Abstract
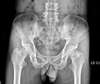
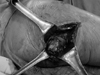
Tuberculous infection of the ischium is a rare condition. It is recommended that antituberculosis chemotherapy is combined with surgical intervention. The patient in this case had an abscess on his right gluteal region and he had undergone an operation without antituberculosis chemotherapy. After eight years, an abscess recurred in the same area and he was treated with surgical resection. Antituberculosis chemotherapy was administered following histopathological confirmation of tuberculosis. At 1 year postoperatively, the patient had no pain and there was no evidence of recurrence.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 3
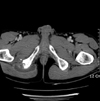
CT scan showing areas of relatively well demarcated low density shades between the gluteus maxmius muscle and the ischial tuberosity.
References
1. Alvarez S, McCabe WR. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis revisited: a review of experience at Boston City and other hospitals. Medicine. 1984. 63:25–55.
2. Moon MS, Ok IY, Ha KY, Shin JC. Tuberculosis of the puboischium -Report of five cases-. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1987. 22:1326–1332.

3. Siegel RS, Jacoby AW, Alicandri FP. A posterior surgical approach to the ischium. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981. 63:466–469.

4. Martini M, Ouahes M. Bone and joint tuberculosis: a review of 652 cases. Orthopedics. 1988. 11:861–866.

5. Abdelwahab IF, Kenan S, Hermann G, Lewis M, Klein M, Rabinowitz JG. Atypical skeletal tuberculosis mimicking neoplasm. Br J Radiol. 1991. 64:551–555.

7. Singh O, Gupta S, Moses S, Jain DK. Spontaneous tubercular enterocutaneous fistula developing in the scar of a surgery done 14 years earlier. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2009. 15:261–263.

8. Bhattacharyya AN. Tuberculosis of the ischium: a report of three cases. Aust N Z J Surg. 1973. 42:389–391.

9. García S, Segur JM, Combalía A. Tuberculosis of the ischium. Acta Orthop Belg. 1994. 60:238–240.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download