Abstract
Purpose
The core of accreditation for nursing education is to improve the ability and quality of graduates through a CQI system based on outcomes. For program outcomes of nursing education accreditation criterion, it is necessary to understand the relationship among education assessment, objective and curriculum.
Methods
The focus of this study was on program outcomes and the assessment. First measures for improving the general problems of program outcomes associated with the assessment system were stated. Detailed measure for practicing program outcomes, the assessment system and the assessment tool using Rubrics were discussed.
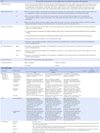
Figures and Tables
References
1. Song JE, Park JW, Yoo MS. Nursing program learning and development of assessment system-centrally about improvement of applying skills of the nursing process based on critical thinking skills-the first time learning and research-based nursing curriculum presentation competition. Seoul: Korean Accreditation Board of Nursing Education (KABONE);2013.
2. Kim BK, Park JY. A study on assessment method of program outcomes. J Eng Educ Res. 2008; 11(4):46–57.
3. Park MJ. A new approach to curriculum development in higher education: Competence-based curriculum. J Curriculum Stud. 2008; 26(4):173–197.
4. Baek SG. Principles of performance assessment. Seoul: Kyoyookbook;2000.
5. Stiggins RJ. Student-centered classroom assessment. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill Prentice Hall;1994.
6. Kim JG. Curriculum and assessment. Seoul: Dongmunsa;2009.
7. McMillan JH. Classroom assessment: Principles and practice for effective instruction. 3rd ed. Boston: Pearson Education Inc.;2004.
8. Park YK. The relationship between course assessment and program objective evaluation in engineering education accreditation: Toward a practical evaluation of program objectives. J Eng Educ Res. 2010; 13(4):87–92.
9. Yu IK. A study on the effective managerial schemes of an accredited engineering program. J Eng Educ Res. 2007; 10(2):62–72.
10. Hur D. Case study with regard to ABEEK assessment process for program outcomes. J Eng Educ Res. 2009; 12(1):57–63.
11. Jin SH, Cho WS. A case analysis of program outcomes assessment systems for engineering education accreditation of South Korea and USA. J Eng Educ Res. 2011; 14(2):13–20.
12. Lee YT, Lim CI. A study on the development of program outcomes assessment system using reflection journal. J Eng Educ Res. 2013; 16(3):42–50.
13. Besterfield-Sacre M, Shuman LJ, Wolfe H, Atman CJ, McGourty J, Miller RL, et al. Defining the outcomes: A framework for EC-2000. IEEE Trans Educ. 2000; 43(2):100–110. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/13.848060.
14. Choi HS. Curriculum and education evaluation. Gyeonggi-do: Kyoyookbook;2008.
15. Bloom BS, Engelhart MD. Committee of College and University Examiners. Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals, Handbook I: Cognitive domain domain. New York: David McKay;1956.
16. Kim JY, Kang SJ, Kang BS, Kim DI. A study on development of the assessment system for the program outcomes on the communication skill competence. J Eng Educ Res. 2011; 14(6):41–47.
17. Kim M, Yoon W, Kim D, Chung JT, Kim B. The study of assessment tool as an outcomes achievement: Part 3 Undergraduate thesis. J Eng Educ Res. 2007; 10(1):97–108.
18. Goodrich H. Understanding rubrics. Educ Leadersh. 1997; 54(4):14–17.
19. Marzano RJ, Pickering D, McTighe J. Assessing student outcomes: Performance assessment using the dimensions of learning model. Alexandria, Va: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development;1993.
20. Arter JA, McTighe J. Scoring rubrics in the classroom: Using performance criteria for assessing and improving student performance. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin;2001.
21. Krathwohl DR, Bloom BS, Masia BB. Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals, Handbook II affective domain. New York, NY: David McKay;1963.
22. Arranz P, Ulla SM, Ramos JL, Del Rincon C, Lopez-Fando T. Evaluation of a counseling training program for nursing staff. Patient Educ Couns. 2005; 56(2):233–239. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2004.02.017.
23. Kim IS, Jang KS, Lee MH, Ha NS, Hong YM, Lee TH. New nursing management. Seoul: Hyunmoonsa;2009.
24. Stuart GW, Sundeen SJ. Principles and practice of psychiatric nursing. 2nd ed. Toronto: Mosby;1983.
25. Yim HB, Koh OJ, Cho H, Kim HK, Chong SO, Shon JN. Study on perceived concept about therapeutic communication of nurses working in psychiatric ward. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 1996; 5(1):88–99.
26. George JB. Nursing theories: The base for professional nursing practice. 5th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall;2002.
27. Hwang EM. Non-verbal behavior for effective communication. Textlinguistics. 2008; 24:313–335.
28. Ju JS. The effects of the communication training program for university students' communication and human relationship [master's thesis]. Daegu: Kyungpook National University;2005.
29. Choi EY. (The) effects of a communication skills group on high school students' self-concept and communication ability [master's thesis]. Busan: Kosin University Graduate School of Education;2004.
30. Hyland T. Reconsidering competence. J Philos Educ. 1997; 31(3):491–503. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1467-9752.00070.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download