Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of study was to identify how patients experienced chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) and quality of life related to CIPN.
Methods
This was a descriptive research. We collected data from 105 patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. They completed a self-reported questionnaire including Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (EORTC) CIPN20 and items related to their disease and peripheral neuropathy. The investigators filled in part of items about disease and treatment.
Results
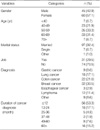
In the study, duration of peripheral neuropathy was 9.4 month and 54.3% of patients used pharmacological or non-pharmacological interventions. Patients reported the highest score for sensory scale and it's score was 38.74±20.24. The scores for motor scale and autonomic scale were 21.95±19.19 and 26.61±21.0 respectively. This showed that patients more suffered from sensory neuropathy than any other domain of neuropathy. The most frequently selected two items were 'did you have tingling fingers or hands?' and 'did you have tingling toes or feet?'.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Wilkes GM. Neurologic disturbances. Cancer symptom management. 1999. Boston: Jones and Bartlett.
2. Ellen ML, Susan LB, Jeffrey C. The total neuropathy score: a tool for measuring chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncology Nursing Forum. 2008. 35:96–102.

3. Sweeney CW. Understanding peripheral neuropathy in patients with cancer: Background and patient assessment. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2002. 6:163–166.

5. Wickhan R. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a review and implications for oncology nursing practice. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2007. 11:361–376.

6. Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Aranishi T, Morita S, Kuroi K, et al. Feasibility and validity of the patient neurotoxicity questionnaire during taxane chemotherapy in a phase III randomized trial in patients with breast cancer: N-SAS BC 02. 2009. Support Care in Cancer, Online first at http://www.springerlink.com/content/e958243151613358/.
7. Armstrong T, Almadrones L, Gilbert MR. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2005. 32:305–311.

8. Boehmke MM, Dickerson SS. Symptom, symptom experiences, and symptom distress encountered by women with breast cancer undergoing current treatment modalities. Cancer Nurs. 2005. 28:382–389.

9. Postma TJ, Heimans JJ. Grading of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy. Ann Oncol. 2000. 11:509–513.
10. Katsumasa K, Kojiro S, Yasuo O, Ayano T, Toshihiko A, Satoshi M, et al. A questionnaire survey of physicians' perspective regarding the assessment of chemotheraphy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with Breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008. 38:748–754.
11. Postma TJ, Aaronson NK, Heimans JJ, Muller MJ, Hildebrand JG, Delattre JY, et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: the QLQ-CIPN20. Eur J Cancer. 2005. 41:1135–1139.

14. Smith EL, Whedon MK, Bookbinder M. Quality improvement of painful peripheral neuropathy. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2002. 18:36–43.

15. Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR. Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1998. 280:1831–1836.

16. Rao RD, Michalak JC, Sloan JA. Efficacy of gabapentin in the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase 3 randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Cancer. 2007. 110:2110–2118.

17. Kautio AL, Haanpaa M, Saarto T, Kalso E. Amitriptyline in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic symptoms. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007. 35:31–39.

18. Balducci S, Lacobellis G, Parisi L, Di Biase N, Calandriello E, Leonetti F, et al. Exercise training can modify the natural history of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Diabetes Complicat. 2006. 20:216–223.

19. Lindeman E, Leffers P, Spaans F, Drukker J, Reulen J, Kerckhoffs M, et al. Strength training in patients with myotonic dystrophy and hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995. 76:612–620.

20. Richardson J, Sandman D, Vela S. A focused exercise regimen improves clinical measures of balance in patients with peripheral neuropathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001. 82:205–209.

21. Diana D. Management of peripheral neuropathy caused by microtubule inhibitor. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2009. 13:686–694.
22. Stillman M, Cata JP. Management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2006. 10:279–287.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download