Abstract
Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (EAH) is a benign, uncommon, combined vascular and eccrine malformation. Most cases of this disorder have been single or multiple nodules or plaques that appear red, yellow, blue, violaceous, or skin colored. EAH may be congenital or appear later in childhood; it rarely arises during puberty or adulthood. A 52-year-old female patient visited our department for tender subcutaneous cystic tumor on the right sole with a one month history. Histopathologic examination confirmed EAH. During excisional biopsy procedure, mucinous discharges were observed which were histopathologically diagnosed as ganglion.
Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (EAH) is a rare, benign, combined vascular and eccrine malformation. It was first described by Lotzbeck1 in 1859, and named by Heyman et al.2 in 1968. Most cases of this disorder present with single or multiple nodules or plaques that appear red, yellow, blue, violaceous, or skin-colored. The lesions are usually asymptomatic, but pain and hyperhidrosis are the most commonly associated symptoms, and have been reported in approximately 42% and 32% of cases, respectively3.
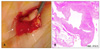
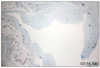
A 52-year-old Korean woman presented with a solitary subcutaneous tumor with intact epidermis on the sole of her right foot (Fig. 1). The tumor was first noticed one month prior to presentation and had slowly increased in size over that time. Physical examination revealed a slightly elevated, 1.5×1.5 cm round subcutaneous mass without epidermal involvement. Sweating was not evoked by physical work or emotional stress. There was no pain, but mild tenderness associated with the lesion. The patient had no history of trauma to the right sole. An excisional biopsy was performed, and histopathologic examination of the lesion showed increased numbers of eccrine glands, as well as dilated vascular channels in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue (Fig. 2, 3). During excisional biopsy, gelatinous material was noted and confirmed as a ganglion cyst by histopathologic findings including a cystic space surrounded with collagenous fibers instead of epithelial lining (Fig. 4). Specific staining with CD 31 revealed no endothelial lining in cystic space (Fig. 5). These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of an EAH with a ganglion cyst.
EAH was first reported by Lotzbeck in 1859, who observed an angioma-like tumor on the face of a child, characterized histologically by numerous clusters of eccrine glands within a stroma containing prominent blood vessels1. In 1968, Heyman et al.2 coined the term EAH and reviewed the literature covering the disease.
EAH is a rare cutaneous hamartoma appearing histologically as a proliferation of eccrine sweat glands with angiomatous vascular elements that are of capillary origin. It often appears at birth or during childhood, and rarely arises during puberty or adulthood, as observed in our case. Few cases of late-onset EAH have been described in the literature (Table 1).
EAH presents as a solitary or multiple plaque, nodule or, less commonly, macule localized mainly to the extremities, in particular the palms and the soles. The color of the lesions may be red, violaceous, blue, brown or pinkish to skin color, as observed in our patient. Atypical clinical variants with superficial changes resembling acanthosis nigricans, linear verrucous lesions, and hypertrichosis have been reported4,5. The lesions of EAH are usually asymptomatic, but associated symptoms of pain and hyperhidrosis have been reported in nearly one-third of reported cases; these were not detected in our patient4. Associated features include knuckle pads, nevus sebaceus, verrucous epidermal nevus, and neurofibromatosis6,7.
Microscopic examination of typical EAH shows dermal proliferation of well-differentiated eccrine glands that are closely associated with thin-walled angiomatous channels. Unusual histopathologic variants include pilar structures5, lipomatous foci8, lymphatics9, mucin10, or dense collagen fibers11.
As a rule, aggressive treatment has not been indicated for this benign, nonneoplastic disorder; however, surgery has been the only definitive therapy for EAH when the condition involves drug-resistant pain or severe hyperhidrosis. Ganglion cysts are the most common soft-tissue tumors of the hand and wrist. Although ganglion cysts occur across all demographic categories, they occur three times as often in women as they do in men12. The etiology of a ganglion cyst has been described as an outpouching of synovium, as an irritation of articular tissue, creating a new formation, or, following the best accepted theory, as a degeneration of connective tissue and cystic space formation13. It has also been suggested that degeneration of the connective tissue is caused by irritation or chronic damage causing the mesenchymal cells or fibroblasts to produce mucin13,14. Hyaluronic acid predominates the mucopolysaccharides that make up the fluid within the cyst's cavity, while collagen fibers and fibrocytes make up the wall lining13. The development of these cysts is histologically observable beginning with swollen collagen fibers and fibrocytes, followed by a degeneration and liquefaction of these elements, a termination of degeneration, and, lastly, a proliferation of the connective tissue, resulting in a border that is dense in texture13. In the present case, EAH was associated with a ganglion cyst on the sole of the foot. We suggest that irritation from an EAH might have played a role in the development of our patient's ganglion cyst.
Most often, a ganglion cyst will present at the dorsal wrist, accounting for 60~70% of all hand and wrist ganglia15, and arise from the scapholunate joint16. About 11% of ganglion cysts are found on the foot, and most of these will present at the extensor tendon of the dorsum of the foot or around the joint area12. Only 2% of ganglion cysts occurring on the foot have been found on the sole17.
In terms of treatment, surgical excision has been recommended for symptomatic cases in both EAH and ganglion cysts. The patient in the current study had neither recurrence nor pain after excisional biopsy.
Figures and Tables
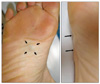 | Fig. 1The patient presented with a solitary subcutaneous tumor with intact epidermis on the sole of the right foot. |
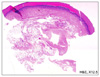 | Fig. 2Histopathologic examination of the lesion showed increased numbers of eccrine glands, as well as dilated vascular channels in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue (H&E, ×12.5). |
 | Fig. 3Increased numbers of eccrine glands were associated with dilated vascular channels in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue (H&E, ×40, ×100). |
References
1. Lotzbeck C. Ein Fall von Schweissdrsengeschwulst an der Wauge. Virchow Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1859. 16:160.
2. Hyman AB, Harris H, Brownstein MH. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma. N Y State J Med. 1968. 68:2803–2806.
3. Pelle MT, Pride HB, Tyler WB. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002. 47:429–435.

4. Martinelli PT, Tschen JA. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2003. 71:449–455.
5. Zeller DJ, Goldman RL. Eccrine-pilar angiomatous hamartoma. Report of a unique case. Dermatologica. 1971. 143:100–104.
6. Campen R, Zembowicz A, Liu V, Wrone D. Linear ectodermal cutaneous hamartoma. Int J Dermatol. 2003. 42:376–379.

7. Castilla EA, Schwimer CJ, Bergfeld WF, Skacel M, Ormsby A. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma in a neurofibromatosis type-1 patient. Pathology. 2002. 34:378–380.

8. Donati P, Amantea A, Balus L. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma: a lipomatous variant. J Cutan Pathol. 1989. 16:227–229.

9. Enjolras O, Mulliken JB. Vascular tumors and vascular malformations (new issues). Adv Dermatol. 1997. 13:375–423.
10. Seraly MP, Magee K, Abell E, Bridenstine J, Jegasothy BV. Eccrine-angiomatous nevus, a new variant. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993. 29:274–275.

11. Sulica RL, Kao GF, Sulica VI, Penneys NS. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (nevus): immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 1994. 21:71–75.

12. Kirby EJ, Shereff MJ, Lewis MM. Soft-tissue tumors and tumor-like lesions of the foot. An analysis of eighty-three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71:621–626.

13. Soren A. Pathogenesis and treatment of ganglion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1966. 48:173–179.
14. Psaila JV, Mansel RE. The surface ultrastructure of ganglia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1978. 60:228–233.

15. Chloros GD, Wiesler ER, Poehling GG. Current concepts in wrist arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2008. 24:343–354.

16. Plate AM, Lee SJ, Steiner G, Posner MA. Tumorlike lesions and benign tumors of the hand and wrist. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003. 11:129–141.

17. Pontious J, Good J, Maxian SH. Ganglions of the foot and ankle. A retrospective analysis of 63 procedures. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1999. 89:163–168.

18. Wolf R, Krakowski A, Dorfman B, Baratz M. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma. A painful step. Arch Dermatol. 1989. 125:1489–1490.

19. Gabrielsen TO, Elgjo K, Sommerschild H. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma of the finger leading to amputation. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1991. 16:44–45.

20. Nakayama H, Mihara M, Hattori K, Mishima E, Shimao S. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma of the sacral region. Acta Derm Venereol. 1994. 74:477.
21. Cebreiro C, Sánchez-Aguilar D, Gómez Centeno P, Fernández-Redondo V, Toribio J. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma: report of seven cases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1998. 23:267–270.

22. Tsuji T, Sawada H. Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma with verrucous features. Br J Dermatol. 1999. 141:167–169.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download