Abstract
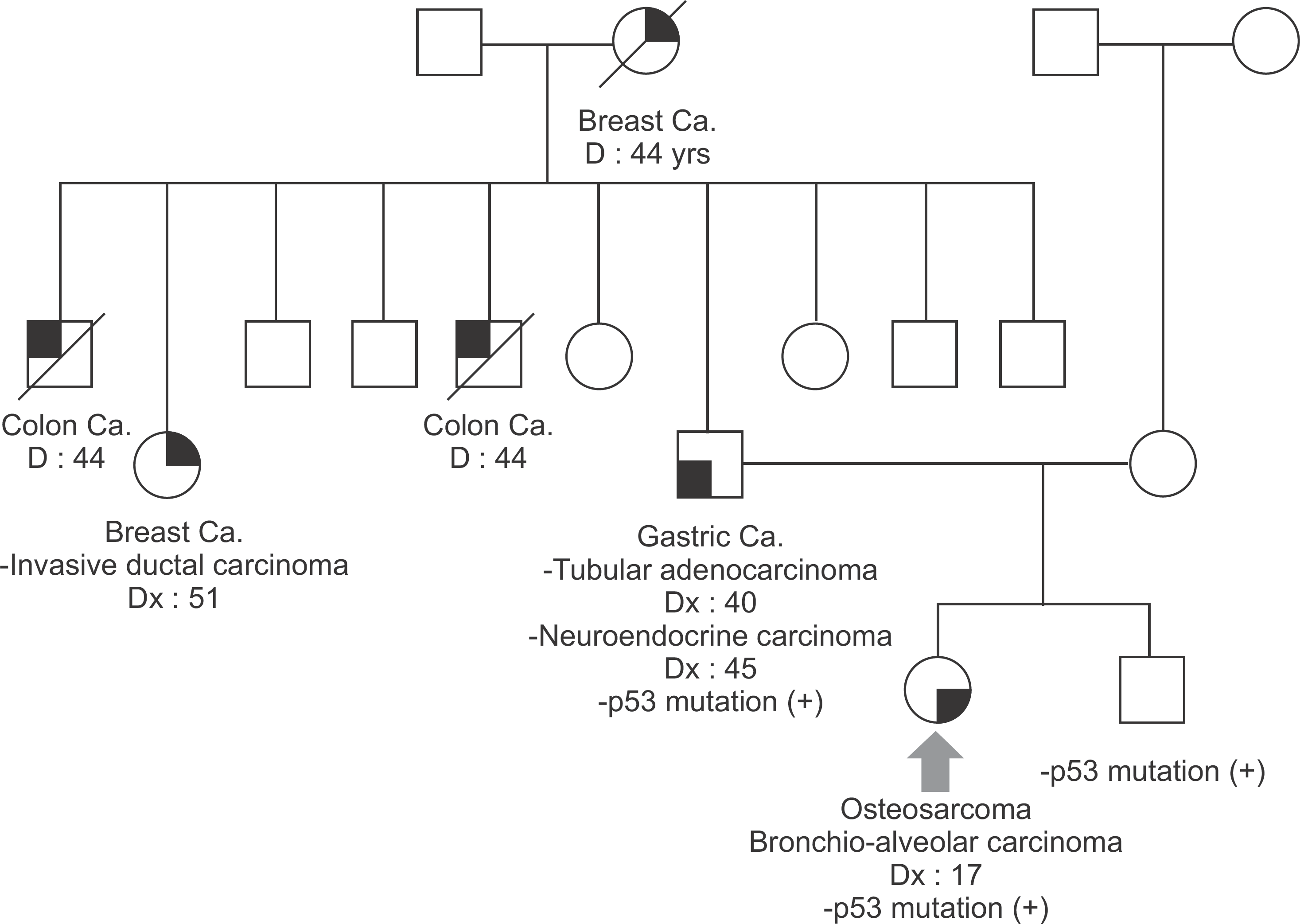
Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) is an autosomal dominant hereditary disorder characterised by a variety of different tumor types in children and young adults. That contains with a germline mutation in the tumor suppressor gene Tumor Protein p53 (TP53). That is extremely rare. Furthermore, this is sometimes overlooked. Here, we report a case of LFS which was confirmed by mutational analysis of the p53 gene. Also, literature review is intended to improve understanding of this disease entity.
Go to : 
References
1. Chompret A, Brugières L, Ronsin M, et al. P53 germline mutations in childhood cancers and cancer risk for carrier individuals. Br J Cancer. 2000; 82:1932–7.
3. Hisada M, Garber JE, Fung CY, Fraumeni JF Jr, Li FP. Multiple primary cancers in families with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998; 90:606–11.

4. Li FP, Fraumeni JF Jr, Mulvihill JJ, et al. A cancer family syndrome in twenty-four kindreds. Cancer Res. 1988; 48:5358–62.
5. American Society of Clinical Oncology. American Society of Clinical Oncology policy statement update: genetic testing for cancer susceptibility. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:2397–406.
6. Speicher MR, Carter NP. The new cytogenetics: blurring the boundaries with molecular biology. Nat Rev Genet. 2005; 6:782–92.

7. Birch JM, Hartley AL, Tricker KJ, et al. Prevalence and diversity of constitutional mutations in the p53 gene among 21 Li-Fraumeni families. Cancer Res. 1994; 54:1298–304.
8. Eeles RA. Germline mutations in the TP53 gene. Cancer Surv. 1995; 25:101–24.
9. Leroy K, Haioun C, Lepage E, et al. Groupe d'Etude des Lym-phomes de l'Adulte. p53 gene mutations are associated with poor survival in low and low-intermediate risk diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 2002; 13:1108–15.

10. Berns EM, Foekens JA, Vossen R, et al. Complete sequencing of TP53 predicts poor response to systemic therapy of advanced breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:2155–62.
Go to : 
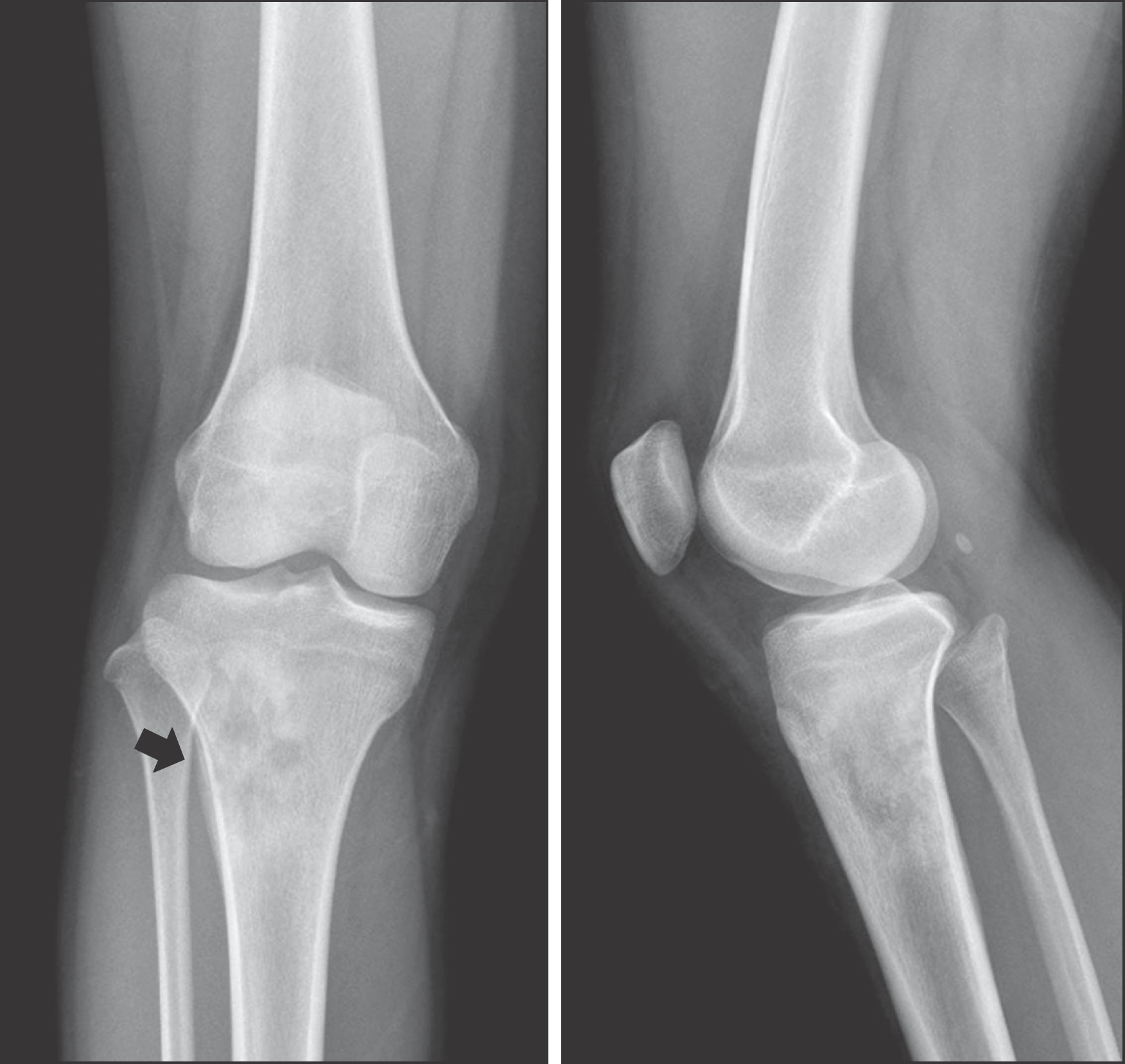 | Figure 1.Plain radiographs showed the 4 cm sized eccentric bone-destructive lesion with permiative pattern on right proximal tibia and the Codman's triangle on lateral cortex. |
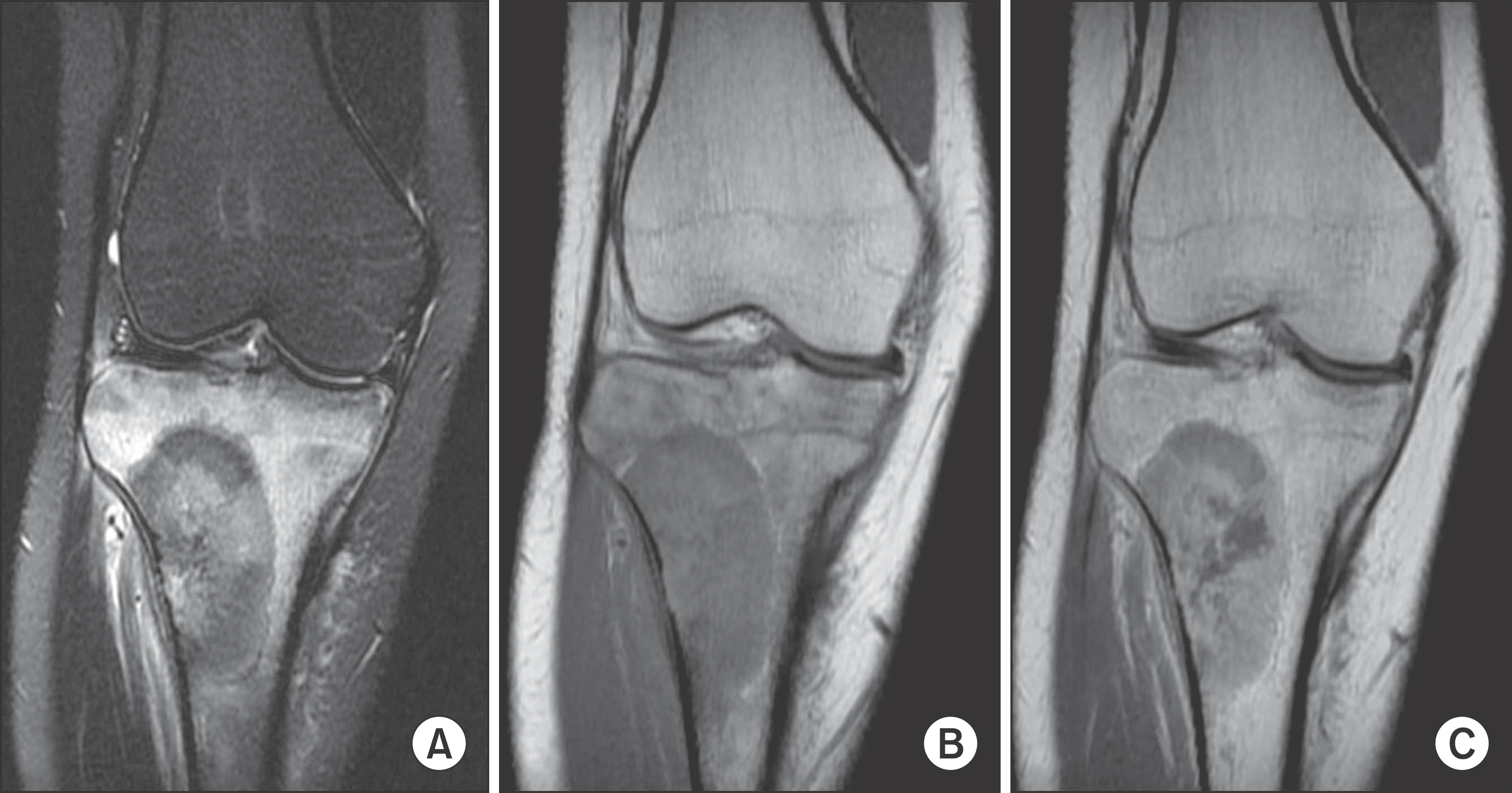 | Figure 2.On magnetic resonance imaging, there was 6×3 cm sized mass that have heterogenous signal intensity on T2-weighted (A) and T1-weighted image (B) GD (C) on lateral metaphysis of the proximal tibia. The periosteal reaction and the extraosseous formation was observed around the lateral cortex. |
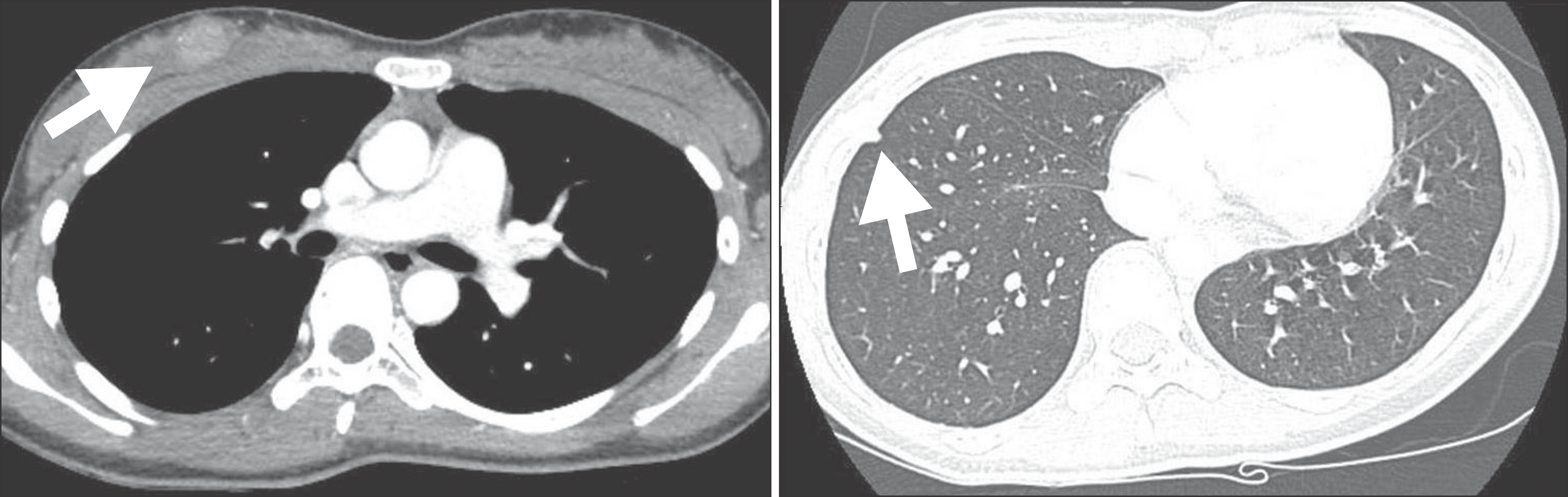 | Figure 3.There are several small peripheral uncharacterized nodules in left lower lobe and right lower lobe of lung on enhanced chest CT. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download