Abstract
An intraosseous epidermal cyst is a rare benign cystic lesion. It is thought to result from congenital factors or trauma and can lead to bone destruction because the cyst develops at the soft tissue around the bone. Radiological findings of intraosseous epidermal cysts are a well-defined radiolucent lesion, with cortical expansion. It is important to differentiate an intraosseous epidermal cyst with other disease developed at distal phalanx because its clinical and radiological findings are similar. We report two rare cases of intraosseous epidermal cysts that developed at the distal phalanx.
References
1. Hinrichs RA. Epidermoid cyst of the terminal phalanx of the hand. Case report and brief review. JAMA. 1965; 194:1253–4.

2. Yang R, Chang MC, Liu Y, Lo WH. Intraosseous epidermoid cyst in distal phalanx of finger: a case reports. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1997; 60:109–12.
3. Takigawa K. Chondroma of the bones of the hand. A review of 110 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971; 53:1591–600.
4. Chakrabarti I, Watson JD, Dorrance H. Skin tumours of the hand: A 10-year review. J Hand Surg Br. 1993; 18:484–6.
5. Adachi H, Yoshida H, Yumoto T, et al. Intraosseous epidermal cyst of the sacrum. A case report. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1988; 38:1561–4.

7. Katz MA, Dormans JP, Uri AK. Aneurysmal bone cyst involving the distal phalanx of a child. Orthopedics. 1997; 20:463–6.

9. Schajowicz F, Aiello CL, Slullitel I. Cystic and pseudocystic lesions of the terminal phalanx with special reference to the epidermoid cysts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970; 68:84–92.
Fig. 1.
(A, B) Radiographs show a round shaped radiolucent lesion with cortical expansion and thinning of left 2nd finger. (C, D) T1-weighted and T2-weighted MR images show lower and higher signal lesion at the left 2nd distal phalanx.
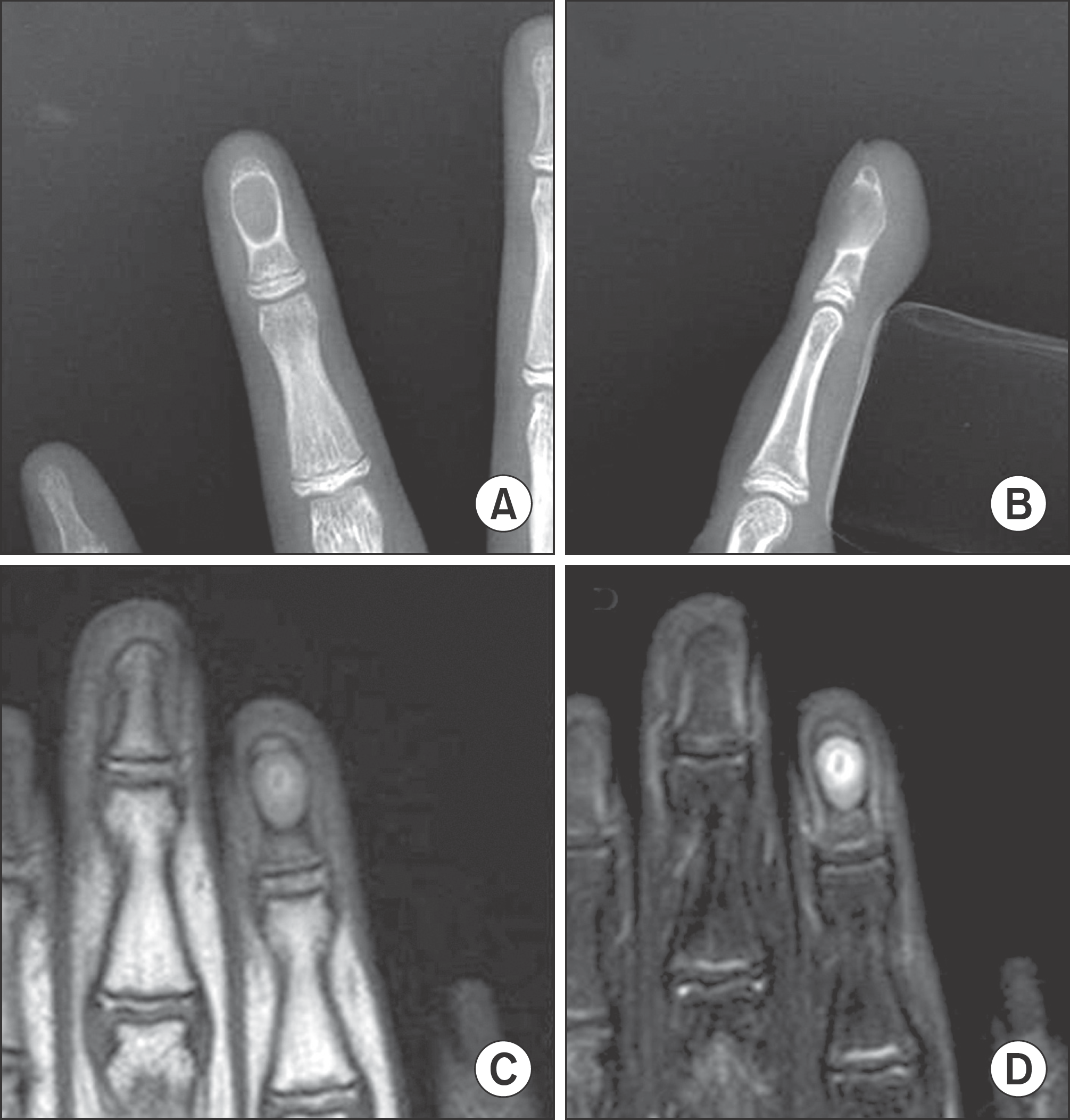
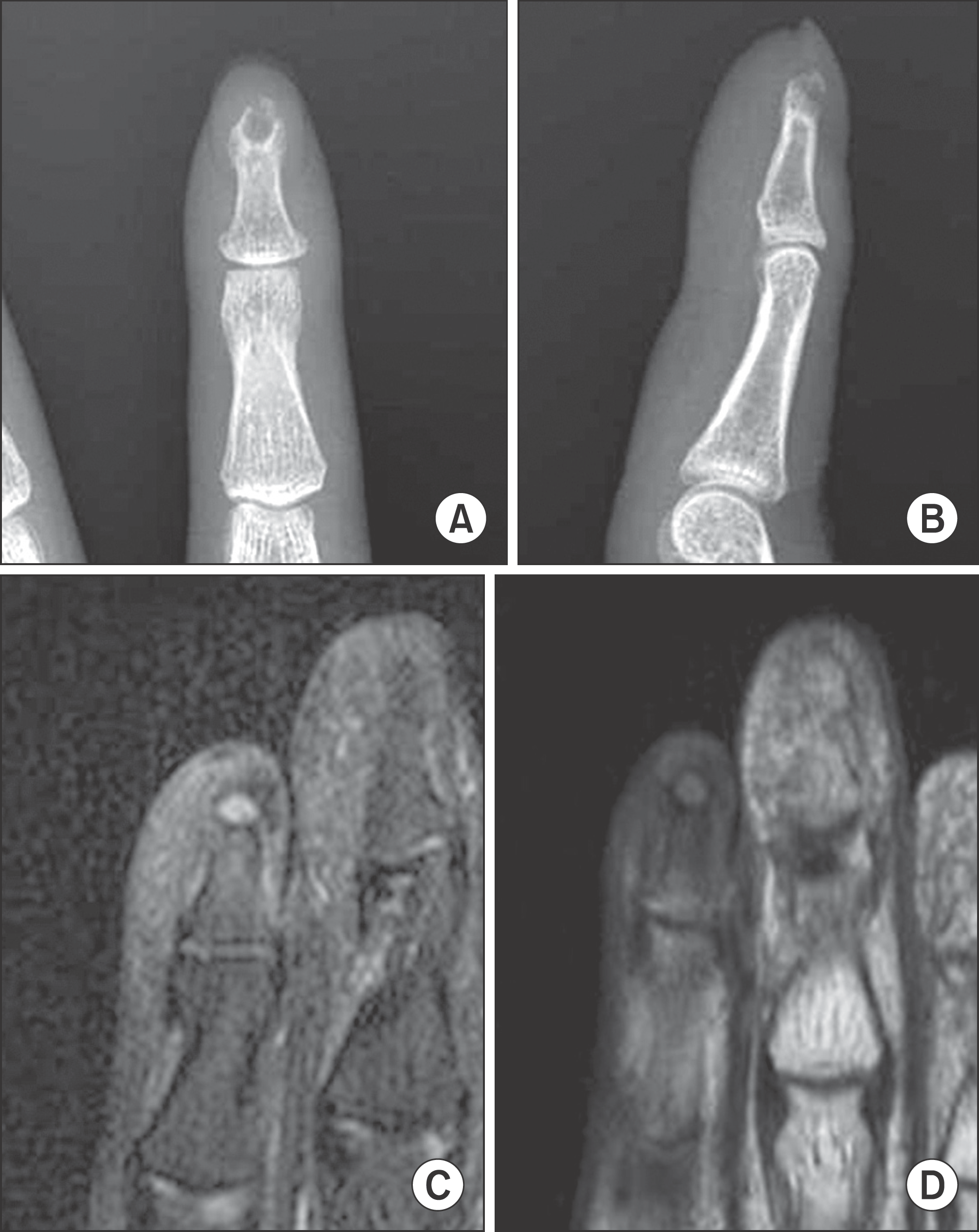
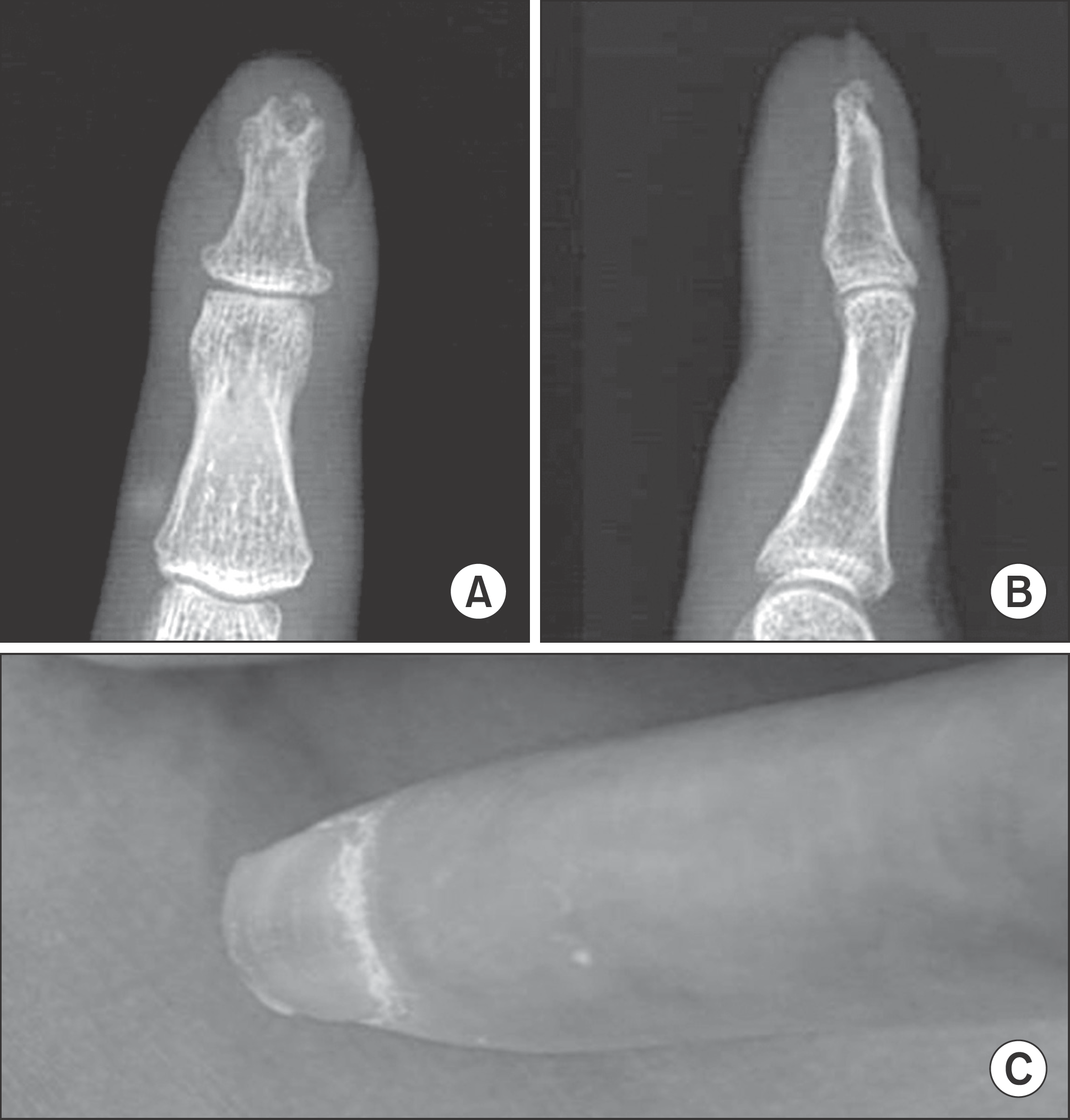
Fig. 2.
(A, B) Intraoperatively, the bone cortex was as thin as an egg shell; when the lesion was incised, yellow-tan cheese like creamy material was released, and a thick layer of tissue was peeled from within the cavity of the lesion. Curettage of the lesion was performed. (C, D) Cyst is lined by cornified epithelium, has a distinct granular layer, and contains lamellated keratin without calcification. Although some of these cysts result from traumatic inclusion for the epidermis, the majority probably arise from cystic dilation of the infundibular portion of hair follicles (×100), (×40).





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download