Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to determine the influential factors related to organizational citizenship behavior of nurses with a focus on authentic leadership and organizational justice.
Methods
The study participants were 186 nurses who work at K University Hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi province. Data were collected in September and October, 2013. A structured questionnaire was used for data collection and data were analyzed using the SPSS/Window program.
Figures and Tables
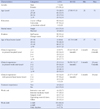
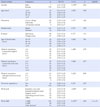
Table 2
Level of Authentic Leadership, Organizational Justice, and Organizational Citizenship Behavior (N=186)

References
1. Lee SH. The relationship between the personal and job characteristics on organizational citizenship behaviors in clinical nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2006; 12(2):295–304.
2. Song US, Kim JH. The influence of job autonomy on the relationship between personal characteristics and organizational citizenship behavior among lower ranking public officials. Korean Public Adm Rev. 2002; 36(1):117–137.
3. Jun HS, Kim MS. Influence of leader-member exchange and organizational commitment on organizational citizenship behavior in nursing organization. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2004; 10(1):97–107.
4. Kim JM, Park HJ, Lee SH. The relationship between organizational socialization and organizational citizenship behavior among nurses in general hospitals. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2012; 18(3):413–423.
5. Kang DS, Chah DO. The impact of organizational justice, lmx quality, and psychological empowerment on service-oriented organizational citizenship behaviors (OCBs). J Organ Manage. 2004; 28(1):263–287.
6. Choi J, Ha NS. The relationship between organizational citizenship behavior and customer orientation on organizational justice in clinical nurses. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2007; 13(1):173–184.
7. Katz D. The motivational bias of organizational behavior. Behav Sci. 1964; 9(2):131–146.
8. Smith CA, Organ DW, Near JP. Organizational citizenship behavior: Its nature and antecedents. J Appl Psychol. 1983; 68(4):653–663.
9. Kim MS, Park HT. Transactional and transformational leadership styles of the nurse administrators. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 1997; 3(1):5–15.
10. Koh MS, Han SS. The survey of staff nurses demand's for first-line nurse manager's leadership program. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 1998; 4(1):183–192.
11. Lee SM, Kim HG. The effects of managerial leadership on organizational culture and organizational commitment: the case of hospital head nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2002; 8(4):551–561.
12. Jeong YJ, Lee SJ, Kim MJ. Transformational leader vs. authentic leader: Transformational leadership revisited. Korean Manage Rev. 2012; 41(3):539–573.
13. Kim SH. Effects of authentic leadership on attitude toward sport team leaders and team effectiveness [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;2012.
14. Jun KH, Park SH, Park HJ, Kim JY. The effect of authentic leadership on organizational behaviors focus on the mediator effect of identification. In : Proceedings of Korean Academy of Management; 2010. p. 1–33.
15. Walumbwa FO, Avolio BJ, Gardner WL, Wernsing TS, Peterson SJ. Authentic leadership: Development and validation of a theory-based measure? J Manage. 2008; 34(1):89–126. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0149206307308913.
16. Organ DW. The motivational bias of organizational behavior. Res Organ Behav. 1990; 12(1):43–72.
17. Kim MH, Nam CH. The Effect of managers' authentic leadership on organizational citizenship behavior: Focused on the mediating effects of psychological capital. J Foodserv Manage. 2013; 16(6):29–47.
18. Kim MS. Influence of organizational justice and commitment on organizational citizenship behaviors of nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2007; 13(4):481–491.
19. Park KM. Effects of Perceived organizational justice and organizational commitment on organizational citizenship behavior of hospital nurses. Chungnam: Kongju National University;2011. [Unpublished master's thesis].
20. Park WY, Yoon SH. The Mediating role of organizational citizenship behavior between organizational justice and organizational effectiveness in nursing organizations. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2009; 39(2):229–236. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.229.
21. Avolio BJ, Gardner WL, Walumbwa FO. Authentic leadership questionnaire for research. [Internet]. Redwood City: CA: Mind Garden;2007. Available from: http://www.mindgarden.com/products/alqconsult.htm.
22. Adams JS. Inequity in social exchange. Adv Exp Soc Psychol. 1965; 2:267–299. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60108-2.
23. Price JL, Muller CW. Handbook of organizational measurement. Marshfield: Mass: Pitman;1986. p. 122–127.
24. Moorman RH. Relationship between organizational justice and organizational citizenship behaviors: Do fairness perceptions influence employee citizenship. J Appl Psychol. 1991; 76(6):845–855.
25. Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie S, Paine JB, Bachrach DG. Organizational citizenship behaviors: A critical review of the theoretical and empirical literature and suggestions for future research. J Manage. 2000; 26(3):513–563. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/014920630002600307.
26. Niehoff BP, Moorman RH. Justice as a mediator of the relationship between methods of monitoring and organizational citizenship behavior. Acad Manage J. 1993; 36(3):527–556. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/256591.
27. Chang JK. The effect of ethical leadership in the development of core values in organization and organizational citizenship behaviors. Seoul: Korea University;2011. [thesis].




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download