Abstract
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related sclerosing disease (RSD) is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by elevated serum IgG4 levels as well as an abundant infiltration of IgG4-positive plasmacytes. Involvement of the paranasal sinus is very rare, so it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. Hence, various differential diagnoses, which typically include elevated serum IgG4 levels and the infiltration of IgG4-postive cells into tissues, need to be excluded, especially for malignant diseases and mimicking disorders. Systemic corticosteroids are generally effective at inducing IgG4-RSD remission. Recently, a 43-year-old woman presented with a mass originating from the ethmoid sinus, suggesting malignancy. The patient underwent biopsy of the lesion. The pathologic specimen revealed the magnitude of IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration, which was consistent with IgG4-RSD. In addition, serum IgG4 levels were markedly increased. After glucocorticoid treatment, the serum IgG4 levels decreased and the symptoms improved. We present a rare case of IgG4-RSD with isolated involvement of the paranasal sinuses.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 2
Paranasal CT scans shows an expansive mass of the left ethmoid sinus with erosion of the lamina papyracea.
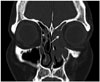
Fig. 3
Paranasal MRI scans shows mass-like lesion of the left ethmoid sinus with isosignal intensity on T1-weighted (A) and T2-weighted MR image (B).
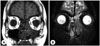
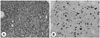
Fig. 4
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining revealed diffuse fibrosis with infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells (HE stain, ×400). B: Immunostain for immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) shows many plasma cells that contain the IgG4 subclass, measuring up to 60/HPF (anti-IgG4 immunostain, original magnification ×400).
References
1. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. New Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.

2. Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, Sato Y, Tsuneyama K, Haratake J, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? Am J Surg Pathol. 2004; 28(9):1193–1203.

3. Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, Unno H, Shiba N, Wajiki M, et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet. 2002; 359(9315):1403–1404.

4. Zen Y, Kitagawa S, Minato H, Kurumaya H, Katayanagi K, Masuda S, et al. IgG4-positive plasma cells in inflammatory pseudotumor (plasma cell granuloma) of the lung. Hum Pathol. 2005; 36(7):710–717.

5. Lee KK, Cho HP, Lee YM, Park JH. A case of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis and dacryoadenitis. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2013; 56(7):444–447.

6. Kitagawa S, Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, Sato Y, Minato H, et al. Abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration characterizes chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Küttner’s tumor). Am J Surg Pathol. 2005; 29(6):783–791.

7. Vandjelovic ND, Humphreys IM. Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease of the paranasal sinuses: A case report and literature review. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2016; 7(2):85–89.

8. Lee JR, Lee BJ, Chung YS. Three Cases of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Nasal Cavity. J Rhinol. 2016; 23(1):44–48.

9. Moteki H, Yasuo M, Hamano H, Uehara T, Usami S. IgG4 related chronic rhinosinusitis: a new clinical entity of nasal disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011; 131(5):518–526.

10. Ishida M, Hotta M, Kushima R, Shibayama M, Shimizu T, Okabe H. Multiple IgG4-related sclerosing lesions in the maxillary sinus, parotid gland and nasal septum. Pathol Int. 2009; 59(9):670–675.

11. Alt JA, Whitaker GT, Allan RW, Vaysberg M. Locally destructive skull base lesion: IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2012; 3(1):e41–e45.

12. Takano K, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Himi T. Recent advances in knowledge regarding the head and neck manifestations of IgG4-related disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017; 44(1):7–17.

13. Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone JH. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74:14–18.

14. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181–1192.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download