Abstract
Purpose:
Evidence exists that deregulation of apoptosis is involved in the mechanisms of cancer development, and the somatic mutations of apoptosis- related genes have been reported in human cancers. Bel- Xᄂ/Bcl-2-assᄋdated death promoter (BAD), a pro-apoptotic member of Bcl-2 family, plays an important role in the intrinsic apoptosis pathway.
Materials and Methods:
To explore the possibility that the genetic alterations of BAD might be involved in the development of human cancers, we analyzed the entire coding region and all splice sites of human BAD gene in 100 human non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
4.Datta SR., Katsov A., Hu L, et al. 14-3-3 proteins and survival kinases cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3 domain phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2000. 6:41–51.

5.O'Connor L: Strasser A., O'Reilly LA, et al. Bim: a novel member of the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EM BO J. 1998. 17:384–395.
6.Inohara N., Ding L., Chen S: Nunez G. harakiri, a novel regulator of cell death: encodes a protein that activates apoptosis and interacts selectively with survival-promoting proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-X (L). EMBO J. 1997. 16:1686–1694.
7.Guo B: Godzik A., Reed JC. Bcl-G: a novel pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:2780–2785.
8.Oda E., Ohki R., Murasawa H, et al. Noxa: a BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of p53-induced apoptosis. Science. 2000. 288:1053–1058.

9.Nakano K., Vousden KH. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 2001. 7:683–694.

10.Chang J: Clark GM., Allred DC: Mohsin S: Chamness G: El ledge RM. Survival of patients with metastatic breast carcinoma: importance of prognostic markers of the primary tumor. Cancer. 2003. 97:545–553.
11.Krajewska M., Zapata JM., Meinhold-Heerlein I, et al. Expression of Bcl-2 family member Bid in normal and malignant tissues. Neoplasia. 2002. 4:129–140.

12.McDonnell TJ: Deane N: Platt FM, et al. bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell. 1989. 57:79–88.

13.Lee JH., Soung YH., Lee JW, et al. Inactivating mutation of the pro-apoptotic gene BID in gastric cancer. J Pathol. 2004. 202:439–445.
14.Kondo S: Shinomura Y., Miyazaki Y, et al. Mutations of the bak gene in human gastric and colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:4328–4330.
15.Rampino N., Yamamoto H., Ionov Y, et al. Somatic frameshift mutations in the BAX gene in colon cancers of the microsatellite mutator phenotype. Science. 1997. 275:967–969.
16.Lee JW., Soung YH., Kim SY, et al. Inactivating mutations of proapoptotic Bad gene in human colon cancers. Carcinogenesis. 2004. 25:1371–1376.

17.Lee SH., Shin MS., Park WS, et al. Alterations of Fas (Apo1/CD95) gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 1999. 18:3754–3760.

18.Lee SH., Shin MS., Kim HS, et al. Alterations of the DR5/TRAIL receptor 2 gene in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:5683–5686.
19.Soung YH., Lee JW., Kim SY, et al. Caspase-8 gene is frequently inactivated by the frameshift somatic mutation 1225 1226delTG in hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncogene. 2005. 24:141–147.
20.Kim HS., Lee JW., Soung YH, et al. Inactivating mutations of caspase-8 gene in colorectal carcinomas. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:708–715.

21.Soung YH., Lee JW., Kim SY, et al. CASPASE-8 gene is inactivated by somatic mutations in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:815–821.
Go to : 
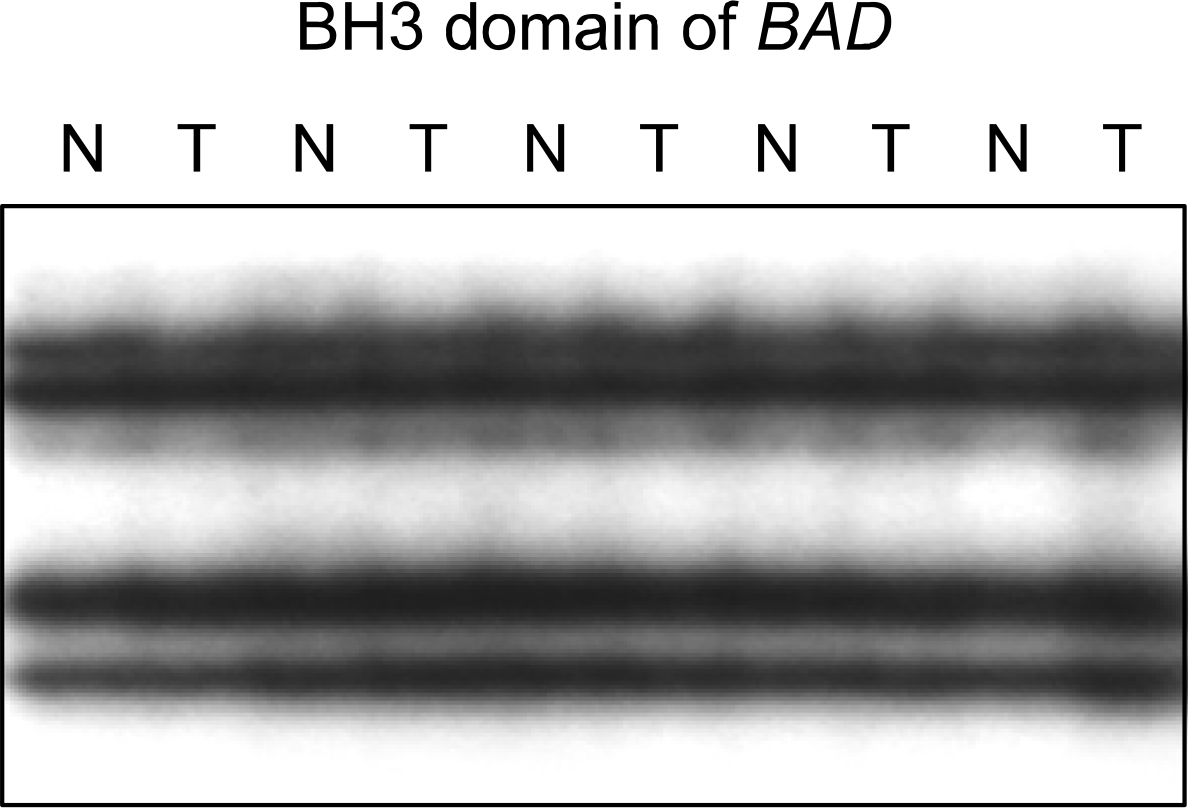 | Fig. 1.Representative SSCP of BAD gene in the non-small cell lung cancers. The exon 2 of the BAD gene were amplified by PGR using a specific primer set. The PCR products from the representative cases of non-small cell lung cancers were visualized on SSCP. SSCP of DNA from the non-small cell lung cancers (T) shows no aberrant bands as compared to SSCPs from the normal tissues (N), |
Table 1.
Sequence of SSCP Primer Sets for BAD




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download