Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
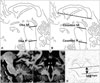 | Fig. 1Schematic diagrams of midsagittal (A and B) and axial (D) images of the brain and parasagittal and coronal (C) T1-weighted volumetric magnetic resonance (MR) images. A: The midbrain area (Oba M) and the pons area (Oba P) were measured using a standard line as described by Oba et al.6 B: The midbrain area (Cosottini M) and the pons area (Cosottini P) were measured using a standard line as described by Cosottini et al.7 C: The MR parkinsonism index (MRPI) was measured using a modified version of Quattrone's method (mMRPI). The middle cerebellar peduncle length measured in a parasagittal image is marked with an asterisk (*). Bilateral superior cerebellar peduncle lengths are marked by arrows (↓). D: The axial length of the midbrain tegmentum, adjusted according to the anterior commissure-posterior commissure length (MBTegm), was measured from the anterior interpeduncular fossa to the center of the cerebral aqueduct at the plane of the mid-mammillary body. Lines between the midbrain and the pons and between the pons and medulla oblongata represent the lower borders of the midbrain and pons areas, respectively. |
 | Fig. 2Receiver operating curve analyses of the brain structure measurements for differentiating progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) from idiopathic Parkinson's disease (IPD). A: PSP vs. IPD, not age matched (n=111). B: PSP vs. IPD, age-matched. C: Probable PSP vs. IPD. Cosottini M/P: ratio of the midbrain area to the pons area in the midsagittal plane, measured by Cosottini's method, Oba M/P: ratio of the midbrain area to the pons area in the midsagittal plane, measured by Oba's method. |
Table 1
Demographic and clinical data in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy

*Numbers of missing data: 7 (8.54%) in the IPD group and 5 (17.24%) in the PSP group.
IPD: idiopathic Parkinson's disease, UK Brain Bank criteria, MMSE: Mini-Mental Status Examination, NS: not significant, PSP: progressive supranuclear palsy, clinical diagnostic criteria of the Society for PSP of the National Institute of Neurological Disease and Stroke, UPDRS: Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale.
Table 2
Receiver operating curve analysis of brain structure measurements for distinguishing progressive supranuclear palsy from idiopathic Parkinson's disease

AUC: area under the receiver operating curve, Cosottini M/P: ratio of the midbrain area to the pons area in the midsagittal plane, measured by Cosottini's method, IPD: idiopathic Parkinson's disease, MBTegm: axial diameter of the midbrain tegmentum adjusted by AC-PC length, mMRPI: modified Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index, NPV: negative predictive value, Oba M/P: ratio of the midbrain area to the pons area in the midsagittal plane, measured by Oba's method, PPV: positive predictive value, PSP: progressive supranuclear palsy, SE: standard error.
Table 3
Comparison of receiver operating curves for different measurements (Oba, Cosottini, mMRPI, and MBTegm) of brain structures

AC-PC: distance from the anterior commissure to the posterior commissure, Cosottini M/P: ratio of the midbrain area to the pons area in the midsagittal plane, measured by Cosottini's method, IPD: idiopathic Parkinson's disease, UK brain bank criteria, MBTegm: axial diameter of the midbrain tegmentum adjusted by AC-PC length, mMRPI: modified Magnetic Resonance Parkinsonism Index, Oba M/P: ratio of the midbrain area to the pons area in the midsagittal plane, measured by Oba's method, PSP: progressive supranuclear palsy, clinical diagnostic criteria of the National Institute of Neurological Disease and Stroke.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download