Abstract
Background
Objective
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Direct binding of alopecia areata antibodies to reactive oxygen species-modified superoxide dismutase (ROS-SOD). (A) Levels of circulating antibodies in alopecia areata (AA) patients, binding to ROS-SOD and native SOD (nSOD). Anti-ROS-SOD antibodies versus anti-nSOD antibodies, p<0.01 in AA patients. (B) Levels of circulating antibodies in normal human (NH) subjects binding to ROS-SOD and nSOD. Anti-ROS-SOD antibodies versus anti-nSOD antibodies, p>0.05 in NH subjects. Microtiter plates were individually coated with ROS-SOD (10 µg/ml) and nSOD (10 µg/ml). OD: optical density or absorbance. |
 | Fig. 2Affinity-purification of immunoglobulin G (IgG). Elution profile of IgG on a Protein A agarose affinity column. |
 | Fig. 3Binding of Protein A-purified alopecia areata (AA) immunoglobulin G (IgG) to reactive oxygen species-modified superoxide dismutase (ROS-SOD) and native superoxide dismutase. (A) Binding characteristic of AA-IgG and normal human (NH)-IgG to ROS-SOD. (B) Binding characteristics of AA-IgG and NH-IgG to native SOD (nSOD). IgG from 12 AA patients and 12 NH subjects were analyzed by direct-binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Microtiter plates were individually coated with ROS-SOD (10 µg/ml) and nSOD (10 µg/ml). For ROS-SOD: AA patients vs. #p<0.01; For nSOD: AA patients vs. NH subjects, p>0.05. OD: optical density or absorbance. |
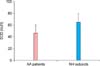 | Fig. 4Disease-related decrease in superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in patients with alopecia areata (AA). Serum levels of SOD activity in AA patients (n=25) compared with normal human (NH) subjects (n=26). Each histogram represents the mean±standard error of the mean. SOD activity in AA patients vs. SOD activity in NH subjects, p<0.05. |
Table 1

Microtitre plates were coated with ROS-SOD (10 µg/ml) and nSOD (10 µg/ml). Inhibitors concentration was 20 µg/ml. AA-IgG: ROS-SOD vs. nSOD, p<0.0001; NH-IgG: ROS-SOD vs. nSOD, p<>0.05. AA-IgG: alopecia areata-immunoglobin G, NH-IgG: normal humans-immunoglobin G, ROS-SOD: reactive oxygen species-modified superoxide dismutase, nSOD: native SOD, SD: standard deviation.
Table 2

ELISA plates were coated with ROS-SOD (10 µg/ml) and nSOD (10 µg/ml). Inhibitors concentration was 20 µg/ml. *p<0.001 versus direct binding of AU-IgG with nSOD; †p<0.05 versus direct binding of AU-IgG with ROS-SOD; ‡p<0.0001 versus direct binding of AU-IgG with ROS-SOD; §p<0.0001 versus competitive inhibition of AU-IgG with nSOD; ∥ p<0.05 versus competitive inhibition of AU-IgG with ROS-SOD; ¶p<0.0001 versus competitive inhibition of AU-IgG with ROS-SOD. IgG: immunoglobulin G, ROS-SOD: reactive oxygen species-modified superoxide dismutase, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, nSOD: native SOD dismutase, AU: alopecia universalis, AAP: alopecia areata patchy persistent, NH: normal human, n: number of samples tested.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download