Abstract
Background and Objectives
Insulin is a peptide hormone that regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood to skeletal muscles. Insulin has been reported to be closely related to cardiovascular, respiratory, and endocrine disease. However, the effect of insulin on production of major mucins in human airway epithelial cells has not been reported. Therefore, this study investigated the relationship between high levels of insulin and mucin in human airway epithelial cells.
Materials and Methods
This study analyzed the effect of high level of insulin on MUC4, MUC5AC, and MUC5B expression using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in human airway epithelial cells.
Go to : 
References
2). Rose MC, Nickola TJ, Voynow JA. Airway mucus obstruction: Mucin glycoproteins, MUC gene regulation and goblet cell hyperplasia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001; 25:533–7.
3). Rose MC, Voynow JA. Respiratory tract mucin genes and mucin glycoproteins in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2006; 86:245–78.

4). Sonksen P, Sonksen J. Insulin: Understanding its action in health and disease. Br J Anaesth. 2000; 85:69–79.

5). Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011; 12:723–38.

6). Miakotina OL, Goss KL, Snyder JM. Insulin utilizes the PI3-kinase pathway to inhibit SP-A gene expression in lung epithelial cells. Respir Res. 2002; 3:27.

7). Chang JH, Kim JH, Lee KW, Cho CI, Chun JH, Kim KS. Suppression of IL-1beta-induced MUC5AC gene expression by ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) in human airway epithelial cells. J Rhinol. 2007; 14:49–55.
8). Singh AP, Moniaux N, Chauhan SC, Meza JL, Batra SK. Inhibition of MUC4 expression suppresses pancreatic tumor cell growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:622–30.
9). Chaturvedi P, Singh AP, Batra SK. Structure, evolution, and biology of the MUC4 mucin. FASEB J. 2008; 22:966–81.

10). Thornton DJ, Rousseau K, McGuckin MA. Structure and function of the polymeric mucins in airways mucus. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008; 70:459–86.

11). Kim KR, Kim NH, Park Y, Kim JH, Lee EJ, Kim KS. Berberine suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced MUC5AC gene expression in human airway epithelial cells. J Rhinol. 2011; 18:116–21.
12). Iwase H, Kobayashi M, Nakajima M, Takatori T. The ratio of insulin to C-peptide can be used to make a forensic diagnosis of exogenous insulin overdosage. Forensic Sci Int. 2001; 115:123–7.

13). Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988; 37:1595–607.

14). Modan M, Halkin H, Almog S, Lusky A, Eshkol A, Shefi M, et al. Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 1985; 75:809–17.

15). Singh S, Prakash Y, Linneberg A, Agrawal A. Insulin and the lung: Connecting asthma and metabolic syndrome. J Allergy. 2013; 2013:627384.

16). Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. Metabolic syndrome-a new worldwide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med. 2006; 23:469–80.

17). Edalat B, Sharifi F, Badamchizadeh Z, Hossein-Nezhad A, Larijani B, Mirarefin M, et al. Association of metabolic syndrome with inflammatory mediators in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2013; 12:8.

18). Ford ES. The metabolic syndrome and C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, and leukocyte count: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Atherosclerosis. 2003; 168:351–8.

19). Karczewska-Kupczewska M, Kowalska I, Nikolajuk A, Adamska A, Otziomek E, Gorska M, et al. Hyperinsulinemia acutely increases serum macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 concentration in anorexia nervosa and obesity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2012; 76:46–50.
20). Ruotsalainen E, Stancakova A, Vauhkonen I, Salmenniemi U, Pi-hlajamaki J, Punnonen K, et al. Changes in cytokine levels during acute hyperinsulinemia in offspring of type 2 diabetic subjects. Atherosclerosis. 2010; 210:536–41.

21). Brestoff JR, Artis D. Immune regulation of metabolic homeostasis in health and disease. Cell. 2015; 161:146–60.

22). Heinrich LF, Andersen DK, Cleasby ME, Lawson C. Long-term high fat feeding of rats results in increased numbers of circulating microvesicles with proinflammatory effects on endothelial cells. Br J Nutr. 2015; 113:1704–11.

Go to : 
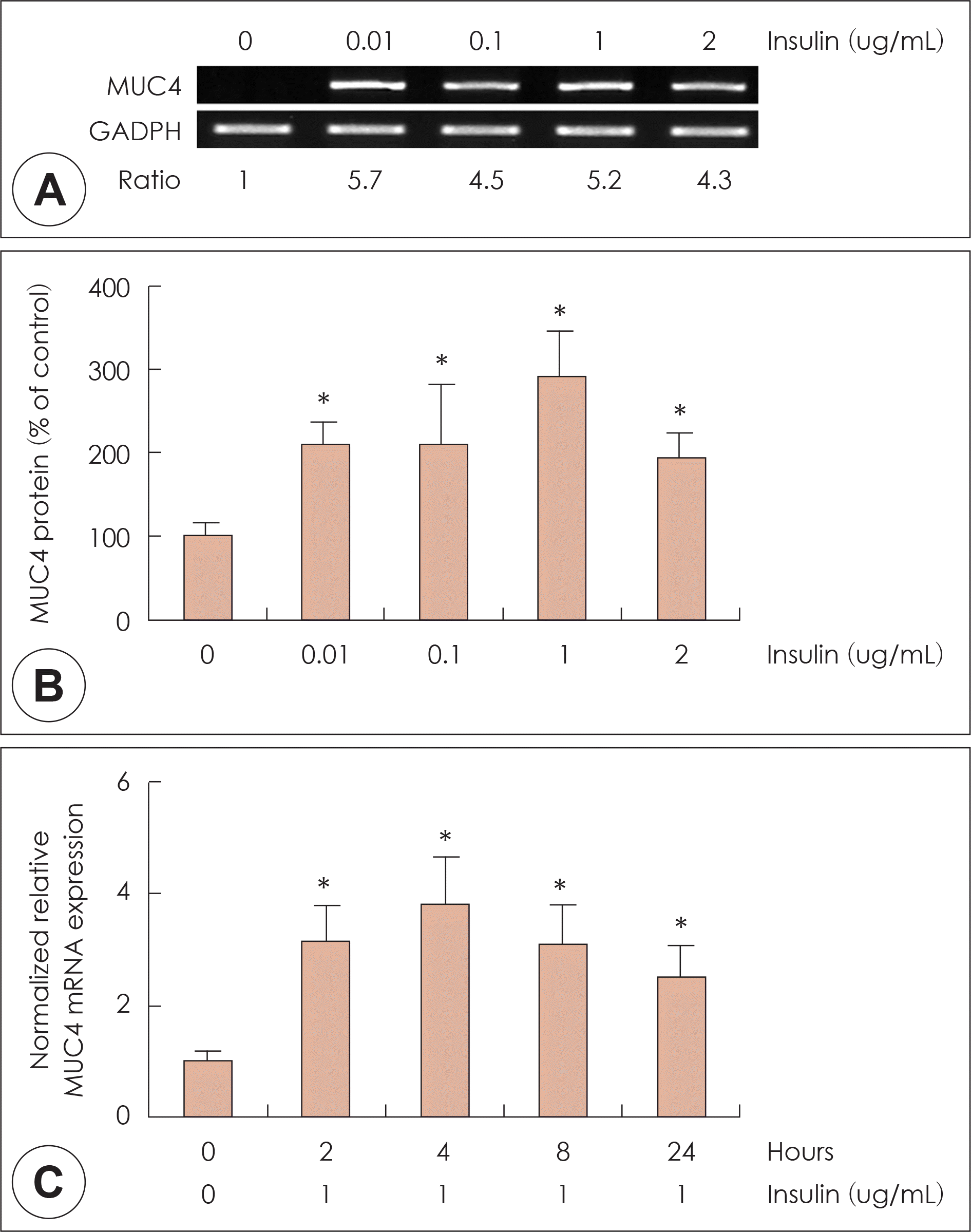 | Fig. 1.Effects of high level of insulin on MUC4 expression in NCI-H292 cells. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with various concentration of insulin for 4hrs. RT-PCR showed that insulin significantly induced MUC4 mRNA expression in human NCI-H292 cells (A). ELISA showed that insulin significantly increased MUC4 protein production in NCI-H292 cells (B). Real-time PCR showed that the insulin-induced MUC4 mRNA expression was increased at all times and peaked at 4 h after treatment with insulin (C). The images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicated. Bars indicate the mean± S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *: p<0.05 compared with zero value. RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
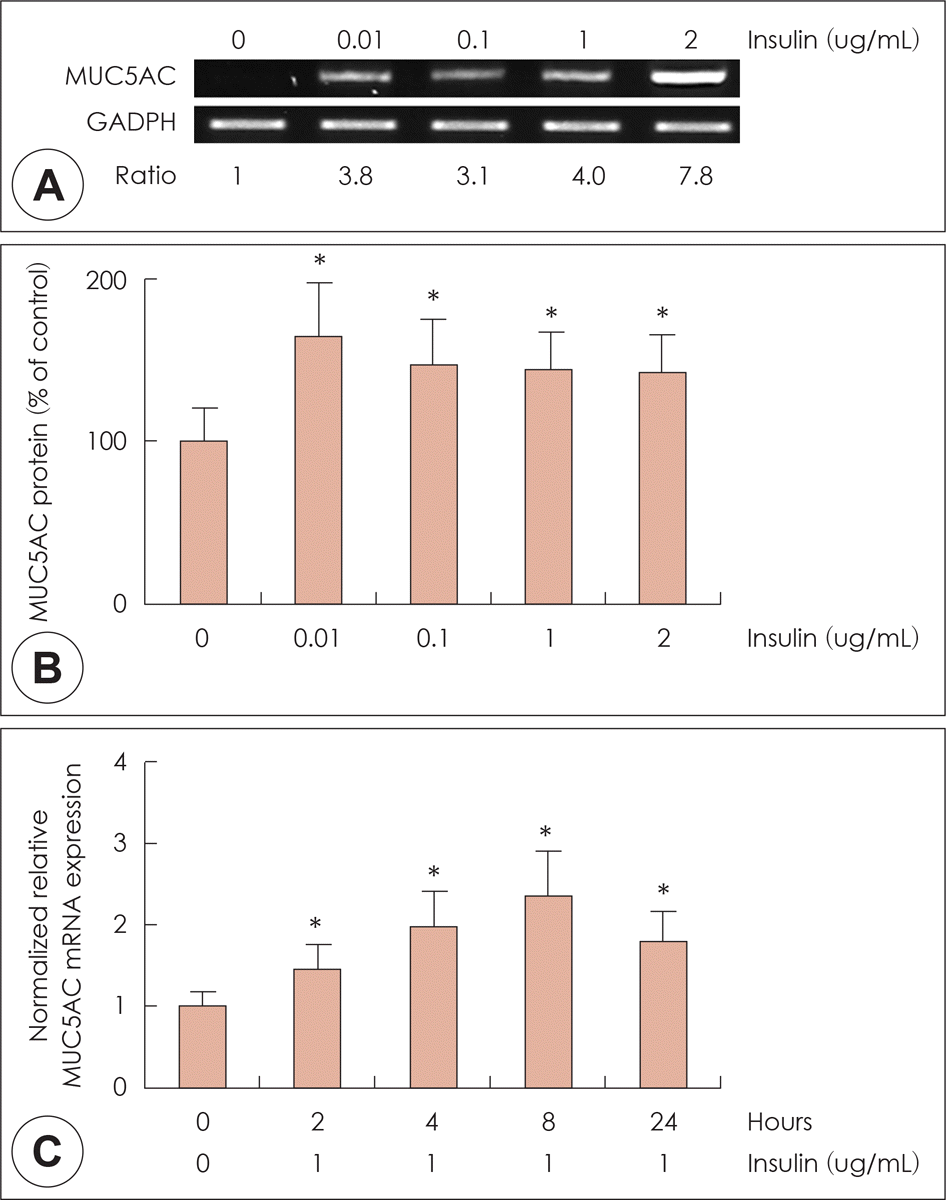 | Fig. 2.Effects of high level of insulin on MUC5AC expression in NCI-H292 cells. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with various concentration of insulin for 8hrs. RT-PCR showed that insulin significantly induced MUC5AC mRNA expression in human NCI-H292 cells (A). ELISA showed that insulin significantly increased MU-C5AC protein production in NCI-H292 cells (B). Real-time PCR showed that the insulin-induced MUC5AC mRNA expression was increased at all times and peaked at 8 h after treatment with insulin (C). The images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicated. Bars indicate the mean± S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *: p<0.05 compared with zero value. RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
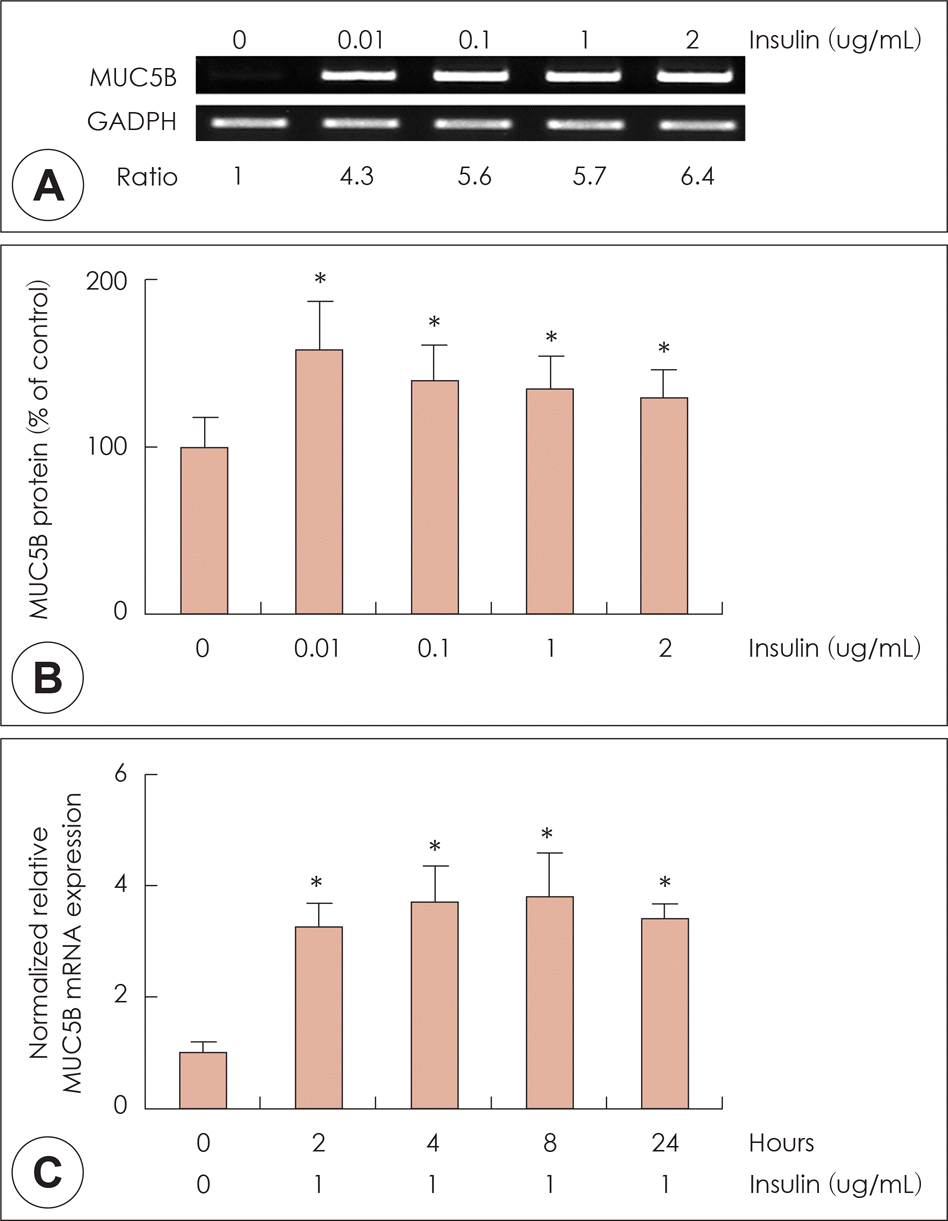 | Fig. 3.Effects of high level of insulin on MUC5B expression in NCI-H292 cells. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with various concentration of insulin for 8hrs. RT-PCR showed that insulin significantly induced MUC5B mRNA expression in human NCI-H292 cells (A). ELISA showed that insulin significantly increased MUC5B protein production in NCI-H292 cells (B). Real-time PCR showed that the insulin-induced MUC5B mRNA expression was increased at all times and peaked at 8 h after treatment with insulin (C). The images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicated. Bars indicate the mean± S.D. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *: p<0.05 compared with zero value. RT-PCR: reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
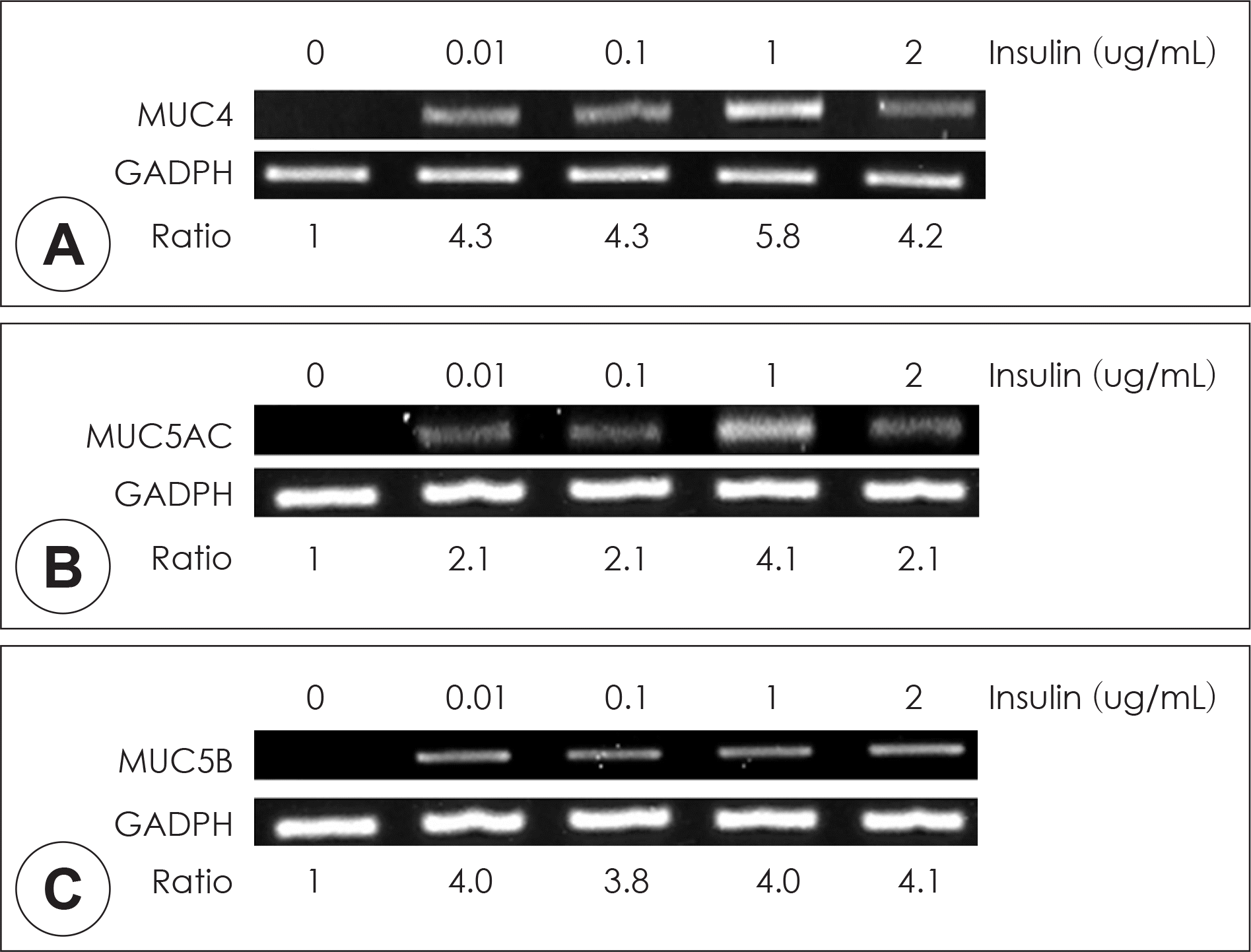 | Fig. 4.Effects of high level of insulin on MUC4, MUC5AC, MUC5B mRNA expression in human nasal epithelial cells. In human nasal epithelial cells, RT-PCR showed that insulin significantly induced MUC4, MUC5AC, and MUC5B mRNA expression (A, B, and C). The images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicated. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download