Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to evaluate validity and reliability of the Korean version of the expanded nursing stress scale (ENSS).
Methods
Forward-backward translation of ENSS from English to Korean was conducted. The translated instrument was pilot-tested and administrated to 285 nurses who worked in five general hospitals in Korea. Internal consistency reliability was assessed using Cronbach's α and composite reliability. Validity was evaluated through construct validity with confirmatory factor analysis, convergent and discriminant validity.
Results
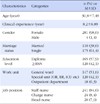
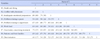
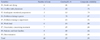
The Korean version of ENSS showed a reliable internal consistency with Cronbach's α.95 and composite reliability .99. Model fit indexes for 46 items were validated by confirmatory factor analysis(goodness of fit index .82, Tucker-Lewis index .92, root mean square error of approximation .04), indicating suitable construct validity. Factor loading of the 48 items (.47~.88) and average variance extracted out of nine factors (.52~.71.) indicated satisfactory convergent validity. Some values of square of the correlation coefficient between factors (.12~.89) were higher than average variance extracted values of each factor (.52~.71) so that it partly satisfied discriminant validity.
Figures and Tables
References
1. OECD. Society at a Glance 2009: OECD Social Indicators. Paris: OECD Publishing;2009. p. 122–123.
2. Abbas SG, Farah A, Apkinar-Sposito C. Measuring the immeasurable: An overview of stress and strain measuring instruments. Mediterr J Soc Sci. 2013; 4(10):480–489. DOI: 10.5901/mjss.2013.v4n10p480.
3. Sauter S, Murphy L, Colligan M, Swanson N, Hurrell J, Scharf F, et al. Report No.: 99-101. Stress at work. DHHS (NIOSH) Publication. Cincinnati, OH: National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health;1999. January.
4. Heo KS. A study on the relationships between job characteristics and organizational commitment of hospital organization. J Hum Resour Manag Res. 2005; 12:21–45.
5. Golubic R, Milosevic M, Knezevic B, Mustajbegovic J. Workrelated stress, education and work ability among hospital nurses. J Adv Nurs. 2009; 65(10):2056–2066. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2009.05057.x.
6. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Ministry of Health & Welfare Statistical Year Book 2015. Sejong: Minister of Health and Welfare;2015. p. 12–13.
7. Kim JH, Jo HS. A comparative study on job stress and satisfaction between ward nurses and outpatient nurses. Korean J Occup Health Nurs. 2013; 22(2):83–92. DOI: 10.5807/kjohn.2013.22.2.83.
8. Lee MH. Analysis of studies on work stress in clinical nurses. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 1996; 8(1):180–200.
9. Choi SR, Jung HS. An analysis of studies on clinical nurses' job stress: A comparative study. Korean J Occup Health Nurs. 2004; 13(1):40–47.
10. Yi Y, Lee B. Research trend of nurses' job stress: A comparative study. Korean J Occup Health Nurs. 2013; 22(1):13–23. DOI: 10.5807/kjohn.2013.22.1.13.
11. Lee B. Trend analysis of nurses' stress based on last 10 years of international research. Korean J Occup Health Nurs. 2012; 21(1):27–36. DOI: 10.5807/kjohn.2012.21.1.27.
12. Kim MJ, Gu MO. The development of the stress measurement tool for staff nurses working in the hospital. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1984; 14(2):28–37.
13. Chang SJ, Koh SB, Kang D, Kim SA, Kang MG, Lee CG, et al. Developing an occupational stress scale for Korean employees. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2005; 17(4):297–317.
14. Cho W, You M. Problems and prospects of nursing research on job stress in Korea. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2013; 19(1):63–75. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2013.19.1.63.
15. French SE, Lenton R, Walters V, Eyles J. An empirical evaluation of expanded nursing stress scale. J Nurs Meas. 2000; 8(2):161–178.
16. Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress. J Health Soc Behav. 1983; 24(4):385–396.
17. Cooper CL, Sloan SJ, Williams S. Occupational stress indicator: management guide. Windsor: NFER-Nelson;1988.
18. Gray-Toft P, Anderson JG. The nursing stress scale: Development of an instrument. J Behav Assess. 1981; 3(1):11–23.
19. Lambert VA, Lambert CE, Itano J, Inouye J, Kim S, Kuniviktikul W, et al. Cross-cultural comparison of workplace stressors, ways of coping and demographic characteristics as predictors of physical and mental health among hospital nurses in J apan, Thailand, South Korea and the USA (Hawaii). Int J Nurs Stud. 2004; 41:671–684. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.02.003.
20. McGilton KS, McGillis HL, Wodchis WP, Petroz U. Supervisory support, job stress, and job satisfaction among long-term care nursing staff. J Nurs Adm. 2007; 37:366–372. DOI: 10.1097/01.NNA.0000285115.60689.4b.
21. Milutinović D, Golubović B, Brkić N, Prokeš B. Professional stress and health among critical care nurses in Serbia. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2012; 63(2):171–180. DOI: 10.2478/10004-1254-63-2012-2140.
22. Galdikiene N, Asikainen P, Balciunas S, Suominen T. Do nurses feel stressed?: A perspective from primary health care. Nurs Health Sci. 2014; 16(3):327–334. DOI: 10.1111/nhs.12108.
23. Principal components and factor analysis: Complete example of FA. In : Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS, editors. Using multivariate statistics. 5th ed. Boston: Pearson/Allyn & Bacon;2007. p. 651–670.
24. World Health Organization. Process of translation and adaptation of instruments [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2013. cited 2013 J une 2. Available from: http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/research_tools/translation/en/.
25. Harrington D. Confirmatory factor analysis. Pocket guides to social work research methods. New York: Oxford University Press;2008. p. 78–99.
26. Hair JE, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE. Multivariate data analysis. 7th ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall Inc;2009. p. 51–92.
27. Fornell C, Larcker DF. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Mark Res. 1981; 18:39–50.
28. Spreng RA, MacKenzie SB, Olshavsky RW. A reexamination of the determinants of consumer satisfaction. J Mark. 1996; 60:15–32.
29. Lee YJ. An analysis of the factors affecting general hospital nurses' intention to leave the job [master's thesis]. Seoul: Hanyang University;2003.
30. Yau SY, Xiao XY, Lee LYK, Tsang YK, Wong SL, Wong KF. J ob stress among nurses in China. Appl Nurs Res. 2012; 25:60–64.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download