Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify effects of action learning approaches on learning outcomes of students taking nursing management courses.
Methods
The questionnaire surveys were completed between March 2011 and June 2012 by 109 undergraduate seniors in the nursing department of C University. Survey data were obtained 3 times: before, in and after the study of nursing management. The course consisted of lectures and clinical practices. Learning outcomes were measured through problem solving skills, team efficacy, and class satisfaction. Collected data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA with the SPSS 20.0 program.
Results
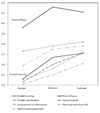
Scores for problem solving skills (F=13.67, p<.001) and team efficacy (F=4.49, p=.012) showed statistically significant increases after the course. The scores also increased significantly after the lectures for 5 of 9 problem solving skill subscales: analysis skill, divergent thinking, decision making, assessment, feedback, and after the clinical practices for 2 subscales: divergent thinking, and execution and risk taking. Class satisfaction score also increased after both the lectures and the clinical practices.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Bandura A. Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. 1997. New York: Freeman.
2. Bong HC. Do action learning for success. 2012. Seoul: Hangseong B wave.
3. Bong HC, Kim JI. A try to escape from desperate dilemma of university education: Management class that action learning has changed. Invited lecture presented at Hanyang University Teaching and Learning Center Symposium. 2003. 03. Seoul, Korea.
4. Bourner TB, Cooper AC, France LF. Action learning across a university community. Innov Educ Train Int. 2000. 37:2–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/135580000362025.
5. Greenwood J. Critique of the graduate nurse: An international perspective. Nurse Educ Today. 2000. 20:17–23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1054/nedt.2000.0424.
6. Heidari F, Galvin K. Action learning groups: Can they help students develop their knowledge and skills? Nurse Educ Pract. 2003. 3:49–55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1471-5953(02)00054-9.
7. Hur YJ. Case study on develop and practical use an action learning program for 'information society's teaching method' of graduate school of education. J Korean Teach Educ. 2009. 25(1):22–52.
8. Jang KS, Baek M, Choi YJ, Ahn SH, Lee SJ, Sim JY, et al. An analysis of nurse managers's common fundamental competencies changes and responses to the application of the action learning. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2006. 12:424–433.
9. Jang SH. Search on morality that Korean society requires: Focused on the case of teaching-learning in elementary moral education applying action learning. Elementary Moral Educ. 2011. 36:111–142.
10. Kim EJ. The effects of students achievement level and communication orientation on cooperative learning class satisfaction. Korean J Educ Res. 2004. 42(3):123–151.
11. Kim HS, Hwang KS, Kwon SC, Hong SU, Oh JS, Koh BS, et al. A study on the core competencies lecture effectiveness analysis adapted action learning. Tamnamunhwa. 2012. 41:78–109.
12. Kim JI, Park YK, Lee KH. A case study on the process reengineering by action learning program: Focusing on a training program in Hyosung corporation. Inf Syst Rev. 2006. 8(1):289–303.
13. Kim YM. Evaluation of design and operation of action learning based nursing professionalism course for nursing students. 2012. Gwangju, Korea: Chonnam National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
14. Kim YM, Kim YH. Development and evaluation of action learning in clinical practice of nursing management. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2010. 10(6):312–322.
15. Korean Accreditation Board of Nursing Education. Key competencies and learning outcomes. 2012. Retrieved November 5, 2012. from http://www.kabon.or.kr/HyAdmin/upload/goodFile/120121105102905.pdf.
16. Kwon EM. The correlation among team efficacy, interpersonal understanding, proactivity in problem solving and team performance. 2010. Seoul, Korea: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.
17. Lee SJ. The effects of action learning program on nurses's problem solving and communication skills. 2009. Gwangju, Korea: Chonnam National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
18. Lee SJ, Chang YK, Lee HN, Park KY. A study on the development of life-skills: Communication, problem solving, and self-directed learning. 2003. Seoul: Korean Educational Development Institute.
19. Lee YM, Kim TJ, Kim JI, Jang SP, Hong JY. The effects of task types and collaboration procedures on task performance and group efficacy in web-based situational learning environment. J Educ Stud. 2006. 37(3):47–75.
20. Marquardt MJ. Silberman M, editor. Action learning: Resolving real problems in real time. The handbook of experiential learning. 2007. San Francisco, CA: Pfeiffer;94–110.
21. Marshall LC. The relationship between efficacy, teamwork, effort and patient satisfaction. 2003. L.A: University of Southern California;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
22. Murphy KR, Cleveland JN. Performance Appraisal. 1991. Boston: Ally and Bacon.
23. Park MS. A longitudinal study on the factors affecting team performance among college students: The development of team efficacy perspective. 2009. Asan, Korea: Hoseo University;Unpublished master's thesis.
24. Roh HL. Identifying design factors of action learning in higher education. J Educ Inf Media. 2007. 13(3):53–78.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download