Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
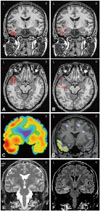 | Fig. 1EEG and MEG dipole source analysis of patient #14 who had left temporal lobe epilepsy. A: EEG dipoles [high-pass filter (HPF)=3 Hz, goodness of fit (GOF) levels ≥70%] were localized in left basal and anterior temporal regions. B: MEG dipoles (HPF=3 Hz, GOF levels ≥70%) were localized in left anterior to middle temporal regions. C: Ictal SPECT showed left temporal hyperperfusion. D: SISCOM showed left anterior to mid temporal hyperperfusion. (E) T2-weighted MRI and (F) FLAIR MRI showed left hippocampal sclerosis. L: left, R: right. |
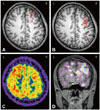 | Fig. 2EEG and MEG dipole source analysis of patient #4 who had right frontocentral lobe epilepsy. A: EEG dipoles [high-pass filter (HPF)=3 Hz, goodness of fit (GOF) levels ≥70%] were localized in right frontal lobe. B: MEG dipoles (HPF=3 Hz, GOF levels ≥70%) were localized in right frontal and parietal regions. C: FDG-PET showed hypometabolism in right frontoparietal cortex. D: SISCOM showed ictal hyperperfusion in the right dorsolateral and medial frontal cortices. L: left, R: right. |
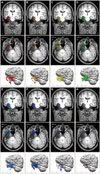 | Fig. 3Different high-pass filter (HPF) setting. The 64 individual dipoles of patient #26 who had left mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. EEG dipoles were analyzed in preoperative boundary element method (BEM) head model in different HPF settings and superimposed on the postoperative MRI. HPF settings were as follow: (A) 0.5 Hz, (B) 1Hz, (C) 2 Hz, (D) 3 Hz, (E) 4 Hz, (F) 5 Hz, and (G) 6 Hz. Low pass filter settings were all 100 Hz. The H shows averaged dipoles of A-G with the matched color. Circles surrounding each dipole indicate confidence ellipsoid range. Each color indicates different HPF setting (red: 0.5 Hz, orange: 1 Hz, yellow: 2 Hz, green: 3 Hz, bright blue: 4 Hz, blue: 5 Hz, violet: 6 Hz). L: left, R: right. |
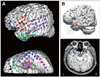 | Fig. 4The comparison between ECoG and EEG dipoles of patient #26. The patient had left mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. A: Intracranial EEG electrode locations were plotted on the patient's three dimensional MRI. Red circle indicates the electrode location of ictal ECoG onset, and bright blue circle indicates the location of interictal spikes frequently recorded on ECoG. B: EEG dipoles of averaged 64 spikes with different high-pass filter settings: red: 0.5 Hz, orange: 1 Hz, yellow: 2 Hz, green: 3 Hz, bright blue: 4 Hz, blue: 5 Hz, violet: 6 Hz. The circle around each dipole indicates confidence ellipsoid range. L: left, R: right. |
Table 1

*Unable to analyze by artifact.
AG: amygdala, AH: amygdalohippocampectomy, ant: anterior, ATL: anterior temporal lobectomy, bas: basal, Bi: bilateral, C: central, CD: cortical dysplasia, CP: centroparietal, CPLE: centroparietal lobe epilepsy, dl: dorsolateral, DNET: dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor, ESI: EEG source imaging, F: frontal, FC: frontocentral, FCT: frontocentrotemporal, FT: frontotemporal, FTLE: frontotemporal lobe epilepsy, HC: hippocampus, HS: hippocampal sclerosis, hyper: hyperperfusion, IED: interictal epileptiform discharge, inf: inferior, L: left, lat: lateral, med: medial, MEG: magnetoencephalography, mes: mesial, MSI: MEG source imaging, mid: middle, MTLE: mesial TLE, NP: not performed, O: occipital, Oper: operculum, OF: orbitofrontal, P: parietal, post: posterior, R: right, R/O: rule out, SISCOM: Subtraction Ictal SPECT coregistered to MRI, sup: superior, T: temporal, TLE: temporal lobe epilepsy, TOLE: temporo-occipital lobe epilepsy, WNL: within normal limit.
Table 2

AG: amygdala, AH: amygdalohippocampectomy, ant: anterior, ATL: anterior temporal lobectomy, bas: basal, Bi: bilateral, ECoG: electrocorticography, ESI: EEG source imaging, F: frontal, FCD: focal cortical dysplasia, HC: hippocampus, HS: hippocampal sclerosis, F/U: follow up, inf: inferior, L: left, lat: lateral, med: medial, mes: mesial, mid: middle, mo: month, MSI: MEG source imaging, NP: not performed, OF: orbitofrontal, P: parietal, post: posterior, R: right, S/O: suggestive of, sup: superior, T: temporal, yr: year.
Table 3





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download