Abstract
Acanthosis nigricans is a symmetric eruption characterized by the presence of a hyperpigmented, velvety cutaneous thickening, that can develop on any part of the body, but characteristically affects the flexural areas of the body. The velvety hyperkeratotic lesions can be located on the dorsum of the hands and feet in dark-skinned people in the form of a variant of acanthosis nigricans called as acral acanthotic anomaly or acral type acanthosis nigricans. Although acanthosis nigricans is associated with malignant tumors, particularly gastric carcinoma, acral type acanthosis nigricans has never been reported to be associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. In our present study, we describe a case of 58-year-old man with acral type acanthosis nigricans and its association with carcinoma of the stomach; a marked improvement was seen in the skin condition of the patient with chemotherapy.
The disease acanthosis nigricans is characterized by the presence of a thick macule with a brown velvet-like surface1. Lesions frequently occur in the axillary region, neck, inguinal region, antecubital fossa, and popliteal fossa. However, it can also be localized to the dorsa of the hand and foot, being referred to in such cases as acral-type acanthosis nigricans. According to the classification system of Schwartz2, there are eight clinical disease types: benign, obesity-associated, syndromic, malignancy-associated, unilateral, acral, drug-induced, and mixed-type. Of these, the forms associated with malignancy develop during the early stages of malignant tumor progression (occurrence of tumor in an internal organ). Although acral-type acanthosis nigricans commonly occurs in healthy black people, we herein report a case of acral-type acanthosis nigricans with gastric adenocarcinoma in a Korean patient.
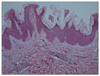
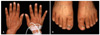
A 58-year-old man visited us complaining of development of asymptomatic hyperpigmented patches in areas around the phalangeal (Fig. 1A) and tarsophalangeal joints (Fig. 1b) from approximate time duration of three months. The skin condition was presented with symmetric dark-brown patches and papillomatous hypertrophy in the phalangeal and tarsophalangeal joints. No other cutaneous (including palm and sole) or mucosal findings were present. Besides these dermatologic symptoms (and mild weight loss), the overall status of the patient was relatively good. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-1, cholesterol and triglycerides, and the results of thyroid and liver function tests, were all within normal limits. A tissue biopsy revealed the presence of hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, increased melanin pigmentation along the tips and sides of rete ridges, and melanophages in the papillary dermis (Fig. 2). It also showed protrusion of the dermal papilla in a digitated form. During a subsequent medical check-up, gastroduodenofibroscopy showed the presence of ulcerative lesions of irregular shape in the gastric fundus, while a tissue biopsy showed that anaplastic epithelial cells had infiltrated into the mucosa. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of gastric adenocarcinoma was made. The patient received anti-cancer chemotherapy for four months. Following the therapy, there was a marked improvement in the condition of skin lesions (Fig. 3). At the time of writing this report, one further round of chemotherapy was planned and the patient is still being followed-up.
The skin is the organ of the body that can be most easily and quickly assessed. In patients with systemic diseases, various types of dermatologic symptoms might occur. These symptoms may often provide clues as to whether the systemic disease is benign or malignant-systemic. Acanthosis nigricans is a well-established marker of malignant tumors, which occur in the internal organs1. In the present case of a 58-year-old man with no history of diabetes, obesity or drug use, skin lesions had developed three months prior to the diagnosis of gastric carcinoma, and there was great improvement with subsequent anti-cancer chemotherapy. Since the skin lesions occurred in the phalangeal and tarsophalangeal joints, we diagnosed this case as acral-type malignant acanthosis nigricans.
In acral-type acanthosis nigricans, lesions are localized to the knee, ankle, phalangeal joint and tarsophalangeal joints3. It is often characterized by hyperpigmentation in the phalangeal joint. In 1981, Schwartz3 reported a case of acanthosis nigricans in the hand and foot of a black patient (aged 60 years), and classified it as being acral-type. According to the author, acral-type acanthosis nigricans occurs in healthy black people and does not, on its own, necessitate the evaluation of afflicted patients for the possible presence of an internal malignancy. However, Melczer and Dvorszky4 reported localization of acanthosis nigricans lesions to the acral region in patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. In addition, acral-type acanthosis nigricans may occur in patients with lymphoma5. In the present case, acral-type acanthosis nigricans was accompanied by the presence of gastric adenocarcinoma. Collectively, these observations led us to conclude that acral-type acanthosis nigricans may also be accompanied with internal malignant diseases and that its presence may therefore necessitate a thorough search for underlying primary malignancies.
Tripe palms are rare paraneoplastic dermatosis, which are clinically characterized by the presence of thickened, velvety palms with pronounced dermatoglyphics. Its association with malignancy is high and frequently perceived in conjunction with acanthosis nigricans. In patients with both, triple palms and acanthosis nigricans, gastric carcinoma is most commonly followed by lung carcinoma1. In our case, we could not find abnormal clinical findings on the patient's palms. The patient's acanthosis nigricans lesions were localized only around the phalangeal and tarsophalangeal joints.
Very little is known about the etiology and pathophysiology of acral-type malignant acanthosis nigricans. It has been speculated, however, that tumor-secreted TGF-α (which acts on tumor cells in an autocrine fashion) is transported via the blood to the skin, where it binds to receptors on epidermal keratinocytes, thereby promoting their proliferation6. The observation that following chemotherapy, there was an apparent disappearance of papillomatosis suggests a chemotherapeutic effect on the factor determining epidermal growth leading to acanthosis nigricans as seen in our patient. An inhibitory effect on the factors affecting epidermal proliferation is assumed, because of the reduction in papillomatosis, as observed clinically. Ellis et al.7 reported that treatment of the malignancy leads to an improvement in skin symptoms. There have been no published reports about the effects of cancer chemotherapy on the condition of skin lesions. Although we have not studied growth factor expression in our patient, it is something that chemotherapy may reduce by controlling cancer growth.
In conclusion, in patients presenting with hyperkeratotic plaques on the knee, ankle, and/or phalangeal and tarsophalangeal joints, acral-type acanthosis nigricans should be considered as a possible diagnosis and the potential presence of an associated internal malignancy must be evaluated.
Figures and Tables
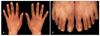 | Fig. 1Velvety, ill-defined hyperpigmentation and papillary hypertrophy are seen at the joints of the fingers (A) and toes (B). |
References
1. Christine AD, Lucinda SB, Stephen PS. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Glichrest BA, Paller AS, Leffel DJ, editors. Cutaneous manifestation of internal malignant disease. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2008. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1494–1498.
4. Melczer N, Dvorszky C. Acanthosisnigricans bei dermatofibroma protuberans mit multiplen hautmetastasen. Hautarzt. 1957. 8:54–58.
5. Song JY, Lim JH, Kim CW, Kim HO. A case of acral type acanthosis nigricans associated with lymphoma. Korean J Dermatol. 2002. 40:841–843.
6. Koyama S, Ikeda K, Sato M, Shibahara K, Yuhara K, Fukutomi H, et al. Transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-α)-producing gastric carcinoma with acanthosis nigricans: an endocrine effect of TGF-α in the pathogenesis of cutaneous paraneoplastic syndrome and epithelial hyperplasia of the esophagus. J Gastroenterol. 1997. 32:71–77.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download