Abstract
Purpose
This study evaluated the results of acetabular medial wall osteotomy to reconstruct the acetabulum in dysplastic hip during total hip arthroplasty.
Materials and Methods
We clinically and radiologically evaluated 30 hips of 30 patients with secondary hip osteoarthritis caused by congenital hip dislocation or acetabular dysplasia who underwent total hip arthroplasty (THA) between March 1999 and October 2002. The average age of subjects was 46.5 years(17 to 73 years), and the mean follow-up period was 5 years(5.3 to 8.7 years). In 26 cases, a cementless hemispherical acetabular cup was inserted in the true acetabulum; in 4 cases a reinforced ring was inserted. Only 2 hips needed structural bone grafting.
Results
The average Harris hip score improved from 56.3 points preoperatively to 93.2 points at the last follow up. Radiographic analysis revealed no aseptic loosening or radiolucent line, and showed stable bony fixation at the true acetabulum. The mean thickness of the medial acetabular wall postoperative was 20.5 mm(10 to 36 mm). Bone union of the medial wall was observed at a mean of four months postoperatively.
Figures and Tables
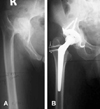 | Fig. 1(A) Preoperative radiograph of a 28-year-old man shows Craw type III dysplasia. (B) 11 month postoperative radiograph shows the medialized the rotating hip center with acetabular reinforcement ring with hook. |
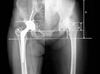 | Fig. 2The radiographic measurements included (A) pelvic height, (B) height of the true acetabulum, (C) proximal migration of the lesser trochanter, (D) Ranawat triangle, (E) thickness of the medial wall, (F) theta angle, (G) medial femoral-neck junction, (H) position of the cup medial to the Ranawat triangle, (I) relationship of the cup to the superior border of the Ranawat triangle, and (J) position of the cup medial to the kohler line. |
References
1. Charnley J, Feagin JA. Low-friction arthroplasty in congenital subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973. 91:98–113.

2. Linde F, Jensen J, Pilgaard S. Charnley arthroplasty in osteoarthritis secondary to congenital dislocation or subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 227:164–171.

3. Gill TJ, Sledge JB, Müller ME. Total hip arthroplasty with use of an acetabular reinforcement ring in patients who have congenital dysplasia of the hip. Results at five to fifteen years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:969–979.

4. Harris WH, Crothers O, Oh I. Total hip replacement and femoral-head bone-grafting for severe acetabular deficiency in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:752–759.

5. Inao S, Matsuno T. Cemented total hip arthroplasty with autogenous acetabular bone grafting for hips with developmental dysplasia in adults: the results at a minimum of ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000. 82:375–377.
6. Kobayashi S, Saito N, Nawata M, Horiuchi H, Iorio R, Takaoka K. Total hip arthroplasty with bulk femoral head autograft for acetabular reconstruction in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85:615–621.

7. Hess WE, Umber JS. Total hip arthroplasty in chronically dislocated hips. Follow-up study on the protrusio socket technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978. 60:948–954.

8. Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS. Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:15–23.

10. Ranawat CS, Dorr LD, Inglis AE. Total hip arthroplasty in protrusio acetabuli of rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980. 62:1059–1065.

11. Wilson PD Jr, Amstutz HC, Czerniecki A, Salvati EA, Mendes DG. Total hip replacement with fixation by acrylic cement. A preliminary study of 100 consecutive McKee-Farrar prosthetic replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972. 54:207–236.
12. Massin P, Schmidt L, Engh CA. Evaluation of cementless acetabular component migration. An experimental study. J Arthroplasty. 1989. 4:245–251.
13. DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 121:20–32.

14. Engh CA, Massin P, Suthers KE. Roentgenographic assessment of the biologic fixation of porous-surfaced femoral components. Clin Orhop Relat Res. 1990. 257:107–128.

15. Jasty M, Freiberg AA. The use of a high-hip center in revision total hip arthroplasty. Semin Arthroplasty. 1995. 6:103–108.
16. Johnston RC, Brand RA, Crowninshield RD. Reconstruction of the hip. A mathematical approach to determine optimum geometric relationships. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:639–652.

17. Stans AA, Pagnano MW, Shaughnessy WJ, Hanssen AD. Results of total hip arthroplasty for Crowe Type III developmental hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. 348:149–157.

18. McQueary FG, Johnston RC. Coxarthrosis after congenital dysplasia. Treatment by total hip arthroplasty without acetabular bone-grafting. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:1140–1144.

19. Dunn HK, Hess WE. Total hip reconstruction in chronically dislocated hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976. 58:838–845.

20. Dorr LD, Tawakkol S, Moorthy M, Long W, Wan Z. Medial protrusio technique for placement of a porous-coated, hemispherical acetabular component without cement in a total hip arthroplasty in patients who have acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81:83–92.

21. Lian YY, Yoo MC, Pei FX, Cho YJ, Cheng JQ, Chun SW. Circumferential osteotomy of the medial acetabular wall in total hip replacement for the late sequelae of childhood septic arthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007. 89:1149–1154.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download