Abstract
Diffuse-type giant cell tumor is relatively rare than localized giant cell tumor. Moreover, diffuse type giant cell tumor is common in intraarticular area, rarely occurs at intramuscular or subcutaneous layer. We experienced 1 case of giant cell tumor within the deltoid muscle. So we report this case with review of the literatures.
References
1. Ushijima M, Hashimoto H, Tsuneyoshi M, Enjoji M. Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath (nodular tenosynovitis). A study of 207 cases to compare the large joint group with the common digit group. Cancer. 1986; 57:875–84.

2. Somerhausen NS, Fletcher CD. Diffuse-type giant cell tumor: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 50 cases with extraarticular disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000; 24:479–92.
3. Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Mertens F. World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer. Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC Press;2002. p. 112–4.
4. Lee GW, Lee KS, Song SH, Kim MK, Yun SH. Snow-man shaped nodular tenosynovitis in the knee. case report. J of Korean Arthroscopy Soc. 1999; 3:44–7.
5. Sanghvi DA, Purandare NC, Jambhekar NA, Agarwal MG, Agarwal A. Diffuse-type giant cell tumor of the subcutaneous thigh. Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36:327–30.

Figure 1.
Anteroposterior simple radiograph of the humerus shows about 3.0 cm sized bulging soft tissue lesion at lateral aspect of right upper arm.
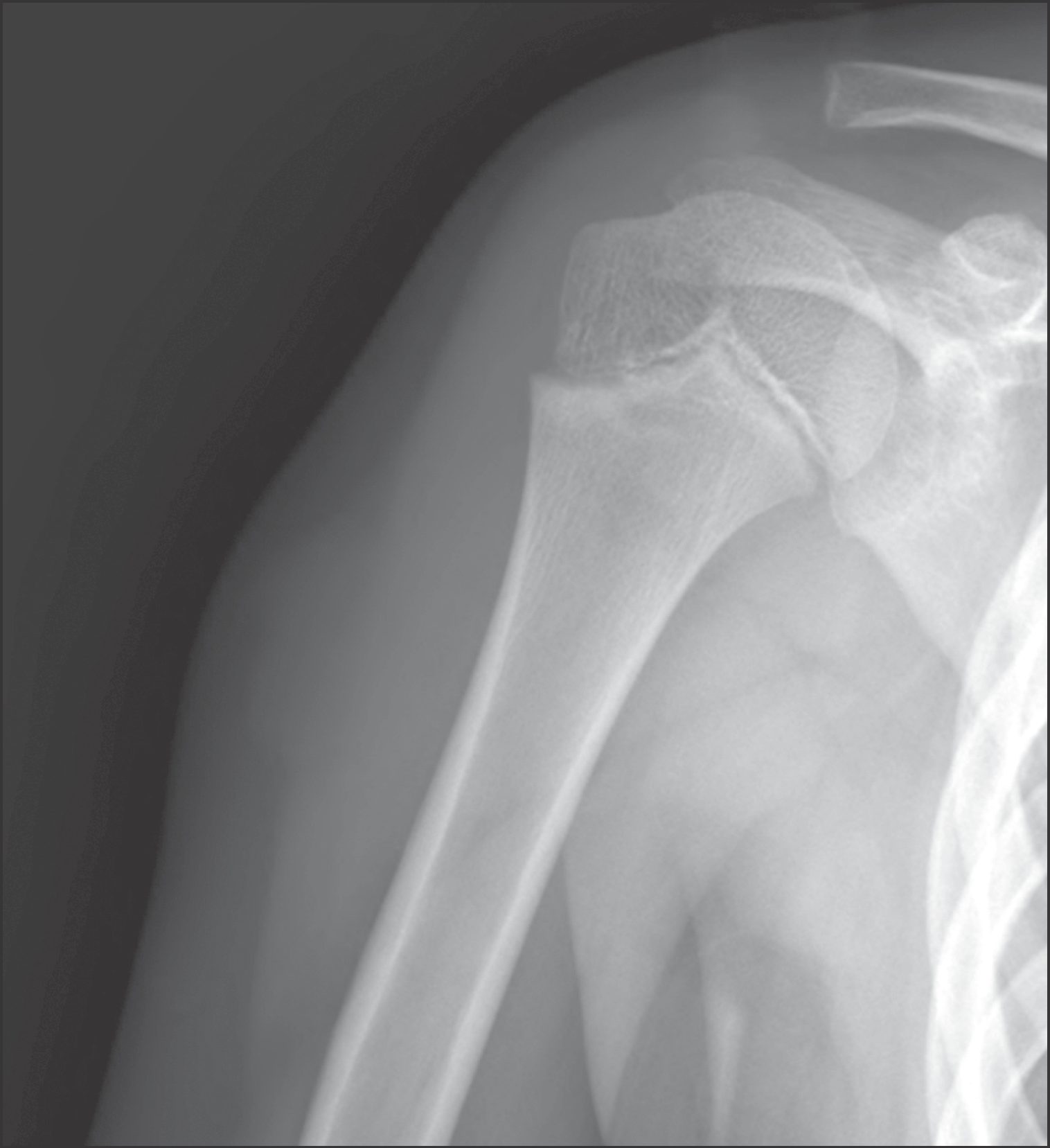
Figure 2.
These are the magnetic resonance findings of the mass. (A) Coronal T1WI shows a mass with lobulations in lateral portion of the deltoid muscle. (B) Coronal T2WI shows low to intermediate signal intensity with heterogeneous enhancement. (C) Axial T1 enhanced image shows high signal intensity with heterogeneous enhancement. (D) Axial T2WI shows low to intermediate signal intensity.

Figure 3.
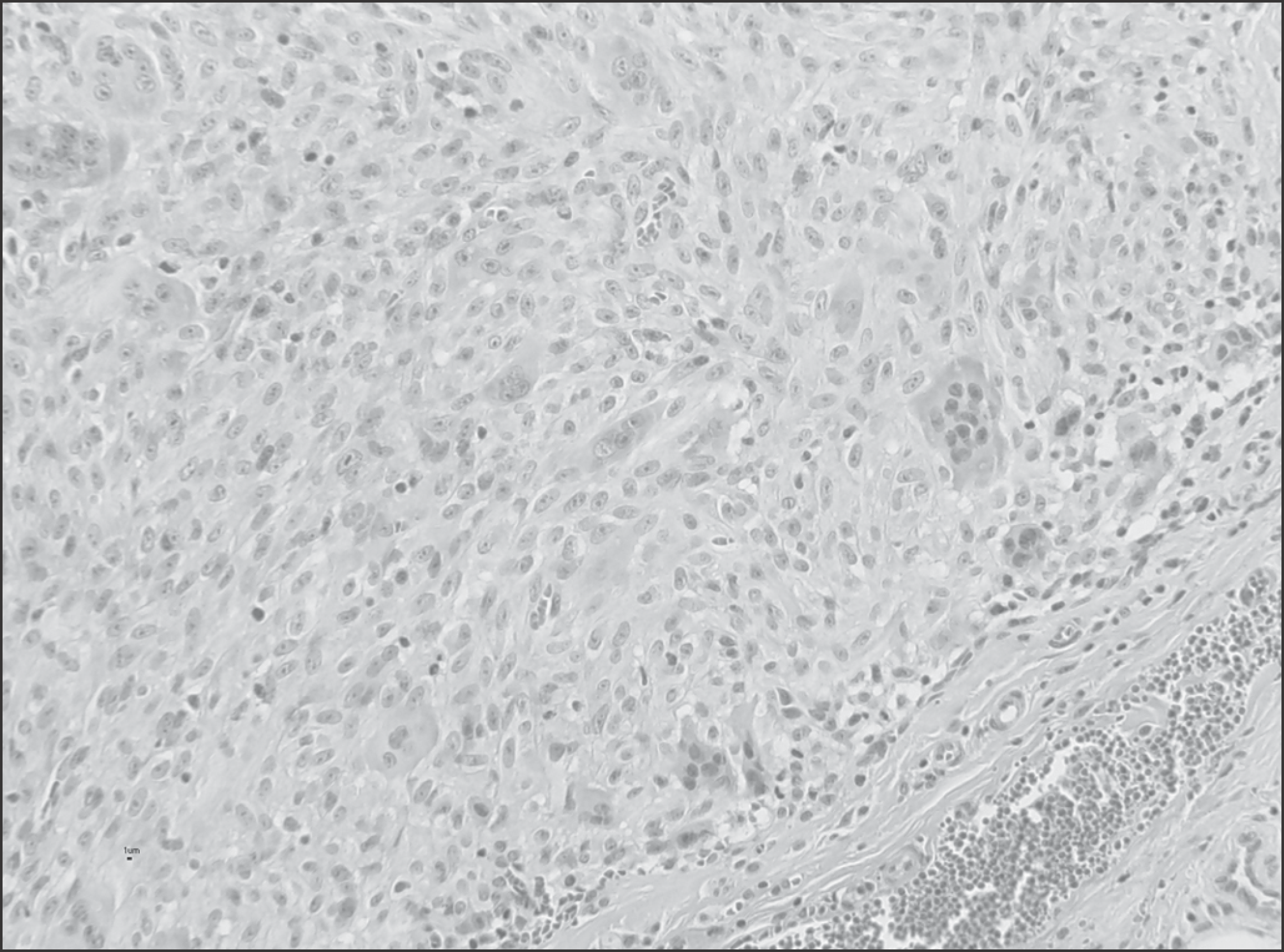
(A) Gross examination reveals an ill-demarcated firm brownish mass. (B) The cut surface is nodular with whitish solid appearance.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download