Abstract
Paget disease is a well-documented skeletal disease and it has an increased rate of tissue breakdown due to the excessive turnover of osteoblasts and osteclasts. Stress fracture is one of the most common complications in the late phase of Paget disease, but the clinical presentation of incomplete pathologic fracture is rare and this is an important clue to plan the treatment. We experienced a case of Paget's disease in a 74 year old woman with a periprosthetic fracture from the undetected, imcomplete stress fracture in the proximal femur.
Figures and Tables
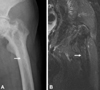
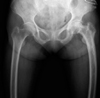 | Fig. 1Preoperative plain x-ray shows both femoral coxa vara and radioopaque lesions in the femoral head and the proximal femur. |
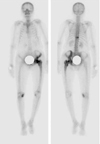 | Fig. 2Bone scan shows hot uptake in the femoral head and proximal femur, some parts of the ilium and T11 which suggests inflammatory bone lesion. |
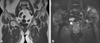 | Fig. 3(A) Preoperative local MRI shows low signal intensity and (B) high signal intensity in the lateral aspect of the femoral head and relatively well preserved articular cartilage. |
 | Fig. 4On the gross examination, there is loss of articular cartilage with exposure of eburnated bone. The subchondral bone is sclerotic with irregular thickening of the trabecular and changes of the cortex. |
 | Fig. 5(A) On the microscopic examination, there are irregularly thickened and disorganized trabeculae lined by increased numbers of osteoblasts (short arrow) and multinucleated osteoclasts (long arrow), (H&E, ×100). (B) Woven bone with irregular, wavy, and curliform cement lines (arrow) is noted (H&E, ×400). |
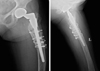
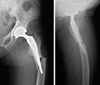 | Fig. 6Transverse fracture line is seen on the convex area of the proximal femur on 6 months after operation. |
References
1. Suk SI, Cho SH, Ahn GH. Paget's disease - one case report -. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1982. 17:1031–1034.
2. Cooper C, Dennison E, Schafheutle K, Kellingray S, Guyer P, Barker D. Epidemiology of Paget's disease of bone. Bone. 1999. 24:Suppl. 3S–5S.

3. Bastin S, Bird H, Gamble G, Cundy T. Paget's disease of bone--becoming a rarity? Rheumatology. 2009. 48:1232–1235.

4. Chung YG, Kang YK, Rhee SK, et al. Skeletal manifestation of Paget's disease in Korean. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002. 37:649–653.

5. Yune SH, Lee KJ, Lee JK, Lee DI, Hwang DS. Paget's disease of bone - 1 case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1982. 17:1227–1232.
6. Kim KH, Cho JL, Kim TS, Kim JS. Paget's disease of bone with pathologic fracture of the femur - A case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1989. 24:316–321.

7. Choi WS, Baik CH, Koh DH. Paget's disease of bone - One case report -. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1991. 26:970–974.
8. Sawardekar UG, Nadimpalli SP, Weisenberg E, Kranzler L. An unusual presentation of Paget disease: pathological fracture of the odontoid. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008. 9:343–346.

9. Kim YU, Jeon YB, Oh IS, Seo KW, Baik IK. Paget's disease - case report -. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1983. 18:592–595.
10. Canale ST, Beaty JH. Cambell's operative orthopaedics. 2007. Vol. 1:11th ed. St. Louise: Mosby;388–389.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download