1. Harman D. The free radical theory of aging. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2003; 5:557–561.

2. Harman D. Aging: a theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J Gerontol. 1956; 11:298–300.

3. Beckman KB, Ames BN. The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol Rev. 1998; 78:547–581.

4. Powolny AA, Singh SV, Melov S, Hubbard A, Fisher AL. The garlic constituent diallyl trisulfide increases the lifespan of C. elegans via skn-1 activation. Exp Gerontol. 2011; 46:441–452.

5. Kitani K, Yokozawa T, Osawa T. Interventions in aging and age-associated pathologies by means of nutritional approaches. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004; 1019:424–426.

6. Martorell P, Bataller E, Llopis S, Gonzalez N, Alvarez B, Montón F, Ortiz P, Ramón D, Genovés S. A cocoa peptide protects Caenorhabditis elegans from oxidative stress and β-amyloid peptide toxicity. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e63283.

7. Park SK, Page GP, Kim K, Allison DB, Meydani M, Weindruch R, Prolla TA. alpha- and gamma-Tocopherol prevent age-related transcriptional alterations in the heart and brain of mice. J Nutr. 2008; 138:1010–1018.

8. Park SK, Kim K, Page GP, Allison DB, Weindruch R, Prolla TA. Gene expression profiling of aging in multiple mouse strains: identification of aging biomarkers and impact of dietary antioxidants. Aging Cell. 2009; 8:484–495.

9. Park SK, Kim JJ, Yu AR, Lee MY, Park SK. Electrolyzed-reduced water confers increased resistance to environmental stresses. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2012; 8:241–247.

10. Park SK, Park SK. Electrolyzed-reduced water increases resistance to oxidative stress, fertility, and lifespan via insulin/IGF-1-like signal in C. elegans. Biol Res. 2013; 46:147–152.

11. Jung BS, Shin MK. Hyang Yak Dae Sa Jeon. 3rd ed. Seoul: Young Lim Sa Publisher;2003.
12. Fujikawa T, Yamaguchi A, Morita I, Takeda H, Nishibe S. Protective effects of Acanthopanax senticosus Harms from Hokkaido and its components on gastric ulcer in restrained cold water stressed rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 1996; 19:1227–1230.

13. Bae EA, Yook CS, Oh OJ, Chang SY, Nohara T, Kim DH. Metabolism of chiisanoside from Acanthopanax divaricatus var. albeofructus by human intestinal bacteria and its relation to some biological activities. Biol Pharm Bull. 2001; 24:582–585.

14. Jung HJ, Nam JH, Choi J, Lee KT, Park HJ. Antiinflammatory effects of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin obtained from the leaves of Acanthopanax chiisanensis in the carrageenan- and Freund's complete adjuvant-induced rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005; 97:359–367.

15. Kim YO, Cho DH, Chung HJ, Kim JH, Chang SY, Yook CS, Yang KS, Oh OJ. Effects of lupane-triterpenoids on mitogen-induced proliferation of lymphocytes. Yakhak Hoeji. 1999; 43:208–213.
16. Jeong SC, Jeong YT, Yang BK, Song CH. Chemical characteristics and immuno-stimulating properties of biopolymers extracted from Acanthopanax sessiliflorus. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2006; 39:84–90.

17. Jeong SC, Yang BK, Jeong YT, Rao KS, Song CH. Isolation and characterization of biopolymers extracted from the bark of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus and their anticomplement activity. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007; 17:21–28.
18. Yoshizumi K, Hirano K, Ando H, Hirai Y, Ida Y, Tsuji T, Tanaka T, Satouchi K, Terao J. Lupane-type saponins from leaves of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus and their inhibitory activity on pancreatic lipase. J Agric Food Chem. 2006; 54:335–341.

19. Ryu AR, Kim JH, Lee MY. Suppressive effect of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus extract on the DNA and cell damage by Dieldrin. Korean J Med Crop Sci. 2012; 20:245–250.

20. Kim HY, Kim K. Protein glycation inhibitory and antioxidative activities of some plant extracts in vitro. J Agric Food Chem. 2003; 51:1586–1591.

21. Wiegant FA, Surinova S, Ytsma E, Langelaar-Makkinje M, Wikman G, Post JA. Plant adaptogens increase lifespan and stress resistance in C. elegans. Biogerontology. 2009; 10:27–42.

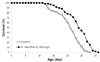
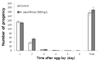
22. Kim CK, Park SK. Effect of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus extracts on stress response and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Sci Technol Res. 2013; 19:439–444.

23. Liu SM, Li XZ, Huo Y, Lu F. Protective effect of extract of Acanthopanax senticosus Harms on dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease mice. Phytomedicine. 2012; 19:631–638.

24. Park SK, Lee MY. Suppressive effects of various antioxidants on melamine-induced oxidative DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2009; 5:243–249.
25. Peto R, Peto J. Asymptotically efficient rank invarient test procedures. J R Stat Soc Ser A Stat Soc. 1972; 135:185–207.
26. Treinin M, Shliar J, Jiang H, Powell-Coffman JA, Bromberg Z, Horowitz M. HIF-1 is required for heat acclimation in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Physiol Genomics. 2003; 14:17–24.

27. Sohal RS, Weindruch R. Oxidative stress, caloric restriction, and aging. Science. 1996; 273:59–63.

28. Hughes SE, Evason K, Xiong C, Kornfeld K. Genetic and pharmacological factors that influence reproductive aging in nematodes. PLoS Genet. 2007; 3:e25.

29. Larsen PL, Albert PS, Riddle DL. Genes that regulate both development and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1995; 139:1567–1583.

30. Gems D, Sutton AJ, Sundermeyer ML, Albert PS, King KV, Edgley ML, Larsen PL, Riddle DL. Two pleiotropic classes of daf-2 mutation affect larval arrest, adult behavior, reproduction and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1998; 150:129–155.

31. Yook CS, Rho YS, Seo SH, Leem JY, Han DR. Chemical components of Acanthopanax divaricatus and anticancer effect in leaves. Yakhak Hoeji. 1996; 40:251–261.
32. Hahn DR, Kim CJ, Kim JH. A study on the chemical constituents of Acanthopanax koreanum Nakai and its pharmaco-biological activities. Yakhak Hoeji. 1985; 29:357–361.
33. Fu J, Fu J, Yuan J, Zhang N, Gao B, Fu G, Tu Y, Zhang Y. Anti-diabetic activities of Acanthopanax senticosus polysaccharide (ASP) in combination with metformin. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012; 50:619–623.

34. Liu XZ, Yan D. Ageing and hearing loss. J Pathol. 2007; 211:188–197.

35. Lee CK, Weindruch R, Prolla TA. Gene-expression profile of the ageing brain in mice. Nat Genet. 2000; 25:294–297.

36. Suthammarak W, Somerlot BH, Opheim E, Sedensky M, Morgan PG. Novel interactions between mitochondrial superoxide dismutases and the electron transport chain. Aging Cell. 2013; 12:1132–1140.

37. Lagouge M, Larsson NG. The role of mitochondrial DNA mutations and free radicals in disease and ageing. J Intern Med. 2013; 273:529–543.

38. Ivanova DG, Yankova TM. The free radical theory of aging in search of a strategy for increasing life span. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2013; 55:33–41.

39. Goto S. Evidence for and against anti-aging effects based on model animal studies. Nihon Rinsho. 2009; 67:1337–1340.
40. Mecocci P, Polidori MC, Troiano L, Cherubini A, Cecchetti R, Pini G, Straatman M, Monti D, Stahl W, Sies H, Franceschi C, Senin U. Plasma antioxidants and longevity: a study on healthy centenarians. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000; 28:1243–1248.

41. Lipman RD, Bronson RT, Wu D, Smith DE, Prior R, Cao G, Han SN, Martin KR, Meydani SN, Meydani M. Disease incidence and longevity are unaltered by dietary antioxidant supplementation initiated during middle age in C57BL/6 mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 1998; 103:269–284.

42. Navarro A, Gómez C, Sánchez-Pino MJ, González H, Bández MJ, Boveris AD, Boveris A. Vitamin E at high doses improves survival, neurological performance, and brain mitochondrial function in aging male mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005; 289:R1392–R1399.

43. Bass TM, Weinkove D, Houthoofd K, Gems D, Partridge L. Effects of resveratrol on lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech Ageing Dev. 2007; 128:546–552.

44. Agarwal B, Baur JA. Resveratrol and life extension. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1215:138–143.

45. Kirkwood TB. Evolution of ageing. Nature. 1977; 270:301–304.

46. Hsin H, Kenyon C. Signals from the reproductive system regulate the lifespan of C. elegans. Nature. 1999; 399:362–366.

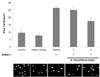
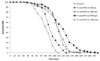
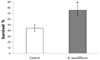
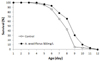






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download