Abstract
Purpose
This study examined the clinical course of subtrochanteric fractures of the femur as well as the risk factors of complications.
Materials and Methods
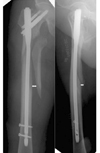
A retrospective study was performed on 56 patients with femoral subtrochanteric fractures who were treated at our hospital from 2004 to 2008. Risk factors, such as the type of fracture, type of implant, soft tissue dissection at the fracture site, communition of the medial cortex and degree of fracture displacement after the reduction, were compared to determine their effect on the rate of complications, such as nonunion and implant failure. Open reduction with a soft tissue dissection at the fracture site was performed in 34 cases, and a closed reduction was performed in 22 cases. Thirty five cases had medial cortex communition and 21 cases did not.
Results
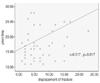
There were 8 cases of nonunion(14.3%). There was a positive correlation between the degree of fracture displacement after the reduction and the union time (P=0.017). The union time was longer when there was communition of the medial cortex. A subtrochanteric fracture using an open reduction tended to have a long union time but this was not statistically significant. There was no correlation between the type of implant and union time.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Nungu KS, Olerud C, Rehnberg L. Treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with the AO dynamic condylar screw. Injury. 1993. 24:90–92.

2. Rohilla R, Singh R, Magu NK, Siwach RC, Sangwan SS. Mini-incision dynamic condylar screw fixation for comminuted subtrochanteric hip fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2008. 16:150–155.

3. Bergman GD, Winquist RA, Mayo KA, Hansen ST Jr. Subtrochanteric fracture of the femur. Fixation using the Zickel nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987. 69:1032–1040.
4. Kinast C, Bolhofner BR, Mast JW, Ganz R. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Results of treatment with the 95 degrees condylar blade-plate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. 238:122–130.
5. Kyle RF, Cabanela ME, Russell TA, et al. Fractures of the proximal part of the femur. Instr Course Lect. 1995. 44:227–253.

6. Siebenrock KA, Muller U, Ganz R. Indirect reduction with a condylar blade plate for osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl. C7–C15.

7. Parker MJ, Dutta BK, Sivaji C, Pryor GA. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Injury. 1997. 28:91–95.

8. Sims SH. Subtrochanteric femur fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002. 33:113–126. vii.
9. Vanderschot P, Vanderspeeten K, Verheyen L, Broos P. A review on 161 subtrochanteric fractures--risk factors influencing outcome: age, fracture pattern and fracture level. Unfallchirurg. 1995. 98:265–271.
10. Asher MA, Tippett JW, Rockwood CA, Zilber S. Compression fixation of subtrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 117:202–208.

11. Trafton PG. Subtrochanteric-intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987. 18:59–71.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download