Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Figures and Tables
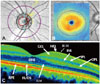 | Fig. 1Optical coherence tomography (OCT) measurements in a healthy subject. A: Peripapillary measures centered on the optic disc. B: Macular measures centered on the fovea. C: High-resolution OCT image of the retinal microstructure. ELM: external limiting membrane, GCL: ganglion cell layer, ILM: inner limiting membrane, INL: inner nuclear layer, IPL: inner plexiform layer, IS/OS: inner/outer photoreceptor segments, NFL: nerve fiber layer, ONL: outer nuclear layer, OPL: outer plexiform layer, RPE: retinal pigment epithelium. |
Table 1
Study group characteristics

Table 2A
Results of optical coherence tomography (OCT) measures in healthy controls (HCs) and patients with multiple sclerosis (MS)

Data are mean (SD) values.
*p<0.01 using t-test to compare values between HCs and all MS patients, †p<0.01 using ANOVA multiple comparison adjusting for age to compare values from HCs, RRMS, and BMS.
AMT: average macular thickness, BMS: benign multiple sclerosis, CMT: central macular thickness, GCL-IPL: ganglion cell layer+inner plexiform layer, RNFL: retinal nerve fiber layer, RRMS: relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, TMV: total macular volume.
Table 2B
Results of OCT measures in RRMS and BMS with optic neuritis (ON)

Data are mean (SD) values.
*p<0.01 using t-test adjusting for age to compare values between HCs and all ON-affected MS patients, †p<0.01 using ANOVA multiple comparison adjusting for age to compare values from HCs and ON-affected RRMS and BMS.
AMT: average macular thickness, BMS: benign multiple sclerosis, CMT: central macular thickness, GCL-IPL: ganglion cell layer+inner plexiform layer, HCs: healthy controls, MS: multiple sclerosis, OCT: optical coherence tomography, RNFL: retinal nerve fiber layer, RRMS: relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, TMV: total macular volume.
Table 2C
Results of OCT measures in RRMS and BMS without ON

Data are mean (SD) values.
*p<0.01 using t-test adjusting for age to compare OCT measures between HCs and all non-ON MS patients, †p<0.05 using ANOVA multiple comparison adjusting for age to compare values from HCs, non-ON RRMS, and non-ON BMS.
AMT: average macular thickness, BMS: benign multiple sclerosis, CMT: central macular thickness, GCL-IPL: ganglion cell layer+inner plexiform layer, HCs: healthy controls, MS: multiple sclerosis, Non-ON BMS: BMS without ON, Non-ON MS: all MS without ON, non-ON RRMS: RRMS without ON, OCT: optical coherence tomography, ON: optic neuritis, RNFL: retinal nerve fiber layer, RRMS: relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, TMV: total macular volume.
Table 3
Association between disease duration with RNFL thickness and GCL-IPL in non-ON RRMS and non-ON BMS

| RNFL thickness change (µm/year) | GCL-IPL thickness change (µm/year) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SE | p | Mean | SE | p | |
| Non-ON RRMS (41 eyes) | -0.54 | 0.24 | <0.05 | -0.43 | 0.21 | <0.05 |
| Non-ON BMS (16 eyes) | -0.11 | 0.27 | 0.76 | -0.24 | 0.24 | 0.32 |
Mean, SE, and p values are from multivariable linear regression models.
BMS: benign multiple sclerosis, GCL-IPL: ganglion cell layer+inner plexiform layer, non-ON BMS: BMS without ON, non-ON RRMS: RRMS without ON, ON: optic neuritis, RNFL: retinal nerve fiber layer, RRMS: relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, SE: standard error.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download