Abstract
Purpose
Belotecan (CamtobellⓇ; Chong Keun Dang Co., Seoul, Korea) is a new camptothecin analog that inhibits topoisomerase I. We evaluated the efficacy and toxicity of belotecan combined with cisplatin in patients with previously untreated extensive-disease small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC) and who were without evidence of brain metastases.
Materials and Methods
Twenty patients with previously untreated ED-SCLC were treated with belotecan (0.5 mg/m2/day) on days 1∼4 and with cisplatin (60 mg/m2/day) on day 1 of a 3-week cycle.
Results
Of the 19 assessable patients, 16 had an objective tumor response, including two complete responses, for an overall response rate of 84.2%. Toxicity was evaluated in all 20 patients who received a total of 106 cycles (median cycles/patient, 5.5; range, 1∼9). The major grade 3/4 hematologic toxicities were neutropenia (67.9% of cycles), anemia (19.8% of cycles) and thrombocytopenia (33.9% of cycles). No grade 3/4 non-hematologic toxicities were observed. No treatment-related deaths occurred. The median progression-free and overall survivals were 7.06 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.98∼10.14 months) and 9.96 months (95% CI, 6.12∼13.80 months), respectively.
Go to : 
References
1. Basili S, Moro S. Novel camptothecin derivatives as topoisomerase I inhibitors. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009; 19:555–574.

2. Lee JH, Lee JM, Kim JK, et al. Antitumor activity of 7-[2-(N-isopropylamino)ethyl]-(20S)-camptothecin, CKD602, as a potent DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor. Arch Pharm Res. 1998; 21:581–590.

3. Lee JH, Lee JM, Lim KH, et al. Preclinical and phase I clinical studies with CKD-602, a novel camptothecin derivative. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000; 922:324–325.

4. Kim SJ, Kim JS, Kim SC, et al. A multicenter phase II study of belotecan, new camptothecin analogue, in patients with previously untreated extensive stage disease small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2010; 68:446–449.

5. Lee DH, Kim SW, Bae KS, et al. A phase I and pharmacologic study of belotecan in combination with cisplatin in patients with previously untreated extensive-stage disease small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:6182–6186.

6. Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:85–91.

7. Hanna N, Bunn PA Jr, Langer C, et al. A randomized phase III trial comparing irinotecan/cisplatin with etoposide/cisplatin in patients with previously untreated extensive-stage disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2038–2043.
8. Hermes A, Bergman B, Bremnes R, et al. Irinotecan plus carboplatin versus oral etoposide plus carboplatin in extensive small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:4261–4267.

9. Eckardt JR, von Pawel J, Papai Z, et al. Open-label, multicenter, randomized, phase III study comparing oral topote-can/cisplatin versus etoposide/cisplatin as treatment for chemotherapy-naive patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2044–2051.

10. Park SH, Cho EK, Kim Y, et al. Salvage treatment with topotecan in patients with irinotecan-refractory small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008; 62:1009–1014.

11. Lee DH, Kim SW, Suh C. Belotecan, new camptothecin analogue, is active in patients with small cell lung cancer: results of a multicenter early phase II study. Ann Oncol. 2008; 19:123–127.
12. Lee DH, Kim SW, Suh C, et al. Multicenter phase 2 study of belotecan, a new camptothecin analog, and cisplatin for chemotherapy-naï ve patients with extensive disease small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2010; 116:132–136.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables
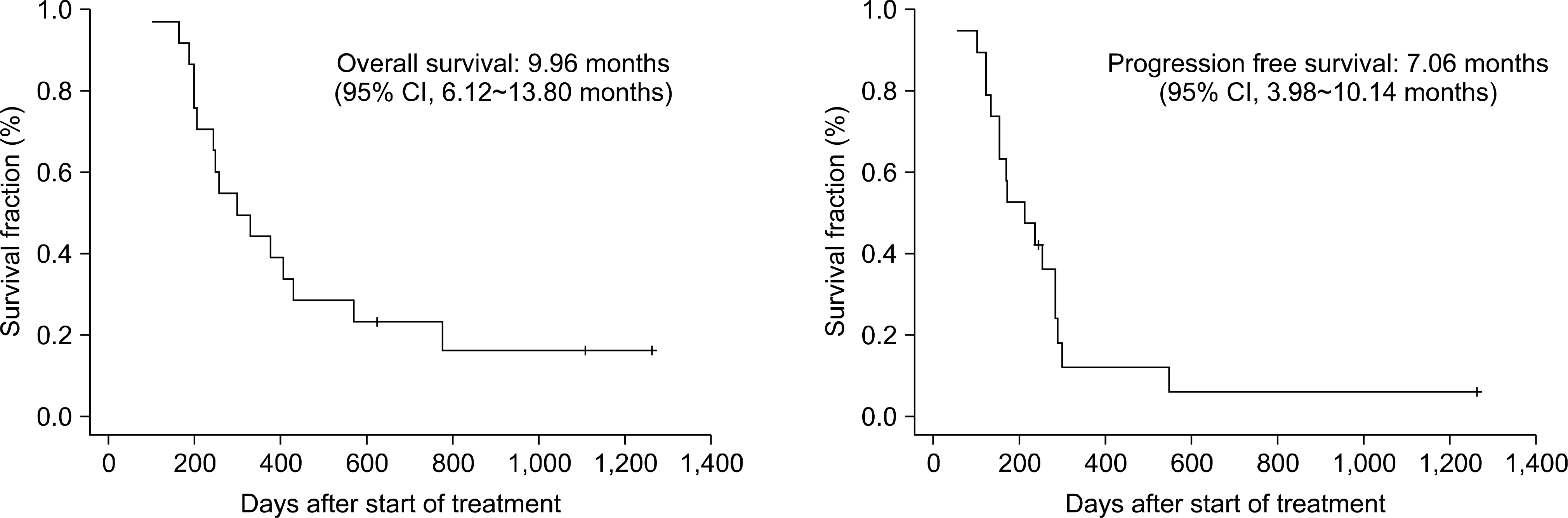 | Fig. 1.Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival outcomes are illustrated. Tick marks indicate censored data. |
Table 1.
Patient Characteristics
Table 2.
Tumor Responses
| Response | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Complete response | 2 (10.5) |
| Partial response | 14 (73.7) |
| Stable disease | 2 (10.5) |
| Progressive disease | 1 (5.3) |
| Objective response | 16/19 (84.2) |
| Total | 19 |
Table 3.
Toxicity Profile by Cycles




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download