Abstract
Purpose
The aim of the present study was to analyze 7-year cumulative survival rate (CSR, %) of dental implants in the controlled diabetic patients and to evaluate the influence of the position, diameter and length of fixture, bone quality, age, gender and the method of maxillary sinus elevation on the survival rate.
Methods
The data of 342 placed implants in the 104 diabetic patients collected between 1995 and 2007 at the Department of Periodontology in Yonsei University Hospital were analyzed.
Results
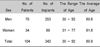
Seven-year CSR of the 342 dental implants in the 104 controlled diabetic patients was 96.5%. The survival rates of the placed implants according the position have no statistically significant difference. The survival rates according to the length or diameter of the fixtures have no statistically significant difference. The survival rates according to the bone quality were 100% (TypeI), 97.1% (Type II), 97.7% (Type III) and 85.7%(Type IV). The difference between the survival rate of Type I, II and III and that of Type IV was statistically significant. The survival rates according to patient gender were 96.8% (male), 95.5% (female). The survival rates according to patient age were 100% (≤59), 93.8% (≥60). The survival rates according to the method of sinus elevation in the maxillary posterior area were 96.8% (without sinus elevation), 92.9% (lateral approach) and 89.8% (crestal approach).
Figures and Tables
Table 7
Survival Rate of Placed Implants According to Bone Quality

*P = 0.010, Bone quality type: Lekholm and Zarb's criteria9)
References
1. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001. 414:782–787.

2. Mealey BL, Ocampo GL. Diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease. Periodontology 2000. 2007. 44:127–153.

3. Mealey BL, Oates TW. Diabetes mellitus and periodontal diseases. J Periodontol. 2006. 77:1289–1303.

4. Taylor GW. Bidirectional interrelationships between diabetes and periodontal diseases: An epidemiologic perspective. Ann periodontol. 2001. 6:99–112.

5. Olson JW, Shernoff AF, Tarlow JL, et al. Dental endosseous implant assessments in a type 2 diabetic population: A prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac implants. 2000. 15:811–818.
6. Peled M, Ardekian L, Tagger-Green N, Gutmacher Z, Machtei EE. Dental implants in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A clinical study. Implant Dent. 2003. 12:116–122.

7. Fiorellini JP, Chen PK, Nevins M, Nevins ML. A retrospective study of dental implants in diabetic patients. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2000. 20:366–373.
8. Farzad P, Andersson L, Nyberg J. Dental implant treatment in diabetic patients. Implant Dent. 2002. 11:262–267.

9. Blanchaert RH. Implants in the medically challenged patient. Dent Clin North Am. 1998. 42:35–45.
10. Balshi TJ, Wolfinger GJ. Dental implants in the diabetic patient: a retrospective study. Implant Dent. 1999. 8:355–359.
11. Morris HF, Ochi S, Winkler S. Implant survival in patients with type 2 diabetes: placement to 36 months. Ann Periodontol. 2000. 5:157–165.

12. Dent CD, Olson JW, Farish SE, et al. The influence of preoperative antibiotics on success of endosseous implants up to and including stage II surgery: a study of 2,641 implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997. 55:19–24.

13. Sbordone L, Barone A, Ramaglia L, Ciaglia RN, Iacono VJ. Antimicrobial susceptibility of periodontopathic bacteria associated with failing implants. J Periodontol. 1995. 66:69–74.

14. Lekholm U, Zarb GA, Branemark PI. Tissue integrated prostheses Osseointegration in clinical dentistry. 1985. Chicago: Quintenssence;199–209.
15. Buser D, Mericske-Stern R, Bernard JP, et al. Long-term evaluation of prospective multi-center study with 2359 implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997. 8:161–172.

16. Cochran DL, Buser D, ten Burugenakte C, et al. The use of reduced healing times on ITI implants with a sandblasted and etched (SLA) surface : early results from clinical trials on ITI SLA implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:144–153.

17. Smith RA, Berger R, Dodson TB. Risk factors associated with dental implants in healthy and medically compromised patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992. 7:367–372.
18. Friberg B, Grondahl K, Lekholm U, Branemark PI. Long-term follow-up of severly atrophic edentulous mandibles reconstructed with short Branemark implants. Clin Implant Dent Rel Res. 2000. 2:184–189.

19. Lekholm U, Gunne J, Henry P, et al. Survival of the Branemark implant in partially edentulous jaws: A 10-year prospective multicenter study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999. 14:639–645.
20. Bryant SR. The effects of age, jaw site, and bone condition on oral implant outcomes. Int J Prosthodont. 1998. 11:470–490.
21. Jemt T. Fixed implant-supported prostheses in the edentulous maxilla. A five-year follow-up report. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994. 5:142–147.

22. Misch CE. Translation of Contemporary Implant Dentistry. 1999. 2nd editon. Seoul: Narae Publishing Inc;205–215.
23. Langer B, Langer L, Herrmann I, Jorneus L. The wide fixture: A solution for special bone situations and a rescue for the compromised implant. Part 1. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993. 8:400–408.
24. Ivanoff CJ, Sennerby L, Johansson C, Rangert B, Lekholm U. Influence of implant diameters on the integration of screw implants: An experimental study in rabbits. Int. J Oral Maillofac Surg. 1997. 26:141–148.
25. Ivanoff CJ, Grondahl K, Sennerby L, Bergstrom C, Lekholm U. Influence of variations in implant diameters: a 3- to 5-year retrospective clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999. 14:173–180.
26. Eckert SE, Meraw SJ, Weaver AL, Lohse CM. Early experience with Wide-Platform Mk II implants. Part I: Implant survival. Part II: Evaluation of risk factors involving implant survival. Int Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001. 16:208–216.
27. Deporter D, Pilliar RM, Todescan R, Watson P, Pharoah M. Managing the posterior mandible of partially edentulous patients with short, porous-surfaced dental implants: Early data from a clinical trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001. 16:653–658.
28. Brocard D, Barthet P, Baysse E, et al. A multicenter report on 1,022 consecutively placed ITI implants: a 7-year longitudinal study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000. 15:691–700.
29. Lazzara R, Siddiqui AA, Binon P, et al. Retrospective multicenter analysis of 3i endosseous dental implants placed over a five-year period. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996. 7:73–83.

30. Jaffin RA, Berman CL. The excessive loss of Branemark fixtures in type IV bone: a 5-year analysis. J Periodontol. 1991. 62:2–4.

31. Meijer HJ, Batenburg RH, Raghoebar GM. Influence of patient age on the success rate of dental implants supporting an overdenture in an edentulous mandible: a 3-year prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001. 16:522–526.
32. Bryant SR, Zarb GA. Osseointegration of oral implants in older and younger adults. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998. 13:492–499.
33. Engfors I, Ortorp A, Jemt T. Fixed implant-supported prostheses in elderly patients: A 5-year retrospective study of 133 edentulous patients older than 79 years. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2004. 6:190–198.

34. Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systemic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003. 8:328–343.

35. Yon JY, Chae GJ, Jung UW, et al. Long-term evaluation of implant placed in sites grafed by lateral window approach on maxillary sinus; a 10-year retrospective study. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2007. 37:691–704.

36. Kim SH, Kim BO, Han KY. A clinical study on the periodontal status of the patient with diabetes mellitus. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 1993. 23:27–36.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print











 XML Download
XML Download