Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Demographic and clinical data for the study patients with temporal lobe epilepsy

All neuropsychological scores are reported as raw scores. The word list included 16 items in CVLT and 15 items in AVLT, and was performed five times with immediate, free recall after each presentation. Therefore, the maximum immediate recall points for CVLT and AVLT were 80 and 75, respectively.
*poor performance on each test, which was determined by age- and education-matched standard scores, †total recall score of 5 trials per maximum point, ‡true positive/false positive.
A: ambidextrous, ATL-AH: anterior temporal lobectomy with amygdalo-hippocampectomy, D: dominant hemisphere, F: female, HA: hippocampal atrophy, IQ: intelligence quotient, K-AVLT: Korean-Auditory Verbal Learning Test, K-CVLT: Korean-California Verbal Learning Test, K-WAIS: Korean-Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, L: left, M: male, MRI: magnetic resonance imaging, ND: non-dominant hemisphere, R: right, RCFT: Rey Complex Figure Test.
Table 2
Test scores obtained before and after temporal lobectomy

Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Data present mean score (% correct) of each test±standard deviation.
CAP: central auditory processing, DTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the dominant hemisphere, LTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the left hemisphere, NDTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the non-dominant hemisphere, RTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the right hemisphere.
Table 3
Frequencies of patients with CAPD before and after surgery and associations between CAPD and surgery

With respect to all CAP tasks, associations between CAPD and temporal lobectomy were considered to be not statistically significant among all patients and patient subgroups (DTLD, NDTLD, RTLE, and LTLE) by Fisher's exact test; two-tailed p-values were >0.99*, 0.358†, 0.755‡, 0.547§, 0.640∥, 0.667¶, 0.684**, and 0.628††. Data present the ratio of the patient with CAPD, % (number of patients with abnormal score/total).
CAP: central auditory processing, CAPD: central auditory processing disorder, DTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the dominant hemisphere, LTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the left hemisphere, NDTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the non-dominant hemisphere, RTLE: patients with temporal lobectomy on the right hemisphere.
Table 4
Associations between postoperative worsening of central auditory processing and parameters (dominant vs. non-dominant, left vs. right, verbal IQ, and non-verbal IQ) by logistic regression tests
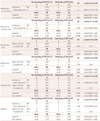
*statistically significant p value, which indicates that patients who underwent operation of the dominant hemisphere have the possibility of experiencing postoperative worsening of CAP in a non-dominant side dichotic test rather than those with non-dominant hemisphere.
CAP:central auditory processing, CI: confidence interval, D: dominant hemisphere, IQ: intelligence quotient, ND: non-dominant hemisphere, OR: odds ratio, SD: standard deviation.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download