Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
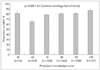 | Fig. 1GBSP rate according to physician's knowledge level. The number (n) in the parenthesis indicates the number of patients treated by physicians with each knowledge score. Error bars indicate standard errors. GBSP: guideline-based statin prescription. |
Table 2

*Risk factor: hypertension, current smoking, familial history of premature CHD, HDL-C<40 mg/dL, age, †CHD equivalent: >50% carotid stenosis, peripheral arterial disease, abdominal aortic aneurysm, or DM.
CE: cardioembolism, CHD: coronary heart disease, DM: diabetes mellitus, GBSP: guideline-based statin prescription, HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LAA: large-artery atherosclerosis, LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, OD: other determined etiology, SVO: small-vessel occlusion, TIA: transient ischemic attack, TOAST: Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment, UD: undetermined etiology.
Table 3

Data are number of patients (%) or mean±SD values.
*Multiple responses were made, **Values of p were obtained using Student's t-test or chi-square test, unless otherwise specified, †By Fisher's exact test, ‡Physicians with higher preference for guidelines indicate those who had a score greater than the median value on rating of responses to 21 questions in physicians' attitude to guidelines.
HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Table 4

Data are number of patients (%) or mean±SD values.
*p-values for Student's t-test or chi-square test as appropriate, comparing the GBSP group with the non-GBSP group, unless otherwise specified, †Fisher's exact test, ‡Geometric mean and SD, and logarithmically transformed values were used to compare the two groups. AF: atrial fibrillation, BMI: body mass index, BP: blood pressure, CE: cardioembolism, CHD: coronary heart disease, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, DM: diabetes mellitus, GBSP: guideline-based statin prescription, HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LAA: large-artery atherosclerosis, LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, OD: other determined etiology, PAD: peripheral arterial disease, SBP: systolic blood pressure, SVO: small-vessel occlusion, TG: triglyceride, TIA: transient ischemic attack, UD: undetermined etiology.
Table 5
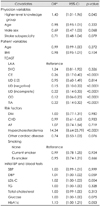
*By GEE analysis, which accounts for a multilevel structure of variables comprising the physicians' and associated patient levels. AF: atrial fibrillation, BMI: body mass index, BP: blood pressure, CE: cardioembolism, CHD: coronary heart disease, CI: confidence interval, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, DM: diabetes mellitus, GBSP: guideline-based statin prescription, GEE: generalized estimating equation, LAA: large-artery atherosclerosis, LDL-C: lowdensity lipoprotein cholesterol, OD: other determined etiology, OR: odds ratio, SBP: systolic blood pressure, SVO: small-vessel occlusion, TG: triglyceride, TIA: transient ischemic attack, TOAST: Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment, UD: undetermined etiology, UD: undetermined etiology.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download