Abstract
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, also known as inflammatory metastatic carcinoma, is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis. It is most commonly caused by breast carcinoma, but rarely associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. Herein, we report an unusual case of carcinoma erysipelatoides in a 55 year-old female who had been diagnosed with signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach metastasizing to ovaries.
Carcinoma erysipelatoides is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis secondary to an internal malignancy. Clinically, the lesion has a well-demarcated, slightly indurated erythematous appearance closely resembling an acute infectious process, such as erysipelas and cellulitis. Carcinoma erysipelatoides is most commonly secondary to breast cancer and has rarely been reported in cancers originating from the stomach1. To our knowledge, only 6 cases of carcinoma erysipelatoides secondary to gastric adenocarcinoma have been reported so far1-6.
Herein, we report an unusual case of carcinoma erysipelatoides originating from signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach.
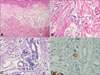
A 55 year-old female presented with a 1-month history of indurated erythematous plaque on the lower abdomen (Fig. 1). Seventeen months ago, she was diagnosed with signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach metastasizing to ovaries. She underwent subtotal gastrectomy and total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salphingo-oophorectomy followed by systemic chemotherapy (Fig. 2). Skin biopsy taken from the indurated plaque in the left lower abdomen revealed scattered infiltration of signet ring cells associated with lymphatic invasion in the dermis (Fig. 3A, B). These cells stained positive for PAS and pan-cytokeratin (Fig. 3C, D). Based on these findings, a diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis secondary to gastric adenocarcinoma was made.
The patient subsequently underwent 8 courses of 5-FU, leucovorin, oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) chemotherapy in a 5-month period. However, no clinical response of the skin lesion was observed even though she tolerated the chemotherapy well.
Advanced gastric carcinoma can metastasize to many parts of the body, particularly the regional lymph nodes, peritoneum, liver, pancreas, colon, lung, ovary and bones, but metastasis to the skin is not common2. In several studies, the incidence of cutaneous metastasis secondary to gastric carcinoma has been reported to be about 0.2~0.4%7,8. The most common clinical presentation is solitary or multiple, firm and non-ulcerated nodules, but they also rarely manifest as carcinoma en cuirasse (leather-like skin change), carcinoma erysipelatoides, neoplastic alopecia, and zosteriform metastasis1-6.
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, also known as inflammatory metastatic carcinoma, is characterized by indurated erythematous patches or plaques with an active spreading border resembling erysipelas. Inflammatory metastatic lesions are considered to represent deposition of malignant cells in dermal lymphatic vessels1,5. In our patient, signet ring cells were observed in the lymphatics.
Carcinoma erysipelatoides is most commonly caused by breast carcinoma, but rarely associated with gastric adenocarcinoma1-3. Thus far, only been 6 cases of carcinoma erysipelatoides originating from gastric carcinoma have been reported in the literature1-6. Including our case, carcinoma erysipelatoides primarily appears in men (5:2), with an average age of 57.3 years (range 36~62 years). In addition, it is diagnosed at the same time as gastric adenocarcinoma, except our case. Moreover, our patient is the first reported case involving low abdominal wall lesion. Table 1 summarizes the 6 reported cases as well as the present case.
Signet ring cells are mainly seen in mucin producing carcinomas, such as stomach cancer and are less frequently associated with breast and lung carcinoma9,10. Therefore, the presence of signet ring cells in a skin biopsy specimen is most often indicative of metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma from the gastrointestinal tract, and less frequently from the breast or lung9. However, cutaneous neoplasms that may contain signet ring cells including non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, liposarcoma, malignant melanoma, primary cutaneous signet ring cell carcinoma of eccrine or apocrine origin, primary cutaneous signet ring basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinoma must be excluded1. Appropriate immunohistochemical staining may assist in formulating differential diagnoses1. Of particular diagnostic utility include the positivity of tumoral cells for cytokeratin and carcinoembryonic antigens, and negativity for HMB-45 and leukocyte common antigen in metastatic signet ring cell caricinoma, features different from cutaneous neoplasms consisted of signet ring cells1.
Among several histologic subtypes of gastric carcinoma, signet ring cell carcinoma has a greater tendency towards distant metastasis1. Several cases of cutaneous metastasis from signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach have been reported, but cases manifesting as carcinoma erysipelatoides have rarely been reported, and there are no reported cases in Korean literature.
Including our patient, there are 7 reported cases of carcinoma erysipelatoides metastasized from gastric carcinoma, and all histologic subtypes of primary gastric carcinoma were signet ring, except in one patient6 whose histologic subtype had not been described (Table 1)1-6. Signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach, histologically an undifferentiated subtype of gastric carcinoma, is generally reported to cause lymphatic metastasis more than other subtypes11. The tendency to metastasize through lymphatic vessels is thought to be the reason behind most carcinoma erysipelatoides originating from gastric carcinoma, and that the histologic subtype of primary gastric carcinoma is predominantly signet ring cell.
Diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis is important because they indicate poor prognosis. The absence of fever and leukocytosis should raise the possibility of a non-infectious process. Thus, if a suspected inflammatory skin condition resembling erysipelas, cellulitis, zoster, or livedo reticularis12 is refractory to therapy, skin biopsy should be performed to exclude carcinoma erysipelatoides. Suspicion should be heightened in patients with known internal malignancy.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Clinical presentation of carcinoma erysipelatoides. (A) Indurated erythematous patch on lower abdomen. (B) Closer view.

Fig. 2
(A) The open resected specimen of stomach. (B) Histopathology of the resected gastric specimen showing atypical cells admixed with signet ring cells and undifferentiated cells (H&E, ×400).
Fig. 3
(A) Biopsy specimen showed upper dermal edematous change and scattered infiltration of tumor cells in the dermis (H&E, ×100). (B) Lymphatic invasion of signet ring cells were observed (H&E, ×400). Signet ring cells presented positivity for (C) PAS and (D) cytokeratin within dilated lymphatics (×400).
References
1. Acikalin MF, Vardareli E, Tel N, Saricam T, Urer S. Erysipelas-like cutaneous metastasis from gastric signet ring cell carcinoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005. 19:642–643.

2. Kavgaci H, Reis A, Ozdemir F, Bektas O, Arslan M, Aydin F. Carcinoma erysipelatoides resulting from gastric adenocarcinoma: an unusual clinical presentation. Med Princ Pract. 2005. 14:61–63.

3. Foo KF, Tao M, Tan EH. Gastric carcinoma presenting with cellulitis-like cutaneous metastasis. Singapore Med J. 2002. 43:37–38.
4. Navarro V, Ramón D, Calduch L, Llombart B, Monteagudo C, Jordá E. Cutaneous metastasis of gastric adenocarcinoma: an unusual clinical presentation. Eur J Dermatol. 2002. 12:85–87.
5. Han MH, Koh GJ, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Koh JK, Moon KC. Carcinoma erysipelatoides originating from stomach adenocarcinoma. J Dermatol. 2000. 27:471–474.

6. Hamamoto Y, Nagai K, Ichimiya M, Yamamoto K, Kinoshita E, Muto M. Regressive effect of intralesional injection of a moderate dose of recombinant interleukin-2 on carcinoma erysipeloides from gastric carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001. 26:42–44.

7. Criep LH, Miller HI. Carcinoma of the stomach with metastases to the skin. J Lab Clin Med. 1933. 18:1023–1029.
8. Kim YC, Cho KH, Lee YS, Ham EK. Cutaneous metastasis from internal malignancy. Korean J Dermatol. 1987. 25:213–221.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download