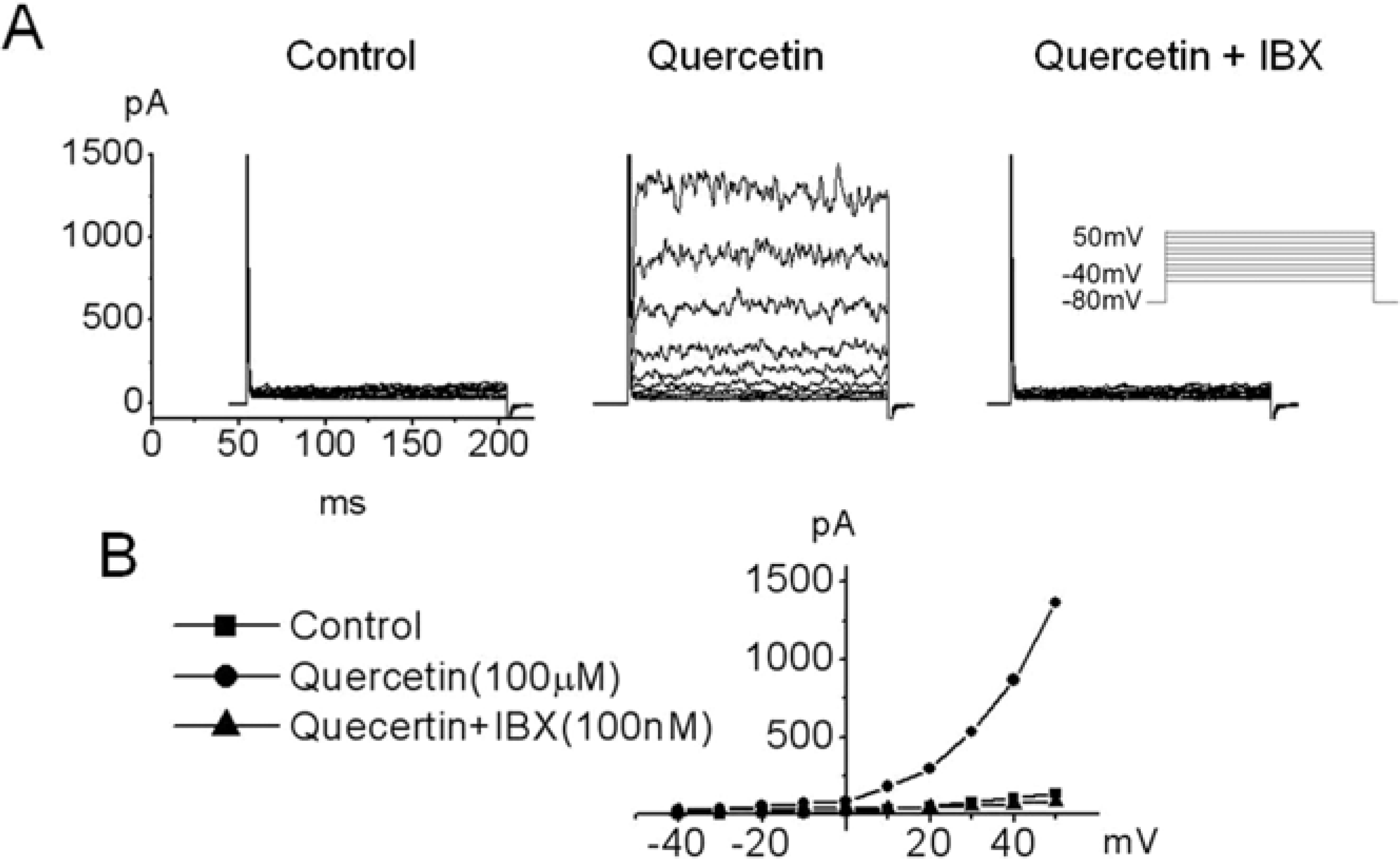
Figure 4.
Effect of quercetin and Iberiotoxin (IBX, a blocker of large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ current) on BKCa in hUC-MSCs. (A) Current traces are shown for 200-ms depolarization pulses from -40 mV to +50 mV (in 10-mV increments) from a holding potential of -80mV. Quercetin activates noisy outward currents in hUC-MSCs. Currents were recorded before (control), after the exposure to quercetin (100 µM) reached a stable level (3 min) and after application with quercetin and IBX solution. (B) The current-voltage relationship (I-V relationship) was plotted from A. I-V relationships of currents showed in the control (■), 100 µM quercetin (●) and 100 µM quercetin with 100 nM iberiotoxin (▲).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download