Abstract
Pityriasis versicolor is a superficial infection of the stratum corneum, which is caused by the Malassezia species. Tge Malassezia species consist of 12 subspecies, including M. furfur, M. pachydermatis, M. symphodialis and M. globasa. The Malassezia species are classified as a normal flora, particularly in the sebum rich areas of the skin, and they convert from saprophytic yeast to parasitic mycelial morpholgic form to cause clinical disease. But majorities of their distributions are in the upper back, the neck, the thighs, and the forearm, and not in the penis. It is well known that the renal transplant patients, who take immunosuppressive agents, have impairment in the protective cell mediated immunity. Thus, they are more susceptible to infectious diseases, such as a fungal infection. Therefore, clinical manifestations show higher incidence of disease, but they mostly occur in an expected distribution. We here report a case of pityriasis versicolor in a renal transplant recipient on penile shaft, which is an unusual area.
Renal transplant recipients, who take immunosuppressive therapy, are much more susceptible to numerous infectious diseases, including a fungal infection, such as pityriasis versicolor. Even if current studies showed high colonization rate of the Malassezia species, as a normal flora on the preputial area up to 49.2%, there are few reports of pityriasis versicolor on penile shaft area. We describe a case of pityriasis versicolor on a penile shaft in a renal transplant recipient who was successfully treated with topical fluconazole and isoconazole.
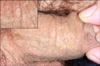
A 29-year-old man with several hypopigmented scaly macules on the penile shaft visited our clinic. He was treated as tinea versicolor on trunk 3 months ago, and there were still several hypopigmented macules on the upper trunk. According to the present medical records, he had been receiving immunosuppresive therapy with tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil and prednisolone for 1 year due to renal transplantation. On physical examination, there were several hypopigmented scaly macules on circumcised penile shaft (Fig. 1). These macules had developed over the course of 1 month, and the number of lesions had increased without pruritus.
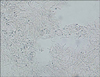
Wood lamp examination on the macules demonstrated a yellowish to greenish florescence. Scales obtained by scraping the lesion with KOH 10% preparation showed clusters of yeast and short mycelia filaments. It showed typical finding of spaghetti and meatball appearance, which is confirmative as the diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor (Fig. 2). The patient was treated with topical fluconazole and isoconazole and demonstrated good clinical results.
Pityriasis versicolor is a superficial infection of the stratum corneum, caused by the Malassezia species. The Malassezia species consist of 12 subspecies, including M. furfur, M. pachydermatis, M. symphodialis and M. globasa1. Each species can be isolated and cultured by modified Dixon and Leeming-Notman agar. Malassezia species are classified as a normal flora, particularly in the sebum rich areas of the skin and it converts from the saprophytic yeast to parasitic mycelial morpholgic form to make clinical disease. Mycelian transitions are associated with warm, humid environment, systemic corticosteroid, oral contraceptive use, hyperhidrosis and immunosuppression, as in our case. Clinically, chest, back, abdomen and proximal extremities are the commonly affected areas manifested with dust-like or furfuraceous scaly macules with various colors from white to reddish brown. White colors are known to be associated with pityricitrin, which vies a specific compound absorbing ultraviolet light synthesized by Malassezia. Other metabolites, such as azelaic acid, lipoxygenase and tryptophan metabolites are also associated by the inhibition tyrosinase and injuring melanocytes2.
Malassezia infection in the genital area is uncommon, despite its colonization as normal flora in the penis. Its colonization rates are quiet high, as 49.2% of the population, but pityriasis versicolor on the penis is rare, which is only reported in several cases (Table 1)3-6. Further, inverse tinea versicolor, which has manifestation limited to the groin and axillae or perineum alone, is distinguished from our case due to the history of its trunk involvement.
In a case control study of superficial fungal infection, in renal transplant recipients, showed an increased incidence of superficial fungal infection, and the most common infection was pityriasis versicolor, as same as in our case7. Also, there are several reports of increased colonization rate of Mallassezia species, of up to 69% in renal transplant patients8. But majorities of their distributions were in the upper back (96%), the neck (25%), the thighs (6%), and the forearm (2%), not in the penis6,9. Since they live on the skin as commensals and also as pathogens, incidence of pityriasis versicolor on renal transplant patients is increased. They suppress the host cell's inflammatory response by an inhibition of interleukin (IL)1α, IL6 and TNFα in yeast state as a normal flora10. When acting as pathogen, it converts to mycelin and initiates the cell mediated immune response, therefore, inflammation begins. In another study, patients with pityriasis versicolor had a lack of increased responses in its active disease state, which means that the protective cell mediated immune responses were inadequate2. In that manner, renal transplant patients have impairment in the protective cell mediated immunity that they are more susceptible for Malassezia's colonization and its conversion.
In a case control study, azathioprine and cyclosporine were suggested as independent risk factors7. But in our case, we administrated tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil and prednisolone. Increased incidence of pityriasis versicolor in patients on corticosteroid therapy is well known11. But interestingly, there is a report that tacrolimus has antifungal effect on half of the Malassezia species. Because it targets calcineurin as it causes toxic effect to the pathogens12. On the other hand, combination regimen with mycophenolate mofetil reports higher rate of fungal infection than with azathioprine13.
In our case, immunosuppression, due to renal transplantation, is believed to be a predisposing factor for pityriasis versicolor. Despite an increased incidence of infection in immunosuppresive state, its involvement on penile shaft is still uncommon.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2008. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1822–1830.
2. Saadatzadeh MR, Ashbee HR, Cunliffe WJ, Ingham E. Cell-mediated immunity to the mycelial phase of Malassezia spp. in patients with pityriasis versicolor and controls. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 144:77–84.

6. Khaddar RK, Cherif F, Ben Hadid R, Mokni M, Ben Osman A. Penile shaft involvement in pityriasis versicolor. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2008. 17:86–89.
7. Güleç AT, Demirbilek M, Seçkin D, Can F, Saray Y, Sarifakioglu E, et al. Superficial fungal infections in 102 renal transplant recipients: a case-control study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003. 49:187–192.

8. Shuttleworth D, Philpot CM, Salaman JR. Cutaneous fungal infection following renal transplantation: a case control study. Br J Dermatol. 1987. 117:585–590.

9. Aridoğan IA, Ilkit M, Izol V, Ates A. Malassezia and Candida colonisation on glans penis of circumcised men. Mycoses. 2005. 48:352–356.

10. Ashbee HR. Update on the genus Malassezia. Med Mycol. 2007. 45:287–303.
11. Boardman CR, Malkinson FD. Tinea versicolor in steroid-treated patients. Incidence in patients with chronic ulcerative colitis and regional enteritis treated with corticotropin and corticosteroids. Arch Dermatol. 1962. 85:44–52.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download