The purpose of computer-aided surgery is to provide new capabilities that transcend human limitation in surgery, increase consistency and quality of surgical treatments, and promote better outcomes and more cost-effective processes in surgical practice. The primary objective is not to replace the technical work or surgeons, but rather assist them in performing difficult tasks more accurately, and repetitive tasks more precisely.
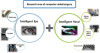
Research area of computer-aided surgery can be classified into two parts; intelligent hands and intelligent eyes. As described in Fig. 1, the intelligent hands cover master robot, slave robot, and diverse medical instruments. The intelligent eyes cover CT and MRI to provide pre-operative images and endoscope and ray for intra-operative procedure. Combination of those two technologies enables the surgeon to produce better outcome in surgery.
Currently, much research to develop future surgical robots is being conducted all over the world. However, tight collaboration among clinician, engineers, and company is required to come up with a successful surgical robot. This special issue on computer-aided surgery is to introduce some results produced by collaboration of clinicians and engineers in Korea [123456789].




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download