Abstract
Purpose
There are numerous opinions about the methods and usefulness of minimizing leg length discrepancies after hip arthroplasty. In this study, we tried to evaluate the usefulness of an intraoperative x-ray in addition to preoperative templating for minimizing leg length discrepancy.
Materials and Methods
We reviewed pre- and post-operative pelvis AP x-rays of 46 patients who underwent hip arthroplasty due to a traumatic femoral neck fracture or intertrochanteric fracture between May 2008 and February 2009. A leg length discrepancy is the difference in vertical distance between a horizontal line drawn along the bottom of the ischial tuberosities and the most inferior points of the lesser trochanter. It was measured in a pelvis AP x-ray. In each case, pre-operative templating was performed and an intraoperative pelvis AP x-ray was taken again to assess the accuracy of preoperative planning. Implant positions were readjusted when necessary.
Figures and Tables
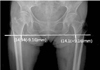 | Fig. 1Method for evaluation of limb length. A line connection the bottom of the ischial tuberosities was drawn, and the differences in limb length were measured using the relationship between this line and the most inferior point of the lesser trochanter. Leg length discrepancy was -9.16 mm. |
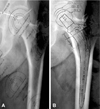 | Fig. 2Preoperative anteroposterior pelvis x-rays of right hip arthroplasty show (A) cup component templated (B) femoral component templated. |
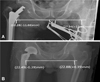 | Fig. 3The patient is a 85-year-old male with right femoral neck fracture. (A) Intraoperative anteroposterior pelvis x-rays of left bipolar hip arthroplasty shows shortened right lower extremity. LLD was 11.6 mm. It can be corrected with a longer femoral head. (B) Postoperative anteroposterior pelvis x-rays shows restoration of leg lengths. LLD was 0.3 mm. |
References
1. White TO, Dougall TW. Arthroplasty of the hip. Leg length is not important. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:335–338.
2. Friberg O. Clinical symptoms and biomechanics of lumbar spine and hip joint in leg length inequality. Spine. 1983. 8:643–651.

3. Bose WJ. Accurate limb-length equalization during total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2000. 23:433–436.
4. Woolson ST, Hartford JM, Sawyer A. Results of a method of leg-length equalization for patients undergoing primary total hip replacement. J Arthroplasty. 1999. 14:159–164.

5. Turula KB, Friberg O, Lindholm TS, Tallroth K, Vankka E. Leg length inequality after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 202:163–168.

6. Edeen J, Sharkey PF, Alexander AH. Clinical significance of leg-length inequality after total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop. 1995. 24:347–351.
7. Ranawat CS, Rodriguez JA. Functional leg-length inequality following total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1997. 12:359–364.

8. Hofmann AA, Skrzynski MC. Leg-length inequality and nerve palsy in total hip arthroplasty: a lawyer awaits! Orthopedics. 2000. 23:943–944.

9. Goodman SB, Huene DS, Imrie S. Preoperative templating for the equalization of leg lengths in total hip arthroplasty. Contemp Orthop. 1992. 24:703–710.
10. Woolson ST, Hartford JM, Sawyer A. Results of a method of leg-length equalization for patients undergoing primary total hip replacement. J Arthroplasty. 1999. 14:159–164.

11. Takigami I, Itokazu M, Itoh Y, Matsumoto K, Yamamoto T, Shimizu K. Limb-length measurement in total hip arthroplasty using a calipers dual pin retractor. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008. 66:107–110.
12. McGee HM, Scott JH. A simple method of obtaining equal leg length in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. 194:269–270.

13. Woolson ST, Harris WH. A method of intraoperative limb length measurement in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. 194:207–210.

14. Ranawat CS, Rao RR, Rodriquez JA, Bhende HS. Correction of limb-length inequality during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001. 16:715–720.

15. Hofmann AA, Bolognesi M, Lahav A, Kurtin S. Minimizing leg-length inequality in total hip arthroplasty: use of preoperative templating and an intraoperative x-ray. Am J Orthop. 2008. 37:18–23.
16. Canale ST. Campbell's Operative Orthopedics. 2008. 11th ed. New York: Mosby;338–342.
17. Seo GT. Leg length discrepancy in total hip arthroplasty. J Korean Hip Soc. 2002. 14:308–311.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download