Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify trends of action learning based nursing education research from 2006 to 2016 and suggest directions for advancing action learning based nursing education.
Methods
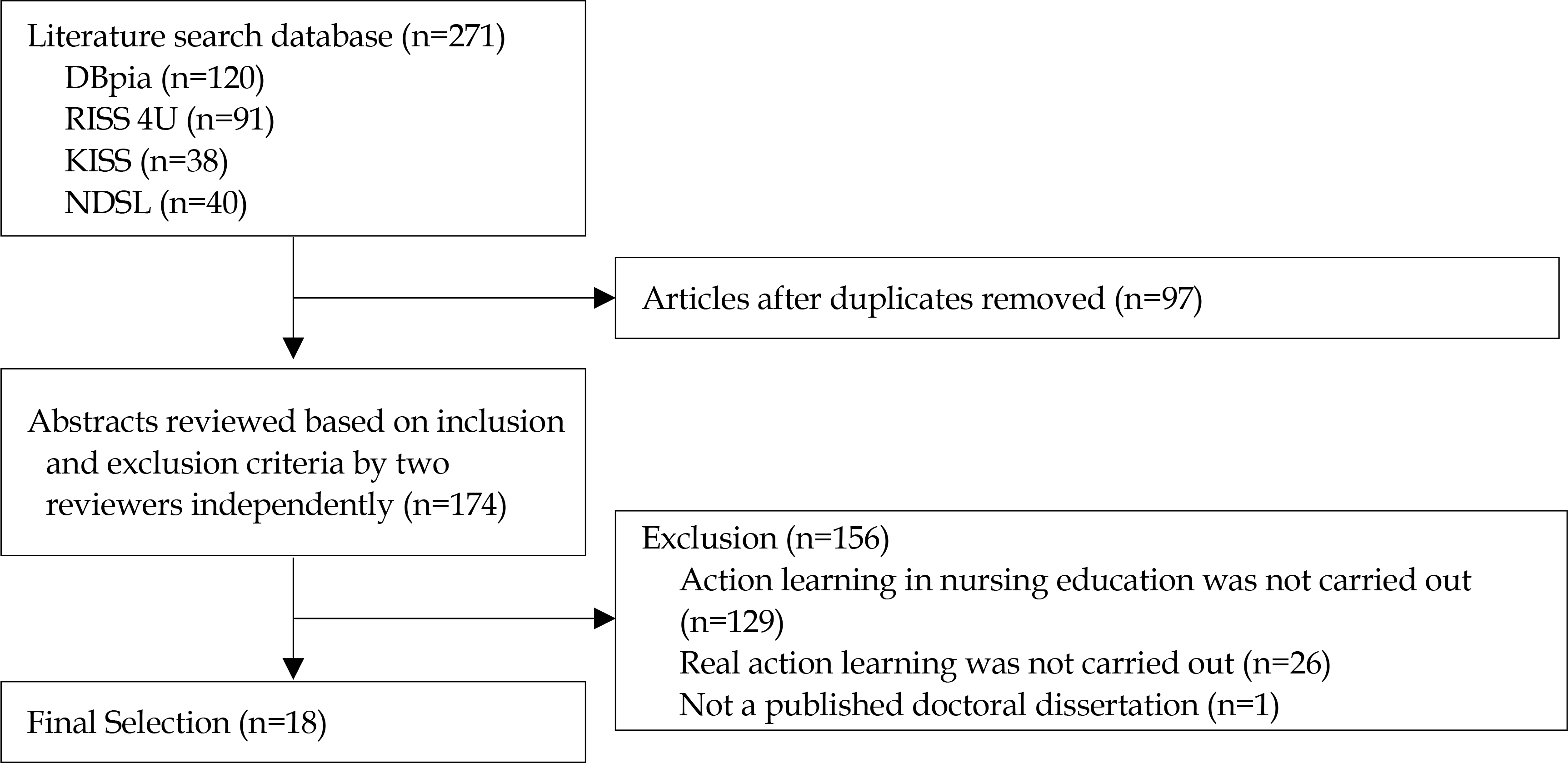
A review was made of 18 studies in nursing education reported in domestic journals. RISS 4U, KISS, DBpia, NDSL databases were searched using analysis criteria developed by the researchers. General and methodological characteristics and outcomes of action learning based nursing education were analyzed.
Results
Of 18 papers, in 14 (77.8%) quantitative design was used, 16 (88.9%) were conducted in university settings, and virtual problem approach was used in 13 studies (72.2%). Writing task description was conducted in 8 studies (44.4%). Norminal group technique and logic tree were used in 6 studies (33.3%). The number of team members was 6-8 in 10 (55.6%) studies. Reflection journaling was used in 16 (88.9%) studies. Action learning was effective in improving core competency of nurses and nursing students such as problem solving ability and communication skill.
Go to : 
References
1. Hyun HH, Lee MS, Hong YH. The effect of action learning teaching-learning method applied to nursing students in U city. Journal of Korean Society for School & Community Health Education. 2016; 17(2):17–30.
2. Choi SE, Kim EA. Effects of learning activities on application of learning portfolio in nursing management course. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2016; 46(1):90–99. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.90.

3. Kim YH, Choi BY. Study of the experience process in action learning for fostering essential competency of university students - Grounded theory approach. Journal of the Korea Contents Association. 2013; 13(11):477–491. https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2013.13.11.477.
4. Bong HC. Key success factors of action learning programs in Korean companies: Contents and relationships. Korean Journal of Economics and Management. 2007; 25(3):1–34.
5. Chung KH. Application of action learning teaching-learning method to improve creativity an problem solving capability. Journal of Nambu University. 2010; 10(1):1–12.
6. Park YI, Kim JA, Ko JK, Chung MS, Bang KS, Choe MA, et al. An identification study on core nursing competency. Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2013; 19(4):663–674. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2013.19.4.663.

7. Kim MW, Park JM, Han AK. Analysis of curriculum of 4-year nursing schools. Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2011; 17(3):416–425.
8. Ko SI, Chang KW. Case study on interpersonal relationship class by action learning. Korea Association of Business Education. 2014; 88:256–581.
9. Chang KW, Koh EH, Ko SI. Analysis of the research trend of action learning in school. The Korean Association for Educational Methodology Studies. 2015; 27(3):429–455. https://doi.org/10.17927/tkjems.2015.27.3.429.
10. Chang HS. A comparative study on action learning programs: Focusing on Korean corporations [master's thesis]. Seoul: Konkuk University;2003. p. 1–79.
11. Choi MM, Kim SY. An exploratory study of action learning in social work education. Korea Journal of Social Welfare Education. 2005; 1(2):81–103.
12. Kim YM, Kim YH. Development and evaluation of action learning in clinical practice of nursing management. Journal of the Korea Contents Association. 2010; 10(6):313–322.

13. Lee IH, Kwon SC. A case study of the action learning-based general arts education. The Korean Association of General Education. 2013; 1(6):145–171.
14. Jang KS, Baek MY, Choi YJ, Ahn SH, Lee SJ, Sim JY, et al. An analysis of nurse managers's common fundamental competencies changes and responses to the application of the action learning. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2006; 12(3):424–433.
15. Kim JH, Park MK. Comparative study on self-leadership, team efficacy, problem solving process and task satisfaction of nursing students in response to clinical training. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2014; 20(4):482–490. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2014.20.4.482.

16. Marquardt MJ. Action learning in action: Transforming problems and people for world class organizational learning. California: Davis Black Publishing;1999. p. 1–259.
17. Jang KS, Chung KH, Baek M, Park HY, Choi O. Action learning and creative problem solving for nursing leadership. Seoul: Hyunmoonsa;2016. p. 3–57.
18. Kwon SC, Kim SB. Study of the self-management competencies program development: Focused on a formative research method. The Korean Association Education. 2014; 8(2):83–127.
19. Jang KS, Park SJ. Effects of action learning approaches on learning outcomes in nursing management courses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2012; 18(4):442–451. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2012.18.4.442.

20. Chung KH. Study on reflection in project-based action learning. Journal of Nambu University. 2013; 13(1):127–140.
21. Kim YM, Jang KS. An action research study on the effects of an action learning-based nursing professionalism course for nursing students. The Journal of Korean Education. 2014; 41(4):123–147.
Go to : 
Table 1.
General Characteristics of the Literature (N=18)
Table 2.
Methodological Characteristics of the Research (N=18)
Table 3.
Identification of the Quantitative Research Outcome (N=16)
| Participant | Dependent variables | n (%) | Intervention period | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nurse (n=2) | Problem solving ability | 2 (100.0) | 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.020) |
| 5 weeks | Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | |||
| Communication | 2 (100.0) | 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.002) | |
| Communication | 2 (100.0) | 5 weeks | Improvement in posttest group (p=.009) | |
| Emotional creativity | 1 (50.0) | 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.028) | |
| Innovation behavior | 1 (50.0) | 8 weeks | No difference between two groups (p=.094) | |
| Decision making | 1 (50.0) | 5 weeks | Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | |
| Presentation skill | 1 (50.0) | 5 weeks | Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | |
| Individual change* | 1 (50.0) | 5 weeks | 3.93±0.69 (p value was not described) | |
| Team member recognition* | 1 (50.0) | 5 weeks | 4.21±0.52 (p value was not described) | |
| Nursing student (n=14) | Problem solving ability | 7 (50.0) | 16 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.012) |
| 14 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| 13 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.020) | |||
| 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | ||||
| 4 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| 2 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| Communication | 4 (28.6) | 13 weeks | LDG: No difference between pretest and posttest groups (p=.756) | |
| HDG: Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | ||||
| 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| Improvement in IG (p<.001) | ||||
| 2 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| Creativity | 3 (21.4) | 16 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.047) | |
| 14 weeks | No difference between pretest and posttest groups (p=.110) | |||
| 13 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| Team efficacy | 3 (21.4) | 8 weeks | Improvement in posttest group (p=.012) | |
| 8 weeks | No difference between two groups (p=.883) | |||
| 2 weeks | No difference between two groups (p=.640) | |||
| Critical thinking disposition | 2 (14.3) | 13 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.003) | |
| 13 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| Problem solving process | 2 (14.3) | 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.005) | |
| 2 weeks | Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | |||
| Self-directed learning skill | 2 (14.3) | 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.003) | |
| 4 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |||
| Leadership | 2 (14.3) | 13 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.025) | |
| 8 weeks | No difference between two groups (p=.161) | |||
| Class satisfaction | 2 (14.3) | 14 weeks | Great satisfaction (p value was not described) | |
| 8 weeks | Great satisfaction (p value was not described) | |||
| Task satisfaction | 1 (7.1) | 8 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.013) | |
| Proactivity in problem solving | 1 (7.1) | 7 weeks | Improvement in IG (p=.026) | |
| Team member exchange relationship | 1 (7.1) | 16 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |
| Culture competency | 1 (7.1) | 13 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |
| Nursing expert instinct | 1 (7.1) | 13 weeks | LDG: Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | |
| HDG: Improvement in posttest group (p=.002) | ||||
| Professional self concept | 1 (7.1) | 8 weeks | No difference between two groups (p=.187) | |
| Evidence-based nursing competency | 1 (7.1) | 7 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |
| Information literacy | 1 (7.1) | 7 weeks | Improvement in IG (p<.001) | |
| Spiritual need | 1 (7.1) | 16 hours | Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | |
| Spiritual well-being | 1 (7.1) | 16 hours | Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) | |
| Spiritual care competence | 1 (7.1) | 16 hours | Improvement in posttest group (p<.001) |
Table 4.
Identification of the Qualitative Research Outcome (N=4)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download