Abstract
Eccrine porocarcinoma (EP) is a rare malignant tumor arising from the intraepidermal eccrine duct. The tumor cells frequently contain glycogen, but prominent clear cell changes in EP are rarely reported. A 78-year-old woman presented with a slightly pruritic, erythematous, verrucous plaque on her left thigh. Histopathological examination revealed intraepidermal tumor cell nests composed of small basaloid cells and duct-like structures lined by periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive cuticles. Besides the typical findings of EP, clear cell changes were predominantly observed in the tumor cell aggregations. Herein we report a case of the clear cell variant of EP rarely reported in previous literature.
Eccrine porocarcinoma (EP) is a rare malignant cutaneous appendageal tumor that develops from the intraepidermal eccrine sweat duct. One characteristic histologic feature of EP is the ductal differentiation of poromatous basaloid epithelial cells, which form an irregular tumor shape. The tumor cells frequently contain glycogen in their cytoplasm, but prominent clear cell changes are rarely reported1. Herein we report a case of the clear cell variant of EP that has never been reported in Korean dermatologic literature.
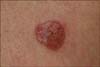
A 78-year-old woman presented with an erythematous plaque on her left thigh. The lesion had been slowly growing for over 1 year. She presented with no discomfort other than an occasional sense of itchiness at the site. There was no history of skin disease at the affected area. Clinical examination revealed a sharply bordered, erythematous, verrucous and erosive plaque of approximately 2 cm in diameter on her left thigh (Fig. 1).
A skin biopsy specimen from the lesion showed intraepidermal aggregations composed of small basaloid cells with sharp demarcations (Fig. 2A). In some aggregations, there were acrosyringium-like, spiral ductal structures lined by periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive cuticles (Fig. 2B). The neoplastic cells with prominent clear cell changes had hyperchromatic, pleomorphic nuclei with conspicuous mitotic figures (Fig. 3A). These cells had ample cytoplasm containing glycogen confirmed by d-PAS staining (Fig. 3B). Also, immunohistochemically, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) decorated the luminal border of intraneoplastic ductal structures, and focal positivity for epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) was detected in tumor nests (Fig. 4). Antibodies to S-100 protein showed scattered positive dendritic cells within the tumor, but neoplastic cells were all negative. The patient has remained lesion free since the excision 6 months ago.
EP, also known as malignant eccrine poroma, is a rare type of malignant tumor from the eccrine glands. First described in 1963 by Pinkus and Mehregan as epidermotropic eccrine poroma2, the lesions of EP are clinically described as verrucous plaques or polypoid growths often mimicking squamous cell carcinoma or Bowen's disease. The lower extremities are the most commonly affected site, followed by the trunk and head3. The origin of the tumor is thought to be in the intraepidermal portion of the eccrine sweat duct (acrosyringium) and histopathologically characterized by tumor cell nests consisting of poroma cells with nuclear pleomorphism and ductal differentiation.
Although glycogen is frequently observed within the tumor cells of porocarcinoma, prominent clear cell changes are rarely reported. First introduced by Requena et al. in 1997, histopathologic examination of the clear cell variant revealed that the lesion was mainly composed of clear cells containing PAS-positive diastase-labile granules within their cytoplasm. The mechanism of accumulation of glycogen and subsequent clear cell changes in EP is poorly understood. Decreased phosphorylase immunoreactivity has been demonstrated in clear cell porocarcinoma4, and identical enzymatic deficiency has been noted in other clear cell neoplasms of the eccrine glands, especially in clear cell syringomas of patients with diabetes mellitus5. Based on these findings, some authors have postulated that a relative deficiency in phosphorylase causes decreased glycogenolysis and subsequent glycogen deposition within the cytoplasm of neoplastic cells, resulting in the clear cell changes4.
The tumor in this case should be distinguished from other tumors showing prominent clear cell changes, such as clear-cell Bowen's disease, sebaceous carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma with adnexal differentiation and balloon cell melanoma6. Clear-cell Bowen's disease and sebaceous carcinoma may result in diagnostic confusion, but our case showed ductal formation with cuticular lining and positive staining for CEA and EMA, which indicated its eccrine origin. Basal cell carcinoma is also included in the list of differential diagnosis, but CEA and EMA are uniformly negative, in contrast to the present case. Balloon cell malignant melanoma with clear cell changes is also differentiated by the presence of ductal formation and negativity for S-100 staining.
Herein, we report an interesting case of the clear cell variant of eccrine porocarcinoma. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of clear cell eccrine porocarcinoma ever reported in Korea.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 2
(A) The intraepidermal aggregations were composed of small basaloid cells with sharp demarcations. Prominent clear cell changes were also noted within the tumor nests (H&E, ×40). (B) Acrosyringium-like, spiral ductal structures were seen in some aggregations (H&E, ×100).

References
1. Rutten A, Requena L, Requena C. Clear-cell porocarcinoma in situ: a cytologic variant of porocarcinoma in situ. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002. 24:67–71.
2. Pinkus H, Mehregan AH. Epidermotropic eccrine carcinoma. A case combining features of eccrine poroma and Paget's dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1963. 88:597–606.
3. Robson A, Greene J, Ansari N, Kim B, Seed PT, McKee PH, et al. Eccrine porocarcinoma (malignant eccrine poroma): a clinicopathologic study of 69 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001. 25:710–720.
4. Requena L, Sarasa JL, Pique E, Farina MC, Olivares M, Martin L. Clear-cell porocarcinoma: another cutaneous marker of diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997. 19:540–544.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download