Abstract
Purpose
This study evaluated the result of fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures using an anti-hypersliding compressive hip screw and a trochanter stabilizing plate.
Materials and Methods
One hundred patients with unstable intertrochanteric fractures who were given an anti-hypersliding compressive hip screw (Group A) or conventional compressive hip screw (Group B) were analyzed. The mean follow-up period was 23.5 months. Radiographic evaluation included the changes of neck-shaft angle, lateral displacement of proximal fragment, distal migration of the lag screw, fixation failure, and union time using plain radiographs taken at postoperative and last follow-up time.
Results
Lateral displacement of the proximal fragment averaged 1.62 mm in Group A and 3.97 mm in Group B, which was statistically significant (p<0.05). The neck-shaft angle was increased in Group B, but has no significance. The average of the Harris hip score and walking ability after surgery is higher in Group A than B, but there was no significant difference. The complication rate was significantly lower in Group A. But union time showed no difference in each group.
Conclusion
Anti-hypersliding compression hip screw with a TSP, which reduces sliding of the lag screw and extreme change of the moment arm, is a another good option for the treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures against an increase of the failure rate from the hypersliding of the lag screw.
Figures and Tables
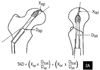
 | Fig. 3Radiographic evaluation according to Doppelt's method of radiologic evaluation17). (A) Immediate postoperative radiographs. (B) Subsequent radiograph. Correction factor=B/b, the extent of sliding=A-a×B/b, the extent of lateral displacement=c-C×B/b. |
References
1. LaVelle DG. Canale ST, editor. Fractures of hip. Campbell's Operative Orthopedics. 2003. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;2873–2938.
3. DeLee J. Rockwood CA, Green DP, Bucholz RW, editors. Fractures and dislocations of the hip. Green's Fractures in Adults. 1991. Philadelphia: Lippincott;1481–1651.
4. Kaufer H, Matthews LS, Sonstegard D. Stable fixation of intertrochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974. 56:899–907.

5. Kyle RF, Gustilo RB, Premer RF. Analysis of six hundred and twenty-two intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:216–221.

6. Alobaid A, Harry EJ, Elder GM, Lander P, Guy P, Reindl R. Minimally invasive dynamic hip screw: prospective randomized trial of two techniques of insertion of a standard dynamic fixation device. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:207–212.
7. Bolhofner BR, Russo PR, Carmen B. Results of intertrochanteric femur fractures treated with a 135-degree sliding screw with a two-hole side plate. J Orthop Trauma. 1999. 13:5–8.

8. McLoughlin SW, Wheeler DL, Rider J, Bolhofner B. Biomechanical evaluation of the dynamic hip screw with two- and four-hole side plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2000. 14:318–323.

9. Bannister GC, Gibson AG, Ackroyd CE, Newman JH. The fixation and prognosis of trochanteric fractures. A randomized prospective controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. 254:242–246.
10. Korner J, Lill H, Müller LP, Rommens PM, Schneider E, Linke B. The LCP-concept in the operative treatment of distal humerus fractures--biological, biomechanical and surgical aspects. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 2. B20–B30.
11. Sommer C. Locking compression plate. Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 2. B4–B5.
12. Strömberg L, Dalén N. Atrophy of cortical bone caused by rigid internal fixation plates. An experimental study in the dog. Acta Orthop Scand. 1978. 49:448–456.

13. Babst R, Renner N, Biedermann M, et al. Clinical results using the trochanter stabilizing plate (TSP): the modular extension of the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for internal fixation of selected unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1998. 12:392–399.

14. Chang JS, Kim KY, Lee SH, Ahn HS, Han BH, Hong SW. Treatment of communited trochanteric fractures with dynamic hip screw and DHS trochanter stabilizing plate. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1997. 32:1206–1213.

15. Jacobs RR, McClain O, Armstrong HJ. Internal fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: a clinical and biomechanical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980. 146:62–70.
16. Steinberg GG, Desai SS, Kornwitz NA, Sullivan TJ. The intertrochanteric hip fracture. A retrospective analysis. Orthopedics. 1988. 11:265–273.

17. Doppelt SH. The sliding compression screw--today's best answer for stabilization of intertrochanteric hip fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1980. 11:507–523.

18. Heyse-Moore GH, MacEachern AG, Evans DC. Treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. A comparison of the Richards screw-plate with the Jewett nail-plate. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983. 65:262–267.
19. Ceder L, Lindberg L, Odberg E. Differentiated care of hip fractures in the elderly. Mean hospital days and results of rehabilitation. Acta Orthop Scand. 1980. 51:157–162.

20. Mulholland RC, Gunn DR. Sliding screw plate fixation of intertrochanteric femoral fractures. J Trauma. 1972. 12:581–591.

21. Baumgaertner MR, Solberg BD. Awareness of tip-apex distance reduces failure of fixation of trochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997. 79:969–971.

22. Rha JD, Kim YH, Yoon SI, Park TS, Lee MH. Factors affecting sliding of the lag screw in intertrochanteric fractures. Int Orthop. 1993. 17:320–324.

23. Davis TR, Sher JL, Horsman A, Simpson M, Porter BB, Cheketts RG. Intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Mechanical failure after internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:26–31.

24. Ekeland A, Benterud J, Strømsøe K, Alho A. Telescoping of intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric femoral fractures treated with hip compression screw. Acta Orthop Scand. 1990. 61:Suppl. 12.
25. Jensen JS, Tøndevold E, Mossing N. Unstable trochanteric fractures treated with the sliding screw-plate system. A biomechanical study of unstable trochanteric fractures. III. Acta Orthop Scand. 1978. 49:392–397.

26. Babst R, Martinet O, Renner N, et al. The dynamic hip screw support plate for management of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Helv Chir Acta. 1993. 59:521–525.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download