Abstract
Radiation therapy has played a key role, together with surgery and systemic chemotherapy, in treating in all stages of non-small cell lung cancer. We have witnessed remarkable improvements in radiation therapy techniques, with the innovations in hardware and software. Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy, which can deliver high radiation dose focused to small target volume, represents one of the state-of-the-art radiation therapy techniques. The technical development of radiation therapy and the role of stereotactic ablative radiation therapy in treating inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer are briefly reviewed.
Figures and Tables
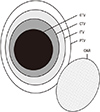 | Fig. 1Schematic illustration of target volumes based on ICRT report 62. GTV, gross tumor volume; CTV, clinical target volume; ITV, internal target volume; PTV, planning target volume; OAR, organ at risk. |
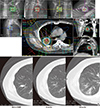 | Fig. 2An example case of SABR: 75 year old male patient with solitary nodule at right lower lobe, diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma. (A) Five beams are focused to the cancer nodule delivering 60 Gy over 4 consecutive days at 15 Gy per fraction. (B) CT images before and after SABR showing complete disappearance of the cancer nodule with minimal radiation lung changes. |
References
1. Purdy JA. Advances in three-dimensional treatment planning and conformal dose delivery. Semin Oncol. 1997; 24:655–671.
2. Prescribing, recording, and reporting photon beam therapy (Supplement to ICRU Report 50). Bethesda: International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU);1999. ICRU Report 62.
3. Dawson LA, Sharpe MB. Image-guided radiotherapy: rationale, benefits, and limitations. Lancet Oncol. 2006; 7:848–858.

4. Leksell L. The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand. 1951; 102:316–319.
5. De Salles AA, Gorgulho AA, Selch M, De Marco J, Agazaryan N. Radiosurgery from the brain to the spine: 20 years experience. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2008; 101:163–168.

6. Raz DJ, Zell JA, Ou SH, Gandara DR, Anton-Culver H, Jablons DM. Natural history of stage I non-small cell lung cancer: implications for early detection. Chest. 2007; 132:193–199.

7. Cai XW, Xu LY, Wang L, Hayman JA, Chang AC, Pickens A, et al. Comparative survival in patients with postresection recurrent versus newly diagnosed non-small-cell lung cancer treated with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76:1100–1105.

8. Rowell NP, Williams CJ. Radical radiotherapy for stage I/II non-small cell lung cancer in patients not sufficiently fit for or declining surgery (medically inoperable). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001; (2):CD002935.

9. Uematsu M, Shioda A, Tahara K, Fukui T, Yamamoto F, Tsumatori G, et al. Focal, high dose, and fractionated modified stereotactic radiation therapy for lung carcinoma patients: a preliminary experience. Cancer. 1998; 82:1062–1070.

10. Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M, Wennberg B, Gagliardi G, Lax I, et al. Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3290–3296.

11. Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA. 2010; 303:1070–1076.

12. Palma D, Visser O, Lagerwaard FJ, Belderbos J, Slotman BJ, Senan S. Impact of introducing stereotactic lung radiotherapy for elderly patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a population-based time-trend analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:5153–5159.

13. Grills IS, Mangona VS, Welsh R, Chmielewski G, McInerney E, Martin S, et al. Outcomes after stereotactic lung radiotherapy or wedge resection for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:928–935.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download