Abstract
Purpose
Unplanned excision of a soft tissue sarcoma is defined as the operation performed for gross removal of a soft tissue sarcoma without regard for preoperative imaging or the necessity to removal a margin of normal tissue covering the cancer. We report our experience of treating primary soft tissue sarcoma after an unplanned excision.
Materials and Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 31 patients referred to our hospital after unplanned excision at other hospitals for treatment of a STS. The clinical information was reviewed with a focus on the patient's age, gender, tumor location, tumor size, tumor depth, presumptive diagnoses at the previous surgery, refer hospital, definitive diagnosis, interval between the initial and additional surgery and local recurrence.
Results
There were 19 males and 12 females with a median age of 48 years (range, 17-75 years) at the time of referral. Seventeen patients (54.8%) had tumors in their lower limb, 6 (19.4%) had tumors in their upper limb, and 8 (25.8%) had tumors in their trunk. Tumor depth could be determined for 8 patients (25.8%), with superficial and 22 deep tumors (71%). The medial interval between unplanned excision to re-excision ranged from 2 weeks to 1 year (median, 5 weeks). Local recurrence was detected in 2 patients. All patients were alive without metastasis at last follow up.
Figures and Tables
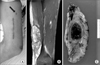 | Figure 1Unplanned excision of thigh mass in a 17-year-old boy who was diagnosed alveolar soft part sarcoma. (A) Clinical photo shows longitudinal skin incision and inappropriate location of drain. (B) MRI which was done before re-excision shows massive hemorrhage. (C) Re-excision was done at 4 weeks later refer to our hospital. Final pathology reports residual alveolar soft part sarcoma, hemorrhage and foreign body type giant cell reaction. Resection margin was free from tumor (safety margin: 2 cm). |
References
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007. 57:43–66.
2. Giuliano AE, Eilber FR. The rationale for planned reoperation after unplanned total excision of soft-tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 1985. 3:1344–1348.
3. Springfield DS, Rosenberg A. Biopsy: complicated and risky. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996. 78:639–643.
4. Chandrasekar CR, Wafa H, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, Tillman RM, Abudu A. The effect of an unplanned excision of a soft-tissue sarcoma on prognosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008. 90:203–208.
5. Fiore M, Casali PG, Miceli R, et al. Prognostic effect of re-excision in adult soft tissue sarcoma of the extremity. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006. 13:110–117.
6. Lewis JJ, Leung D, Espat J, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF. Effect of reresection in extremity soft tissue sarcoma. Ann Surg. 2000. 231:655–663.
7. Potter BK, Adams SC, Pitcher JD Jr, Temple HT. Local recurrence of disease after unplanned excisions of high-grade soft tissue sarcomas. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. 466:3093–3100.
8. Kawaguchi N, Matumoto S, Manabe J. New method of evaluating the surgical margin and safety margin for musculoskeletal sarcoma, analysed on the basis of 457 surgical cases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1995. 121:555–563.
9. Kawaguchi N, Ahmed AR, Matsumoto S, Manabe J, Matsushita Y. The concept of curative margin in surgery for bone and soft tissue sarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. (419):165–172.
10. Greene FL. American Joint Committee on Cancer. American Cancer Society. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 2002. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag.
11. Kepka L, Suit HD, Goldberg SI, et al. Results of radiation therapy performed after unplanned surgery (without re-excision) for soft tissue sarcomas. J Surg Oncol. 2005. 92:39–45.
12. Zornig C, Peiper M, Schröder S. Re-excision of soft tissue sarcoma after inadequate initial operation. Br J Surg. 1995. 82:278–279.
13. Sugiura H, Takahashi M, Katagiri H, et al. Additional wide resection of malignant soft tissue tumors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. (394):201–210.
14. Manoso MW, Frassica DA, Deune EG, Frassica FJ. Outcomes of re-excision after unplanned excisions of soft-tissue sarcomas. J Surg Oncol. 2005. 91:153–158.
15. Rougraff BT, Davis K, Cudahy T. The impact of previous surgical manipulation of subcutaneous sarcoma on oncologic outcome. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 438:85–91.
16. Siegel HJ, Brown O, Lopez-Ben R, Siegal GP. Unplanned surgical excision of extremity soft tissue sarcomas: patient profile and referral patterns. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2009. 18:93–98.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download