Abstract
Heterotopic ossification (HO) is a frequent complication associated with spinal cord injury and can lead to significant problems during rehabilitation. Surgical resection of HO could be applied to patients who do not respond to conservative treatment. To reduce the risk of recurrence after the operation, radiation therapy and NSAID or bisphosphonate administration may be utilized. We report the case of a 48-year-old male with a T3-sparing spinal cord injury who underwent successful treatment of immature HO in the iliacus muscle with a combination of surgical resection, radiation therapy, and NSAID administration.
Figures and Tables
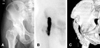 | Fig. 1(A) There is increased irregular and faint change of density on pelvis AP simple X-ray at intertrochanter area. (B) Increasing tubular shape density of isotope from internal area of anterior superior iliac spine to lower area of lesser trochanter by Bone scan. (C) From oblique 3D image, there is Immature heterotopic ossification without the invasion of hip joint area. |
References
1. Garland DE. A clinical perspective on common forms of acquired heterotopic ossification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 263:13–29.

2. Han DY, Choi CH, Lee YT. Surgical resection of heterotopic ossification in the brain-injured. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1993. 28:1836–1841.

3. Jamil F, Subbarao JV, Banaovac K, El Masry WS, Bergman SB. Management of immature heterotopic ossification (HO) of the hip. Spinal Cord. 2002. 40:388–395.

4. Ko HS, Lee WC, Ko KH, Lee C, Nam KH, Rha JD. Heterotopic ossification around the hip in an adult spastic patient. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2001. 36:531–536.

5. Garland DE, Alday B, Venos KG, Vogt JC. Diphosphonate treatment for heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injury patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983. 176:197–200.

6. Carlier RY, Safa DM, Parva P, et al. Ankylosing neurogenic myositis ossificans of the hip. An enhanced volumetric CT study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:301–305.
7. Stover SL, Neimann KM, Tulloss JR. Experience with surgical resection of heterotopic bone in spinal cord injury patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 263:71–77.

8. Freebourn TM, Barber DB, Able AC. The treatment of immature heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injury with combination surgery, radiation therapy and NSAID. Spinal Cord. 1999. 37:50–53.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download